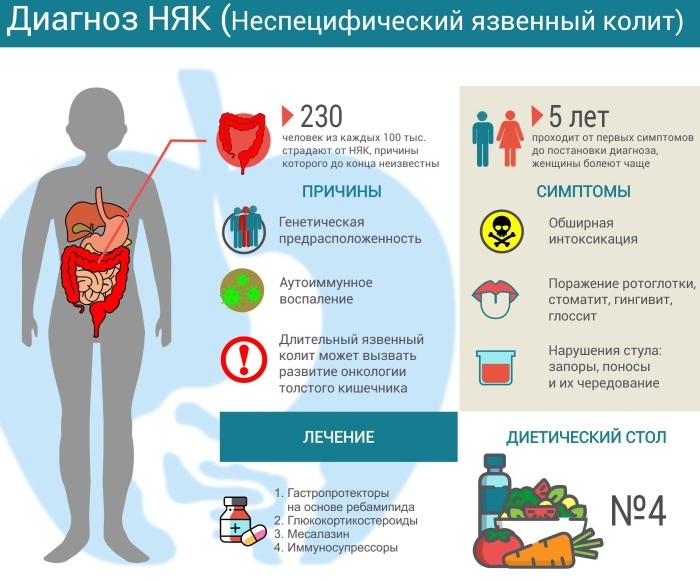
At ulcerative colitis the mucous membrane of the large intestine is affected. The inflammation is often chronic. The disease is quite difficult to diagnose, it often develops quite severely, seriously affecting the intestines and disabling many body systems, and also cannot be completely cured.
Record content:
- 1 The mechanism of development of the disease
- 2 The reasons for the development of the disease
- 3 Risk factors
- 4 Symptoms of pathology
-
5 Diagnostics
- 5.1 Laboratory research
- 5.2 Hardware diagnostics
- 6 Treatment of the disease
- 7 Medication
- 8 Folk remedies
- 9 Diet therapy
- 10 Prognosis and complications
- 11 Clinical guidelines for patients
- 12 Video about NNC
The mechanism of development of the disease
The mechanisms of the development of the disease, like some other autoimmune diseases of the intestine, have not been determined for certain.
Ulcerative colitis can be triggered by a number of factors in the aggregate, when, along with genetic a predisposition to this disease in the body develops an immune response and the intestinal cells are perceived as alien.
Often, the situation is aggravated by disturbed flora, as well as intestinal infections that join, which leads to inflammation of the tissues of the large intestine.
Most researchers assign the main role in the development of NUC to genetic predisposition. It is known that the risk of colitis in first-degree relatives is quite high and amounts to about 18.39%.
However, the development of the disease is often provoked by various negative factors, which are a kind of trigger mechanism for a person's immunity to begin to reject his own intestines. Such factors are stress, long-term violation of the diet, intestinal infections.
Most often, colitis affects young people aged 16-35 years, as well as elderly patients who have crossed the 60-year mark. In most patients with UC, inflammation begins to manifest itself first in the rectum, but gradually other areas of the large intestine may also be affected. The larger the area of the mucous tissue of the large intestine is affected, the more severe the disease progresses.
The reasons for the development of the disease
Ulcerative colitis is classified as a disease, the reliable causes of which have not yet been established.
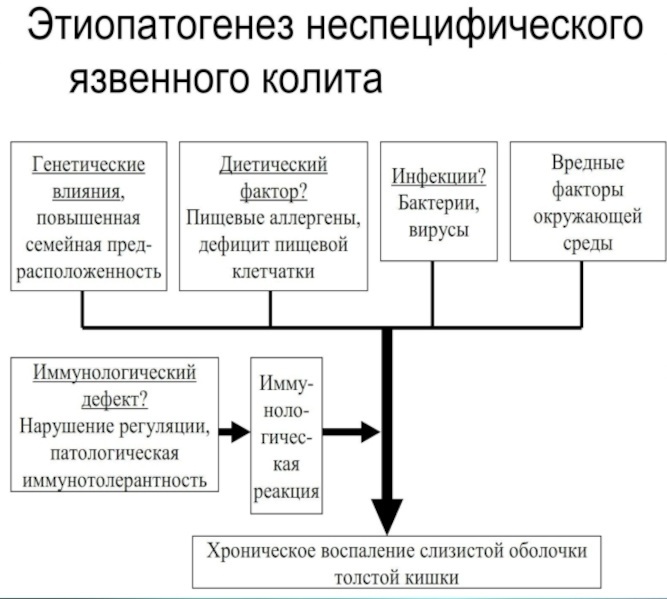
Physicians and research scientists have several versions of the origin and development of this pathology:
- hereditary (genetic) - there is evidence that inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including NUC, are more likely to affect people whose close relatives also suffered from similar diseases. The risk of developing nonspecific colitis in offspring with this disease in parents is 15-20% higher than in children whose parents do not suffer from this disease. If NUC is diagnosed in both parents, then the likelihood that the child will also develop symptoms of this disease by the age of 20-25 increases significantly and is 50-55%. It is believed that parents with UCN pass on a certain set of altered genes that predispose to this disease;
- infectious - the beginning of the pathological process in the intestine is given by a certain pathogen. With colitis, dysbiosis almost always develops in the intestine, which directly depends on the severity of the inflammatory process in the intestine. What specific pathogen can lead to damage to the walls of the large intestine and the development of NUC is still being studied. The question also remains open of what is primary in the development of the disease - the appearance of an infection or its progression against the background of a suddenly manifested disease, but on this score there are also no reliable data. Among the viruses that aggravate the course of the disease and have a bad effect on therapy against NUC, there are rotaviruses, reoviruses, cytomegaloviruses;
- allergic - based on the fact that most patients with UC do not tolerate milk well. This theory retains its significance at the present time, but in addition to milk with NUC, intolerance to other products (spicy, cereal) may occur. Confirmation of this version is that in such patients, an increased content of immunoglobulins E, indicating an allergic reaction, and a high level of histamine in the mucous membranes intestinal tissues;
- psychogenic - this theory in explaining the origin of NNC prevailed in the 30s. XX century. Subsequently, they began to take it into account again, since in some of the patients the manifestation of the disease was associated with psycho-emotional overstrain, stress. But still, it is not entirely true to say that stress alone is the trigger for the development of this disease, since often the illness itself and the changes that it makes to the habitual life act as stress for the patient rhythm. A number of researchers attribute NUC to psychosomatic diseases and often such patients in a psychiatric history have unresolved problems and conflicts, which are psychotraumas;
- autoimmune - detection of antibodies to cells of the large intestine allows us to conclude that the causes of the development of the disease can be autoimmune processes in the body, when the normal intestinal environment is perceived by the body as autoantigens. In this case, the body's immunity recognizes intestinal cells as foreign and begins to attack them, which leads to pathological inflammation.
It should be noted that none of the above versions explains the causes of NUC and most doctors and researchers agree that the development of the disease is influenced to some extent by all described causes.
Risk factors
Ulcerative colitis is a disease that can affect anyone, but some people are at greater risk of being affected.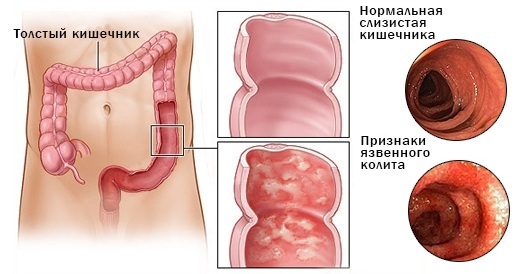
| Age | It can develop at any age, but most often affects young people around the age of 30 or older people (over 50). |
| Long-term therapy with non-steroidal drugs | Long-term use of Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Piroxicam and some other similar drugs can lead to the occurrence of symptoms characteristic of ulcerative colitis or aggravate the course of an existing NUC. |
| Ethnicity and race | People of the Mongoloid and Negroid race are less susceptible to this unpleasant disease than people with white skin. Studies have shown that Jews are at very high risk of intestinal colitis. |
| Heredity | The genetic factor plays an important role, as having a close relative (parents, children, brothers and sisters) with this disease is more likely to develop colitis. |
| Isotretinoin treatment | This special acid is prescribed for the treatment of skin defects (scars, acne), as well as some types of cancer. As in the case of non-steroidal drugs, the causal relationship between the use of isotretionine and intestinal inflammation is not proven, but researchers still have data on an increase in the incidence of ulcerative colitis after using this drug funds. |
Symptoms of pathology
Ulcerative colitis is characterized by a number of different symptoms, which can be divided into 2 large groups:
- intestinal;
- extraintestinal.
The intestinal manifestations of this disease are:
- upset stool - most often it is diarrhea with bloody impurity and mucus, but sometimes constipation can also be observed, or one condition replaces another. In this case, the frequency of bowel movements with diarrhea, depending on the severity of the course of the disease, can reach up to 50 times a day (in severe form);
- abdominal cramps and pains, colic - may not be present in all patients, most often localized on the left side;
- increased body temperature - develops in connection with pathological inflammatory processes occurring in the intestine;
- severe dehydration - develops as a result of a stool disorder, which negatively affects the body's water and electrolyte balance and kidney function;
- weight loss, lack of appetite - due to an upset stool, a person with UC will quickly lose weight, but at the same time, the desire to eat is not experiences, since the food taken comes out very quickly and is not absorbed, which has a suppressive effect not only on appetite, but also on the psychological state patient;
- nausea, vomiting;
- intestinal bleeding;
- tenesmus - false urge to defecate, which are accompanied by the appearance of pulling and cutting spasmodic pains in the large intestine.
Intestinal manifestations of ulcerative colitis are similar to other IBD, such as Crohn's disease, gastritis, IBS (syndrome irritable bowel), therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, doctors pay attention to extraintestinal symptoms, accompanying NNC.
Such manifestations include:
- damage to the organs of the visual apparatus - inflammation of the conjunctiva, blurred vision;
- joint diseases - arthritis, arthrosis;
- skin problems - erythema nodosum, uveitis;
- inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity - stomatitis, ulcers;
- problems with blood vessels - thrombophlebitis, thromboembolism.
The severity of certain signs depends on the severity of the course of the disease and which parts of the large intestine are affected by inflammation. So with a general total defeat of the large intestine, frequent loose stools with a bloody admixture are more often observed, there may be pain. If the distal zones of the colon are affected, then patients often complain of constipation, tenesmus.
For a severe form of the course, general intoxication of the body is characteristic, when weakness, vomiting, nausea develops, and a high increase in body temperature is noted.
It should also be noted that the disease is recurrent in nature, when periods of remission (extinction of almost all symptoms) are replaced periods of exacerbation, although in some cases it can turn into a chronic form, in which even temporary remission is not is achieved.
Diagnostics
At the initial visit, the doctor examines the patient's history, assesses the clinical picture of the disease and examines the rectum using his fingers. To confirm or refute the diagnosis, a number of examinations are assigned, which can be divided into 2 large groups:
- hardware;
- laboratory.
Often, when making a diagnosis, difficulties arise, since in its symptomatology NUC is in many ways similar to Crohn's disease, which also affects the intestines, but inflammatory pathological processes occur not only in the colon.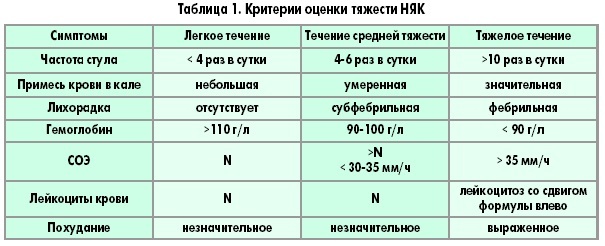
To clarify the diagnosis, a number of laboratory tests are carried out to determine specific antibodies, which will make it possible to reliably establish the diagnosis.
Also, in addition to Crohn's disease, diseases such as colon cancer, amebiasis, dysentery, and helminthic invasions are characterized by similar manifestations with UC.
Laboratory research
To clarify the diagnosis, a number of laboratory tests are prescribed by the attending physician (proctologist, coloproctologist, gastroenterologist):
- general blood test (simple clinical analysis) - when decoding with an exacerbation of the NUC, the doctor can see such signs of inflammation as:
- a decrease in hemoglobin - associated with a reduced absorption of beneficial nutrients due to pathological inflammation;
- an increase in leukocytes, platelets, an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) - all this indicates that the body is actively undergoing an inflammatory process;
- detailed (biochemical) blood test - indicators indicating the presence of inflammation of the intestinal mucous tissues are:
- increased levels of C-reactive protein and gamma globulins;
- a decrease in the concentration of Fe (iron) in the blood serum;
- increased immunoglobulins G.
- study of excrement (feces) - determine the level of fecal calprotectin, which increases with exacerbation of NUC. They also make bacterial cultures of feces, examine the biomaterial by the PCR method, examine it for the presence of helminths.
Hardware diagnostics
However, despite the importance of traditional laboratory tests, hardware methods occupy a key place in the diagnosis of NUC, since only only having in his hands a complete picture of the examination, which will include the results of both studies, the doctor is able to determine the exact diagnosis.
To clarify the diagnosis of UC, the doctor may prescribe such examinations as:
- Hardware ultrasound of the hepatoiliary system (gallbladder, ducts, liver) - since with NUC, general intoxication of the body is observed, it is important to track how the liver and gallbladder cope with the increased load;
-
Colonoscopy - the most effective endoscopic method of bowel examination, since the inserted endoscope able to study the surface of not only the entire large intestine, but also the thermal ileum intestines. For the procedure, a flexible and long video-optical device is used - an endoscope. In some cases, such an intervention can be quite painful, therefore, it is carried out under anesthesia. The method allows not only to establish a diagnosis, but also to carry out other actions during the procedure - take a biopsy, remove polyps.
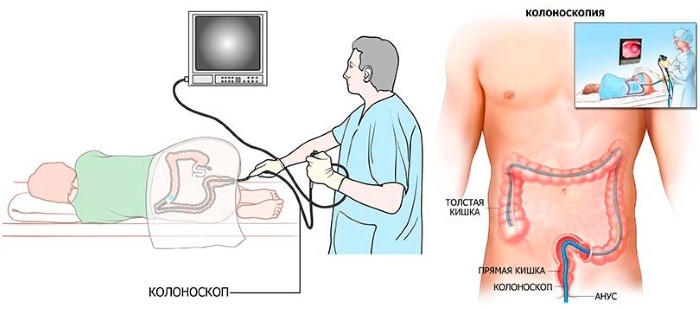
- Sigmoidoscopy - is carried out using a device called a sigmoidoscope, which is a tube that has a lighting device and a device for supplying air. During the examination, the rectal cavity is inflated with air and then the examination is carried out using the attached eyepiece. The depth of examination with sigmoidoscopy is less than with colonoscopy and is only 20-25 cm from the anus, which allows examining the rectum and 1/3 of the sigmoid colon. This procedure is not painful and has practically no contraindications. This method helps to identify neoplasms in the intestine, examine its mucous membrane, and, if necessary, take biomaterial for biopsy.
- Irrigoscopy - this study of the intestine is carried out using X-ray equipment. In order for the sections of the intestine to be visible in the pictures, a contrast solution is injected into it, and after emptying, all the necessary actions are performed. The technique allows you to assess the condition of the colon, visualize fistulas, tumors, diverticula. The method is less traumatic than colonoscopy, however, it does not give a complete picture of changes in the mucous membrane in the large intestine, and also does not allow tissue sampling for research.
All 3 methods of bowel examination require careful preparation. To do this, patients are given enemas, or they are prescribed cleansing compounds (Fortrans).
Treatment of the disease
Ulcerative colitis is sometimes difficult to treat. In this regard, treatment regimens in each specific case are selected individually, taking into account the prevailing symptoms (exacerbation are associated with constipation or diarrhea, how severe is the attack of the disease, whether there is blood loss), as well as the accompanying diseases.
With a mild course of the disease, the patient can receive treatment on an outpatient basis. For moderate colitis, the need for hospitalization is determined by the doctor. In severe cases, when many vital signs are reduced, and the patient's quality of life is noticeable worsens due to aggressive symptoms, hospitalization and constant medical attention are indicated the control.
Medication
The goals of medical treatment for ulcerative colitis are:
- removing the patient from the stage of exacerbation (achieving remission) - when taking medications is aimed at stopping the acute symptoms accompanying the disease;
- maintenance of remission - when a maintenance dose of certain drugs is prescribed, allowing the patient to maintain a stable condition.
The action of all groups of drugs is aimed at reducing foci of inflammation in the intestine and healing existing erosions and ulcerations. Also, prescribed medications can reduce the amount of blood secreted from the intestines, stabilize stools and eliminate unpleasant pain sensations.
All drugs that are used to treat NUC can be divided into several groups:
- drugs of the 5-ASA group - These are drugs that contain aminosalicylic acid, which is similar in action to aspirin. Depending on the form of release, they are taken orally, or they are placed rectally, if these are suppositories. The most effective medicines of this group are for mild and moderate disease, as well as as supportive therapy. These include:
-
Salofalk - in case of inflammation, 250 mg of Salofalk is prescribed rectally 3 times a day. In tablet form, with an exacerbation, 1-2 tablets of 500 mg are prescribed 3 times a day, to maintain remission - 1 tablet 3 times a day;

- Sulfasalazine - in case of exacerbation 2-4 tablets 4 times a day, 500 mg, as maintenance therapy - 1 tablet 2-4 times a day;
- Mesacol - with a mild course of the disease - 3-6 tablets of 400 mg per day, with a moderate form - 6-12 tablets per day. To maintain the condition - 2-6 tablets per day;
- Pentasu - 1 tablet contains 500 mg of mesalazine, to stop an exacerbation, up to 4 g (8 tablets) of mesalazine are prescribed per day, and to maintain a stable state - up to 2 g (4 tablets).
- drugs that modulate immunity - they are designed to suppress the body's immunity. This is necessary so that the immune system of a person suffering from UC stops destroying intestinal cells and supporting inflammation. Drugs of this group are prescribed to patients in whom the use of hormonal drugs and drugs of the 5-ASA group did not give a positive effect. They also help reduce dependence on hormonal medications. Immunomodulators include:
- Azathioprine - The daily daily dose can range from 1 mg per kg to 5 mg per kg. The remedy is prescribed for a long time.
- Methotrexate - prescribed at 2.5 mg per day;
- hormonal drugs (corticosteroids) - suppress the immune system, are prescribed for severe and moderate disease. They can be administered rectally, orally, as well as intravenously and intramuscularly. They help in the fight against exacerbations, but they are not suitable for long-term use, as they have many side effects. These include:
- Prednisolone;
- Budesonide;
- Dexamethasone.
Dosages and treatment regimens are selected purely individually based on the history of a particular patient;
- antibiotics - are designed to fight infections and abscesses that often occur with IBD. Most often, for colitis, Metronidazole and Ciprofloxacin are prescribed, which are prescribed in courses of 7-10 days, and the dosage is calculated on the patient's weight;
-
biological product Remicade Is a highly effective new generation product that works, in contrast to of the above drugs, the body is different and has an effect on the mechanism itself, provoking intestinal inflammation.
 The advantage of this drug is fewer side effects, and the disadvantage is its high cost. For treatment, the drug is administered at 5 mg for each 1 kg of body weight every 14 days until the 6th week, and then continue to use the drug every 8 weeks.
The advantage of this drug is fewer side effects, and the disadvantage is its high cost. For treatment, the drug is administered at 5 mg for each 1 kg of body weight every 14 days until the 6th week, and then continue to use the drug every 8 weeks.
Folk remedies
Nonspecific bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis, in many cases respond well to adjunctive therapy with the use of herbs, natural oils and various dietary supplements, which can be carried out in parallel with the main course treatment.
Among the most effective recipes are:
- eating blueberries (berries and leaves) - mix 3 tbsp in a container. blueberry berries and leaves and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Let the drink brew for 7-8 hours and take 250 ml at a time. Such a remedy helps to hold the feces together and reduce intestinal irritation;
- microclysters with sea buckthorn oil - for this, 40-50 ml of oil is collected in a small enema and the previously cleaned intestines are irrigated with it. For an enema, use a decoction of St. John's wort and chamomile;
- collection that stops bleeding and diarrhea - for its preparation, take 2 parts of the herb of shepherd's purse and 1 part of Potentilla and Burnet (rhizomes). All raw materials are ground in a blender and 6 hours. l. the resulting composition is poured into 400 ml of water and boiled in steam (water bath). It is taken after the infusion has cooled down, 100 ml per day for 30 minutes. before meals;
- collection from mint, dill seeds and valerian rhizomes - this collection will help to cope with bloating, increased gas production and constipation, since colitis can be accompanied not only by diarrhea, but also, on the contrary, with stool retention. All raw materials are combined, mixed and 4-5 tbsp. l. the mixture is poured with boiling water in a 250 ml glass. Take a ready-made infusion 3 times a day, 50-60 ml.
Diet therapy
The most important point in the treatment of ulcerative colitis is the adjustment of the patient's diet. Patients undergoing treatment in a hospital are usually assigned a dietary table No. 4.
In case of exacerbation, you should completely exclude:
- some drinks - strong coffee, all types of soda, whole milk, kvass, white wines;
- foods high in fiber - cabbage, watermelon, zucchini,
- legumes - beans, chickpeas, peas, corn;
- conservation - jams, pickled mushrooms and vegetables;
- fermented milk products and sour cream;
- sausages of different varieties, canned meat and fish;
- fresh butter bread;
- some types of cereals - barley, oat.
To stabilize the condition and maintain remission, patients are advised to adhere to a specific diet, including:
- lean fish varieties;
- boiled lean meat (rabbit, chicken), as well as steamed meatballs made from it;
- green and black tea;
- compotes and jelly from blueberries, quince, pears;
- slimy soups with vegetable broths;
- fruits - bananas, baked apples;
- mashed porridge - rice, semolina.
The daily diet of a person suffering from NUC will look something like this:
- breakfast - mashed rice or semolina porridge, unsweetened black tea;
- second breakfast - a little cottage cheese with a banana;
- lunch - soup with chicken meatballs, dried apple fruit compote;
- afternoon tea - baked apple, several crackers;
- dinner - steamed fish, mashed potatoes, blueberry jelly.

Even during the period of remission, it is worth adhering to the restrictions, since improper diet can provoke exacerbations.
Prognosis and complications
In addition to the unpleasant course and recurrent nature of the NUC, it has a high risk of such dangerous complications as:
- opening of intestinal bleeding - occurs when perforation (perforation, rupture) of the intestinal walls due to erosion and ulcers, without medical care can be fatal;
- development of oncological processes - such patients have an increased risk of polyps degeneration into colorectal cancer;
- intestinal obstruction - when, as a result of inflammation, the intestinal lumen narrows.
The prognosis for NUC depends on the severity of the disease. So with mild and moderate forms, in most cases, with the help of the therapy, it is possible stop all symptoms, and patients can live a normal life with some gastronomic restrictions.
With a severe attack of ulcerative colitis, in some cases, surgery and long-term rehabilitation may be required.
Clinical guidelines for patients
Patients who have been diagnosed with NUC are advised to:
- undergo colonoscopy regularly to minimize the risk of cancer;
- diet for life;
- avoid stressful situations;
- avoid physical activity (especially in the abdomen);
- take prescribed medications to maintain remission;
- if symptoms of exacerbation occur, consult a doctor immediately.
Ulcerative colitis is a serious, recurrent condition. In some cases, with total intestinal damage, it is impossible to achieve remission. The causes of this pathology are currently not known for certain.
A wide range of hormonal, antibacterial and immunomodulatory drugs, which together help relieve exacerbation and maintain remission.
Video about NNC
About ulcerative colitis:



