Painful sensations always indicate the presence of a disease. This is a classic symptom of most diseases. This symptom is also typical for myofascial syndrome. However, the main difference between the latter is involuntary muscle contractions.
Record content:
- 1 Myofascial syndrome: what is it
-
2 Causes and risk factors
- 2.0.1 Cervical
- 2.0.2 Thoracic department
- 2.0.3 Lumbosacral
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Diagnostic methods
- 5 Complications and prognosis
-
6 Treatment activities
- 6.1 Drug therapy
- 6.2 Physiotherapy
- 6.3 Physiotherapy
- 6.4 Massage
- 6.5 Post-isometric relaxation
- 6.6 Acupuncture
- 6.7 Surgery
-
7 ethnoscience
- 7.1 Homeopathy
- 8 Video about myofascial syndrome
Myofascial syndrome: what is it
Myofascial syndrome is a pathological condition of the nervous system, manifested by involuntary muscle work in conjunction with the manifestation of severe pain syndrome. The described clinical symptoms negatively affect the general well-being of the patient, worsening the quality of his health and life.
The area of muscle tissue where the pathological contraction occurs has a locality and a dense structure. According to the medical literature, such sites are called trigger points, which are located along the path of the motor nerve, which allows muscle fibers to fulfill their main functions.
The structure of striated (or skeletal) muscles consists of structural and functional units - fibers. In turn, the fibers are represented by myofibrils, consisting of a smaller unit of structure called a sarcomere. In the sarcomere, thick and thin protein filaments or myofilaments are secreted.
Any movement performed by the human body occurs as follows:
- The cerebral cortex gives the command to perform an action.
- The impulse travels along the motor nerve to the muscle.
- To begin movement, thick myofilaments contract relatively thin ones.
These processes take place under the influence of neurotransmitters, with the participation of ATP, calcium channels, sodium ions. Summarizing the whole process of work of the striated muscles, trigger points provide a kind of wedging of muscle fibers relative to each other during contraction.
In the place of "delay" of muscle movement, the pressure becomes much higher, and blood with oxygen and nutrients is not able to penetrate into the areas subjected to spasm. Accordingly, a zone of ischemia arises. Due to the spasm, a seal can be felt in this place.
There are 2 types of trigger points:
- Active trigger point. Its location is the site of contact of the nerve with muscle tissue. It is quite easily determined at rest and during the period of muscular work. On palpation and activation of this point, unbearable sharp pain ("jump symptom") appears in the form of seizures. Irradiation of pain extends far beyond the affected muscle, so it is difficult to find out the exact location of the point. Local manifestations can be distinguished:
- increased sweating in the affected area;
- discoloration of the skin;
- increased hair growth.
-
The latent trigger point is more common. Pain, as the main symptom, appears most often during muscle tension. If a physical impact is exerted on such a point in the form of pressure, the pain will be aching, "bearable". However, any negative influence of endogenous and exogenous factors (stressful situations, hypothermia, prolonged forced position of the body) can transform the latent point into an active one.
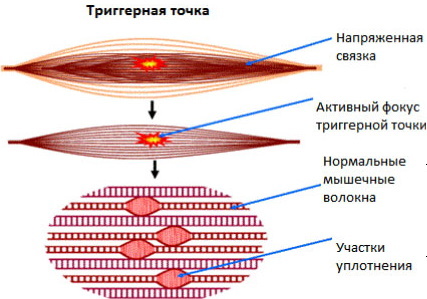
As a result of the influence of negative external and internal factors by the type of reflex, there is a sharp, quick, excruciating pain in the muscles, fascia, constrained by tension.
It is very problematic to stop the pain syndrome. However, most patients do not pay special attention to the symptoms that have arisen, believing that this is a temporary problem. This approach to the problem is absolutely not correct, since the intensity of pain only increases over time.
The most common mistake of patients with myofascial syndrome is the opinion that all problems come from the spinal column. The spine does a tremendous job in the human body, but without the joint work of muscles, ligaments and fascia, it would be powerless. And these "helpers" can just cause big trouble.
Causes and risk factors
Myofascial syndrome is a disease that is most often not associated with genetic defects. Any negative influence may be sufficient for its development.
The reasons for the manifestation of the syndrome:
- Sports injuries or excessive physical activity. Under the influence of hard physical labor, microtrauma occurs in muscle tissue: isolated muscle bundles are damaged. An inflammatory focus is formed at the site of microtraumas. In such a situation, the goal of the body's defense reaction is to scar the muscle. For the formation of the syndrome, the location of this scar is important: if it is close to the nerve tissues, then the formation of a trigger point is soon possible.
A striking example of the formation of pathology in sports can be a volleyball game. During the game, at the end of the ball throw, in order to protect the anterior deltoid and pectoral muscles from injury, the points of their attachment to the back corset are shifted back by the back muscles.
This manipulation causes lightning-fast muscle contraction and, in the future, the formation of trigger zones. This is the most common reason for the formation of trigger zones in the trapezius, dentate muscles.
- The second most common cause is osteochondrosis. Most people have a history of this diagnosis. Osteochondrosis causes irritation of the Lutsak nerve, which affects the muscular "corset" of the spinal column. Long-term muscle spasm will sooner or later lead to the formation of trigger points.
- Negative habits. Doctors distinguish in this group the habit of clenching the jaws in stressful situations, since the muscles of the face are affected.
- Congenital pathology of the development of the musculoskeletal system. It is not so common, but if it is present, the risk of developing the syndrome is very high. An example would be different lengths of the lower limbs (the difference should be more than 1 cm). When moving, there is a different load on the muscles of the feet, lower legs, thighs, lumbar spine and spine. Muscles that are in constant contraction will soon be indicated by trigger points and symptoms of myofascial syndrome will appear in the future.
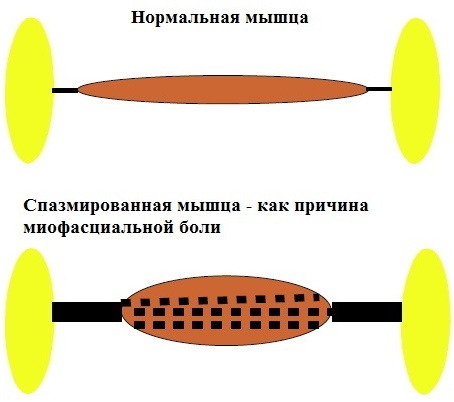
Predisposing factors or risk factors for the development of pathology:
- Poor posture, stoop.
- Clothing and jewelry that cause discomfort, restraining movement.
- Professional sports areas.
- Overweight.
- Limited mobility, forced immobilization.
- Pathology of the spinal column, skeleton.
- Emotional lability, stress.
- Hypovitaminosis, lack of vitamins A (thiamine, pyridoxine, folic acid, cyanocobalamin).
- Lack of minerals and vitamins.
- Dysfunction of the endocrine system - diabetes mellitus, obesity, thyroid disease. Disorders of the endocrine system leads to impaired absorption of essential microelements and vitamins.
- Metabolic disorders - gout or a predisposition to its development.
Any external stimulus affects receptors that are not ready for stress. In response, there is an involuntary reflex muscle contraction.
Cervical
The cervical spine is the most active in the motor plan. Accordingly, the muscle corset of the cervical spine is prone to muscle spasms.
Myofascial syndrome of the cervical spine is often formed due to the presence of stress factors. These factors can serve as such phenomena as anxiety, depression, systematic psychological overload and any disturbances in the psycho-emotional background.
They lead to an involuntary contraction of the muscles of the neck, trapezium. The trapezius muscle is called the "stress muscle". Every second inhabitant of the planet admits that after any anxiety, a pulling pain appears in the area of the trapezius muscle.
Postural stresses are manifested in an excessive load on the muscles due to the incorrect position of the body in space. For example, a student's cervical spine suffers while taking notes on lengthy lectures.
A non-anatomical sleep pillow (large or small) can also contribute to the formation of latent trigger points.
After sleeping on such a pillow, sensations arise:
- "Brokenness"
- headache (migraine),
- drawing pain and heaviness in the neck.
Thoracic department
This is the largest section of the spinal column. Incorrect posture plays the main negative role.
Her reasons:
- desktop, does not match the height,
- hours of work with a computer,
- wearing uncomfortable shoes affects the muscles of the thoracic region.
Myofascial syndrome is a condition when, in addition to pain, fear appears. Especially with the involvement of the pectoralis major and minor, when there are signs of shortness of breath.
You can forget about such problems if:
- use an orthopedic mattress for sleeping,
- avoid heavy irrational physical exertion,
- do stretching.
Paravertebral muscles (located on both sides of the spinal column) are the site of the formation of trigger points with gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, pyelonephritis and other diseases of organs located above the small pelvis.
Lumbosacral
The lumbosacral region, like the cervical, is systematically subjected to increased stress. It is easy to disrupt the correct functioning of the department.
Enough:
- use improperly selected shoes,
- high heels,
- be in a certain position for a long time, for example, sitting on uncomfortable furniture.
Among the diseases of the internal organs that affect the lumbosacral spine, there are chronic colitis, various urological and gynecological pathologies. Congenital pathologies, leading to the corresponding skewing of the pelvis and the development of compensatory scoliosis, exert a strong stress.
Symptoms
Clinical symptoms can be extensive, since ischemic areas of spasmodic muscles disrupt the nutrition of other organs. The most important symptom in myofascial syndrome, in addition to pain, is considered a "functional block of movement". Because of the pain, the range of motion of the affected area of the body is limited.
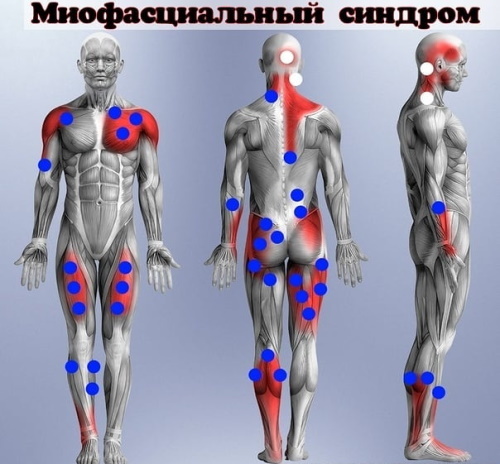
Below are the areas of the lesion and possible symptoms:
| Presumptive diagnoses, manifestations | Location of trigger points |
| Headache with muscle tension and sharp pain in the occiput, atypical migraine. | Back muscles of the neck, suboccipital and temporal muscles. |
| Heart pain (angina) | Pectoral muscles |
| Subacromial bursitis | Deltoid muscle, in particular the middle part. |
| Gynecological disorders (in particular, problems with the menstrual cycle). | The projection of the lower part of the rectus abdominis muscle. |
| Chronic abdominal pain, appendicitis. | Abdominal muscles |
| Tennis elbow | Supporter |
| Frozen shoulder | Suprascapularis muscle |
Diagnostic methods
On the basis of many years of practice, palpation by the hands of a doctor has become a well-deserved, the only correct way of diagnosis. With its help, the doctor determines the position of the trigger points. During the examination, the doctor assesses the general psycho-emotional state, posture and coordination of movements.
In a conversation, they learn information about cases of numbness, tingling or cramping sensations. For a full assessment of the neurological status, reflexes are checked. It is especially important not to miss all possible harmful factors; in some situations, consultations of other narrow specialists and testing may be required.
Initially, the attending doctor is obliged to exclude:
- spinal diseases,
- compression injuries of the spine,
- inflammatory processes.
Having excluded all the described pathologies, one should correctly "probe" the sore points. During a manual examination, the doctor stretches the muscle fibers lengthwise, thereby stimulating the onset of pain. There will be a long tight cord along the relaxed muscle, gradually, studying it, they reveal a painful spot or trigger point. When pressing, the doctor will detect the places where the pain is radiating.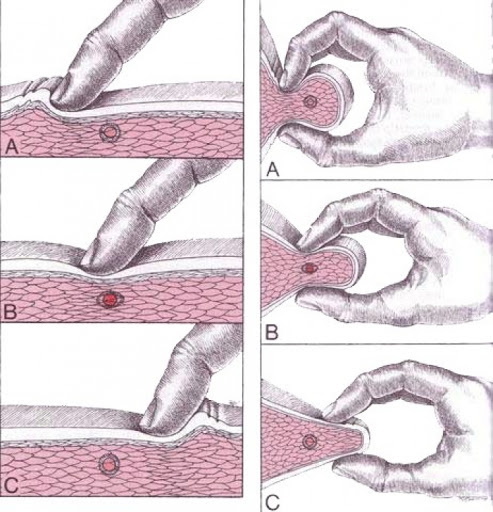
Palpation of trigger points is:
- Tick-borne technique. A section of muscle is grasped between the thumb and the rest of the toes and rolled between them.
- Deep technique. A professional, grasping a muscle fiber with his fingertips, evaluates it, passing in the transverse direction.
Examining muscles with your hands allows you to:
- detect or not detect points of pain,
- assess the condition of the muscles (hypotrophy or hypertrophy),
- how far the pain spreads
- what kind of pain occurs (sharp, lightning-fast or pulling).
Despite this simple, affordable method, other diagnostic methods for assessing the work of internal organs cannot be ruled out.
Therefore, they additionally apply:
- daily monitoring by Holter;
- ECG;
- coronary angiography.
Complications and prognosis
Myofascial syndrome is such a common disease that causes many complications.
For the general concept of "health", the following complications are dangerous:
- A trigger that exists for a long time intensifies its pain impulses at the expense of the spinal cord.
- The contracted muscle negatively affects the intervertebral discs, nerve roots, fascia, contributing to their destruction, and the appearance of new pathologies.
- On the territory of pain irradiation, new latent triggers can form.
- The final stage of the trigger point and the disease is considered to be fibrosis of muscle tissue. If the muscle is contracted, minor injuries occur when trying to stretch it. The body directs fibroblasts that synthesize collagen fibers to the places of these muscle cracks. They "envelop" the muscle at a great distance, after which the "saved" muscle is painless, but at the same time resembles a tendon cord, and is completely weakened.
- Fibromyalgia, or a condition characterized by regular, symmetrical pain throughout the body. At the same time, normal sleep and digestion are disrupted, and the concept of "chronic fatigue" is formed.
In the context of modern medicine and timely treatment, the prognosis for life is not so depressing.
Treatment activities
The pain syndrome is stopped by drugs, and the causes are neutralized using different methods of treatment.
Drug therapy
This branch in the treatment relieves pain.
The following medications help in this:
- NSAIDs. The duration of the course is no more than 14 days. Preparations: Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Nurofen.

- If the pain syndrome is maximally pronounced, disrupts the patient's sleep, the quality of life and affects the general psychoemotional state, mild sedatives are prescribed, for example, Diazepam.
- With advanced forms of the disease, antidepressants are recommended.
- Muscle relaxants of central action in small dosages. Example, Midocalm, Baclofen.
- Topical preparations (ointments, gels, creams), which include NSAIDs.
- Multivitamin complexes.
Physiotherapy
In the treatment of the syndrome, physiotherapy is prescribed individually, according to certain indications.
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment include:
- Electrophoresis.
- Cryoanalgesia.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Electrical stimulation.
- Ultrasound.
Physiotherapy
Both physiotherapy and exercise therapy are complementary treatments. Physical therapy is recommended during a certain period of treatment, otherwise, the risk of worsening pain is very high.
Massage
The positive effect of massage in this pathology:
- Resumes mobility in the affected area.
- Improves blood circulation.
- Eliminates muscle tension.
With the disappearance of the pain syndrome, it is permissible to perform canned massage.
Post-isometric relaxation
This is a special method of manual therapy. Its purpose is to eliminate pain and relax muscles. Immediately before the procedure, the affected area is warmed up with a light massage and anesthetic ointments. Thus, the lesion is warmed up. The site is slowly stretching. 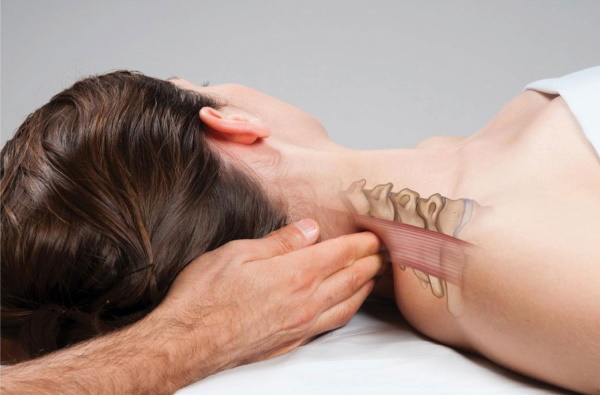 In the course of execution, a change in body posture is permissible.
In the course of execution, a change in body posture is permissible.
Acupuncture
Trigger points are located in places of acupuncture, whereby they are stimulated. The trigger relaxes and the muscle receives the necessary blood flow. This method of treatment is especially useful and available for pain with pathology of the spine.
Surgery
Surgical intervention for this pathology is an urgent need when conservative treatment has not yielded results. The disease is progressing or is already in advanced form.
ethnoscience
As a treatment, traditional medicine will only help treat mild symptoms.
An example of folk ways:
- Paraffin thermal wraps. Technique: warm paraffin under cling film to the trigger site. Duration no more than 30 minutes.
- "Salt" bandage. Technique: put dry hot coarse salt in place of pain.
Homeopathy
Like other treatments, homeopathy focuses on relieving muscle spasms. The most common drugs are Spascuprel, Rustoxycodendron.
Myofascial syndrome is a rather formidable disease that leads to a violation of the quality of life. This is a condition in which delaying the issue of treatment can lead to serious disorders throughout the body.
Video about myofascial syndrome
Doctor OROS. Myofascial syndrome:



