 Morganyi-Adams-Stokes syndrome( MAS syndrome) is a syncope that occurs with a sudden disturbance of the heart rhythm, and which entails cerebral ischemia and a sharp decrease in cardiac output.
Morganyi-Adams-Stokes syndrome( MAS syndrome) is a syncope that occurs with a sudden disturbance of the heart rhythm, and which entails cerebral ischemia and a sharp decrease in cardiac output.
Morgani syndrome occurs due to cerebral ischemia, which occurs with a sharp decrease in cardiac output. This occurs when the heart rate or heart rate is disturbed.
Morganyi Adams Stokes seizures are often caused by the atrioventricular blockade. The attack occurs when the blockade occurs, followed by the development of sinus rhythm or supraventricular arrhythmia.
Contents
- Reasons for provoking diseases and factors
- Features of the clinical picture
- Emergency first aid
- Diagnosis
- Treatment of the
- syndrome Medication
- Surgical treatment
- Prevention of attacks and relapses
- Than it is fraught?
Reasons causing diseases and factors
Syndrome attacks occur in such processes in the body: 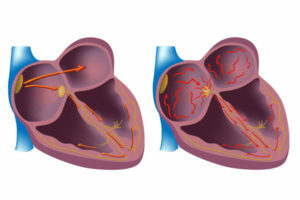
- atrioventricular block;
- transition of incomplete atrioventricular blockade to full;
- cardiac rhythm disorder, which is accompanied by a decrease in the contractility of the myocardium( with febrile, ventricular flutter, paroxysmal tachycardia, asystole);
- tachyarrhythmia and tachycardia with a heart rate of more than 200 beats;
- bradyarrhythmia and bradycardia with a heart rate less than 30 beats.
The risk of developing a syndrome exists if the following conditions are present in the history:
- Chagas disease;
- inflammatory processes localized in the cardiac muscle, and which spread to the conduction system;
- diffuse growth of scar tissue, and subsequent defeat of the heart with Leva-Lehner's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, Liebman-Sachs disease, systemic scleroderma;
- disease with general neuromuscular changes( genetic diseases, myotonia);
- intoxication with medical preparations( beta-adrenoblockers, calcium antagonists, cardiac glycosides, Amiodarone, Lidocaine);
- ischemia of the cardiac muscle in cardiomyopathies, myocardial infarction, infarction;
- increased iron deposition in hemochromatosis and hemosiderosis;
- systemic amyloidosis;
- functional conduction abnormalities in the atrioventricular node.
Clinical features of
 Syndrome is observed in 25-60% of patients with complete atrioventricular block. The frequency and number of seizures varies in each clinical case. Morganya Edens Stokes seizures can occur with a frequency of every few years, and can occur several times during one day.
Syndrome is observed in 25-60% of patients with complete atrioventricular block. The frequency and number of seizures varies in each clinical case. Morganya Edens Stokes seizures can occur with a frequency of every few years, and can occur several times during one day.
Provoke sudden seizures, sharp changes in body position, nervous overload, stress, emotional stress.
The attack is preceded by the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- a sudden concern;
- weakness;
- darkening in eyes;
- headaches;
- noises in the ears and head;
- increased sweating;
- nausea, vomiting;
- pallor of the skin;
- blue lips;
- movement coordination disorders.
After a while( about 1 minute) the patient has an attack, and he loses consciousness. Syncope occurs with a heart rate of less than 30.
Syncope, often short-lived, and does not last more than a few seconds. During this time, compensatory mechanisms are activated that allow the elimination of arrhythmia. After exiting this condition, the patient has retrograde amnesia, and he does not remember what happened.
In case of an attack of Morganya Adams Stokes syndrome, the following symptoms are typical:
- pallor of the skin;
- swelling of the cervical veins;
- blue lips and fingertips;
- spontaneous defecation and urination;
- cold sweat( sticky);
- weak muscle tone, convulsions;
- inability to determine pulse;
- reduced blood pressure;
- deaf and arrhythmic heart sounds;
- dilated pupils;
- rare and deep breathing.
Depending on the degree of intensity of symptoms, several forms of attack are distinguished:
- Light - there is no loss of consciousness, the patient is dizzy, sensitivity is disturbed, noise in the ears and head appears.
- of moderate severity - the patient has a loss of consciousness, but there are no signs such as voluntary urination and defecation, seizures are also not observed.
- Heavy - present the entire symptom complex.
Emergency First Aid
In case of an attack of Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome, the patient needs emergency medical care, on which the duration of the attack and the life of the patient will depend.
The first step is mechanical defibrillation, also called a precordial stroke. It is necessary to strike with the fist in the chest, namely in its lower part. You can not make a stroke in the heart. After mechanical defibrillation, the heart reflexively begins to contract.
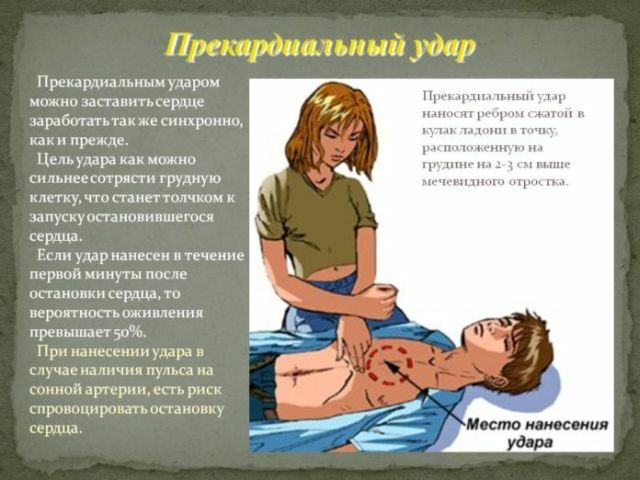
In the absence of effect, electrical defibrillation is performed. To do this, electrodes are placed on the patient's chest and a shock is produced by the current discharge. After that, the right rhythm of the heartbeat must return.
In the absence of breathing, artificial ventilation is provided. To do this, air is blown into the patient's mouth using a special device, or by mouth-to-mouth.
Cardiac arrest is an indicator for the injection of Adrenaline( intracardiac) or Atropine( subcutaneously).
If the patient retains consciousness, then it is necessary to give the preparation of Iazrin under the tongue( the effect is similar to Adrenaline, Ephedrine, Noradrenaline, but there is no increase in blood pressure).
The patient must be taken to the intensive care unit of the hospital. In the hospital, emergency care is accompanied by monitoring on the ECG apparatus. To the patient several times a day subcutaneously injected drugs Atropine sulfate and Ephedrine, give under the tongue of Iazdrin. If necessary, electrostimulation is performed.

Statement of diagnosis
Loss of consciousness is possible with various diseases. Therefore, during the diagnosis, the Adams-Stokes-Morgagni syndrome must be differentiated with such conditions:
- Meniere's syndrome;
- hypoglycemia;
- stroke;
- hysteria;
- orthostatic hypotension;
- attack of transistor ischemic attack of the brain;
- sharp aortic stenosis;
- pulmonary embolism;
- thrombosis of the heart chambers;
- epilepsy.
To determine the syndrome, apply such diagnostic methods:
- electrocardiogram( ECG) in dynamics;

- monitoring of a cardiogram on a Holter device( allows to identify temporal changes, combination of flutter and atrial fibrillation);
- long-term monitoring of the electroencephalogram;
- contrast coronary angiography;
- myocardial biopsy.
Treatment of
Syndrome The onset of treatment involves first aid in case of an attack. Then follows therapy, the purpose of which is the prevention of recurrence of attacks of Morgagni Adams Stokes syndrome. Medical measures are performed in the cardiology department.
Initially, the causes of seizures are identified, a detailed examination of the heart is performed, the diagnosis is clarified and a set of therapeutic measures is appointed. Such methods of therapy are used.
Medical treatment
After the patient's admission to the intensive care unit, medicinal preparations are treated. Droppers  with the introduction of Ephedrine, Orciprenaline are used. Every 4 hours the patient is given Isadrin. Injections of ephedrine, Atropine are produced.
with the introduction of Ephedrine, Orciprenaline are used. Every 4 hours the patient is given Isadrin. Injections of ephedrine, Atropine are produced.
Inflammatory processes are removed with the help of corticosteroids. Since bradycardia is accompanied by tissue acidosis and hyperkalemia, it is necessary to take diuretics, an alkaline solution. This helps to remove potassium from the body and normalize blood pressure.
After stopping the attack, prescribe preventive therapy with antiarrhythmic drugs, and also send treatment to get rid of the underlying cause of the syndrome( ischemia, intoxication, inflammatory process).
Surgical treatment of
In the event that there is a risk of sudden cardiac arrest and recurrence of attacks, the necessary measure is the implantation of a pacemaker. It is possible to use two types of pacemakers: with full blockade - the device that provides a constant heart stimulation, with incomplete blockade - the device that works when there are irregularities.
During surgery, the electrode is inserted through the vein and fixed in the right ventricle of the heart. The body of the stimulant is fixed in the rectus abdominis muscle( in men), or in the retromammary space( in women).
The pacemaker should be checked for operability once every 3-4 months.
Prophylaxis of attacks and relapses
The use of preventive measures is possible in attacks that are caused by paroxysms of tachyarrhythmia or tachycardia. In this case,  patients are prescribed various antiarrhythmic drugs.
patients are prescribed various antiarrhythmic drugs.
Also, it is necessary to exclude the factors that lead to the onset of an attack - sudden movements, sudden changes in body position, experiences, nervous overload, emotional stress, intoxication.
With full atrioventricular blockade, the main preventive method is the pacemaker installation.
Than it is fraught?
The severity of the consequences directly depends on the frequency of seizures and their duration. Frequent and prolonged brain hypoxia leads to a negative prognosis of the disease.
Hypoxia lasting more than 4 minutes brings irreversible brain damage. The absence of resuscitative measures( indirect heart massage, artificial respiration) can lead to the cessation of cardiac activity, the disappearance of bioelectric activity and death.
When the surgery is performed, the prognosis is positive. Implantation of the pacemaker allows to return the quality of life, work capacity and health of the patient.

