Hand antiseptics are used to disinfect the skin and kill pathogenic microorganisms. Most drugs in this category are effective against bacterial, viral and fungal infections.
Antiseptic medicines for external use are available in the form of liquid solutions, gels and sprays. Each drug in this group has a unique biochemical composition based on organic or inorganic compounds.
Record content:
- 1 Classification of antiseptics
- 2 Composition of disinfectants
-
3 Antiseptics for hand disinfection
- 3.1 Gels
- 3.2 Sprays
- 3.3 Creams
- 3.4 Napkins
-
4 Means for the treatment of wound surfaces
- 4.1 Ethanol
- 4.2 Hydrogen peroxide
- 4.3 Iodine, povidone-iodine
- 4.4 Chlorhexidine bigluconate
- 4.5 Benzyldimethyl-myristoylamino-propylammonium
- 4.6 Potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate)
- 4.7 Brilliant green solution
- 4.8 Fukortsin
- 4.9 Octenidine (as octenidine dihydrochloride)
- 5 What products are forbidden to use for children
- 6 Product Videos
Classification of antiseptics
Antiseptic agents for treating the skin of hands are a separate pharmacotherapeutic category of drugs that differ in the mechanism of action on pathogens.
The table below describes in detail the classification types of medicines in this group that can be used to disinfect the upper limbs and household surfaces.
| Classification of antiseptics | Characteristics of disinfectants |
| Polyguanidines | Polyguanidines are antiseptic agents that are made on the basis of chemical compounds containing chlorides and phosphates. The principle of action of medicines of this group is that the active components of the disinfectant solution penetrate into the cells of the pathogenic microorganism. After this, the production of enzymes necessary for the further division of infectious agents is blocked. A distinctive feature of antiseptic agents from the polyguanidine group is that they do not possess toxic properties, and can also be used by people who are prone to the manifestation of allergic reactions. |
| Halogenated medicines | Halogenated agents for antiseptic treatment of hands and surfaces of household items are represented by drugs that are produced on the basis of iodine and chlorine. Medicines in this category are especially effective against bacterial microorganisms. Halogenated antiseptics include Chloramine, Chlorhexidine, Iodinol, and an alcohol solution of Iodine. |
| Oxidants | Oxidants are a separate pharmacological group of external disinfectants. The principle of their antiseptic action lies in the fact that at the moment of their contact with human tissues, a biochemical reaction occurs with the release of a large number of oxygen molecules. This effect allows you to achieve a short-term disinfecting effect. Most pathogens on the surface of epithelial tissues die. The main disadvantage of oxidative antiseptics is that after 15-20 minutes. complete restoration of pathogenic microflora is possible. Disinfectants of this group include a solution of potassium permanganate and hydrogen peroxide. |
| Acids | Several types of inorganic acids are used for external treatment of hands and environmental surfaces. Salicylic and boric acids are referred to drugs of this classification type. Antiseptics of this group are not very popular due to the low disinfecting effect, as well as the negative effect on the surface of epithelial tissues. |
| Alkalis | For disinfecting purposes, only one antiseptic agent based on an alkaline compound is used. This is an ammonia solution that is used for hand washing. This drug has pronounced disinfecting properties. The ammonia solution can be added to the water used for cleaning floors and disinfecting household items. |
| Alcohols | Aliphatic alcohols are used for antiseptic treatment of hands. Disinfectants of this group are produced in the form of liquid solutions of 60-70% concentration. Medicines in this category include ethyl alcohol, propyl alcohol, and isopropyl alcohol. |
| Multicomponent drugs | Modern antiseptics are distinguished by the fact that they simultaneously contain several biochemical components with different disinfectant and pharmacological properties. For example, thickeners, pH stabilizers, buffer systems and antioxidants are added to disinfectants, which neutralize the aggressive properties of the antiseptic. |
| Plant-based products | Medicines of this classification type have moderate disinfecting properties. The principle of action of antiseptics on a natural basis is the manifestation of the biochemical activity of alkaloids that are contained in the composition of plants. The medicines of this group include alcoholic tinctures and water decoctions of lingonberry leaves, calendula flowers, bearberry. |
Most of the above antiseptics are produced in the form of liquid solutions. This form of release of disinfectants is the most practical and convenient to use for disinfecting the skin of the hands, as well as environmental items.
Composition of disinfectants
Disinfectants can be organic or inorganic.
The following antiseptics are classified as chemical compounds of the first category:
- phenols;
- derivatives of furacilin and nitrofuran;
- brilliant green solution and methylene blue;
- formaldehyde-based products;
- various types of alcohols;
- biguanides (the most famous antiseptic in this category is Chlorhexidine);
- detergents;
- antibacterial complexes for external use (in this case, Novoimanin, Gramicidin, Heliomycin preparations can be used for antiseptic treatment of hand tissues).
To preparations for disinfecting the skin of hands and the surface of environmental objects, which have an inorganic composition, include antiseptics of the following category:
- halogen-containing solutions (Chloramine, Iodinol, Iodine alcohol solution);
- oxidizing agents;
- compounds based on metal salts;
- derivatives of alkali and acids.
The mechanism of action of antiseptics directly depends on what chemicals are in their composition. Disinfectants based on organic and inorganic compounds can be used in health care facilities, at home to treat household items.
Antiseptics for hand disinfection
Hand antiseptics come in various forms that are intended for external use only.
Gels
Antiseptic gels are medications that are meant to be used on a daily basis. Disinfectants of this group are effective against bacterial and viral microorganisms. The principle of using gels with antiseptic properties is that a person applies 3-5 ml of this agent directly to the epithelial tissues of the hands.
Then it spreads the disinfectant over the entire skin surface. Antiseptic gels are available in plastic bottles with a capacity of 20 to 250 ml. Disinfectants of this group are used in health care institutions, at home conditions, as well as in industrial plants where strict adherence is required sanitary and hygienic standards.
Sprays
Antiseptic sprays are medicines that are liquid disinfectants sprayed with a mechanical device.

Preparations of this form of release are applied simultaneously to several areas of the skin of the hands, and then the disinfecting solution is rubbed over the entire surface of the skin. The use of sprays is convenient and practical, since in this case the antiseptic treatment of hands takes no more than 30-45 seconds.
Creams
Creams for disinfecting the surface of the skin of the hands have a distinctive mechanism of action. Antiseptics of this form of release are applied to the epithelial tissues of the upper extremities with their uniform distribution over the entire area of the treated area of the body.
As the disinfectant cream dries, a thin film forms, which subsequently acts as a protective barrier of the skin against the effects of pathogenic microorganisms. The main advantage of using drugs of this group is the simultaneous disinfection and moisturizing of tissues.
The disadvantages of antiseptic creams include the fact that in most cases their components are effective only against bacteria, but are not able to deactivate viruses.
Napkins
Antiseptic wipes are medical products that are impregnated with disinfectant solutions. The most commonly used alcohol is high concentration. Antiseptic wipes are available in individual packages, are completely sterile, and also have a wide range of applications.
Pharmaceutical products of this type can be used for the daily processing of hand tissues. If necessary, these wipes are used to disinfect environmental objects. To use this antiseptic, it is enough to open the individual packaging, remove a napkin from it, and then wipe your hands thoroughly.

It is important to remember that in the process of daily use of these products, the appearance of increased dryness of the skin is possible.which loses moisture due to exposure to alcohol.
Means for the treatment of wound surfaces
Most antiseptic preparations with different biochemical compositions can be used not only for disinfecting the skin of the hands, but also for disinfecting open wounds. At the same time, medicines of one pharmacological group do not cause discomfort, and after applying other means, a person experiences burning pain.
Ethanol
Hand sanitizers may contain an ethyl alcohol solution. Moreover, this substance is also used to disinfect soft tissues that have been damaged as a result of injury. The principle of the disinfecting effect of ethyl alcohol is that it is able to denature the protein of pathogenic microorganisms.
This substance damages the cells of the pathogenic agent, which soon dies. A small amount of ethyl alcohol is applied directly to the open wound, or to sterile cotton wool, with the help of which the injured area of the body is treated. The main disadvantage of this antiseptic is that it causes burning pain.
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide belongs to the category of antiseptics with an oxidative effect. At the time of treatment of an open wound with the use of this disinfectant, a biochemical reaction is formed with the release of a large amount of oxygen, which destroys the pathogenic microflora.
Hydrogen peroxide does not cause pain, does not cauterize epithelial tissues, but also does not have a long-term antiseptic effect. This tool is suitable as a preparation for the primary sanitization of open wounds. Hydrogen peroxide is applied directly to tissues that show signs of injury.
Iodine, povidone-iodine
Antiseptics in the form of an alcoholic solution of Iodine, as well as Povidone-iodine are chemicals that which can be used not only to disinfect an open wound, but also to cauterize epithelial fabrics.
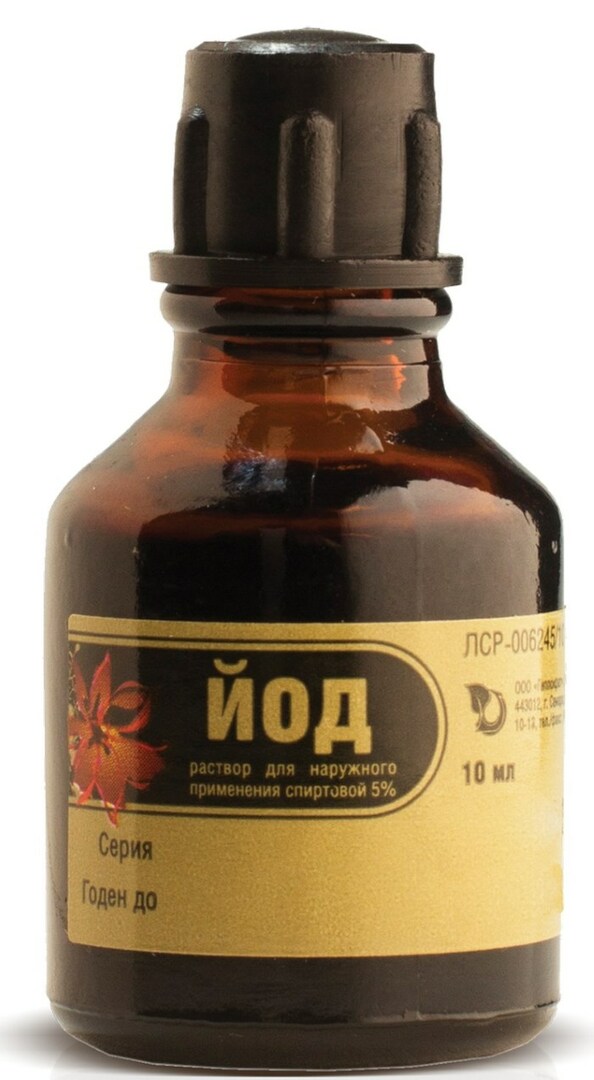

The principle of using these medicines requires the following algorithm of actions:
- Open a bottle with an alcoholic solution of Iodine.
- In this antiseptic solution, moisten the edge of a cotton swab.
- Treat an open wound with an alcohol solution of Iodine.
At the moment this drug enters the surface of damaged tissues, a burning sensation may appear, the severity of which depends on the depth of the wound. The use of iodine-based antiseptics is contraindicated in people who have iodism.
Chlorhexidine bigluconate
Chlorine-based hand sanitizers can also be used to decontaminate open wounds. In this case, the drug Chlorhexidine bigluconate can be applied directly to the injured part of the body, or an open wound is wiped with a cotton swab dipped in this disinfectant means.
A distinctive feature of Chlorhexidine bigluconate is that this solution is equally effective against bacteria, viruses and fungal microorganisms. This antiseptic is produced on the basis of hypochloric acid derivatives.
Benzyldimethyl-myristoylamino-propylammonium
Benzyldimethyl-myristoylamino-propylammonium is a topical antiseptic that has antiviral and antibacterial effects.
This drug is effective against the following types of microorganisms:
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- streptococcal infection;
- salmonella;
- colibacillus;
- shigella;
- treponema;
- chlamydia trachomatis;
- the causative agent of candidiasis.
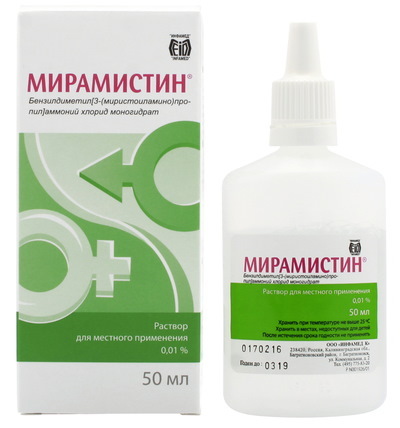

Benzyldimethyl-myristoylamino-propylammonium is applied directly to the diseased area of the skin, which has signs of damage. This drug can be used as a first aid tool, and is also used to treat purulent wounds.
Potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate)
A solution of potassium permanganate is one of the most affordable and simple means of antiseptic treatment of open wounds.
Potassium permanganate has the following properties:
- disinfects damaged tissues;
- prevents the development of suppuration;
- relieves the inflammatory process;
- damages the cellular structure of pathogens.

To prepare a solution of potassium permanganate, it is enough to take 2-3 crystals of potassium permanganate, and then dissolve them in 300 ml of boiled water at room temperature. The resulting product is used to wash the damaged tissue. The antiseptic procedure is performed 2-3 times a day until the wound is completely healed.
Brilliant green solution
Brilliant Green Solution is a first aid disinfectant that is applied to damaged areas of the body. Also, a small amount of this drug is used to treat epithelial tissues located in the circumference of the wound.

A solution of brilliant green is made on the basis of the chemical compound triphenylmethane. At the time of application of this drug, a pronounced burning sensation appears on the surface of an open wound.
Fukortsin
Fukortsin is a solution that has a deep dark red color, and also has a pronounced smell of phenol. This drug has a complex antiseptic effect and is effective against fungal microorganisms.
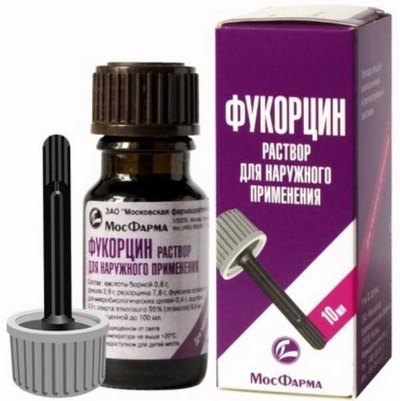

Fukortsin is applied to the affected area of the body with a cotton swab 2 to 4 times a day. After that, the dried wound can be treated with ointment or anti-inflammatory paste.
Octenidine (as octenidine dihydrochloride)
Octenidine dihydrochloride is a chemical that has antimicrobial properties. On the basis of this component, antiseptic preparations by MestaMidin-Sense, as well as Octenisept, are produced.
In this solution, sterile gauze or cotton swabs are moistened, with the help of which the disinfectant treatment of the wound is performed. The therapeutic procedure is carried out 2 times a day. The duration of the therapeutic course is 14 days.
What products are forbidden to use for children
Iodine-based antiseptics are contraindicated in children under 5 years of age.
Restrictions in the use of these drugs are associated with a high risk of local allergic reactions. Phenol-based medicines are not recommended for children., since disinfecting solutions of this group have a strong irritating effect.
Hand sanitizers are liquid solutions, creams, gels, and wipes that contain chemicals with antimicrobial properties. Medicines in this category are intended for external use only.
The application of medicines is carried out on the epithelial tissues of the upper extremities. If necessary, antiseptics can be used to treat open body wounds that have formed as a result of injury.
Product Videos
Hand antiseptics - how to make at home:



