Gilbert's syndrome is a disorder symptoms similar to jaundice. Yellowing of the skin and eyes is caused by an increased amount of bilirubin in the blood. Treatment is not always required, because the syndrome proceeds without complications.
Record content:
- 1 Reasons for development
- 2 Symptoms
- 3 Well-being during the period of remission of pathology
- 4 Classification
- 5 Hyperbilirubinemia in newborns
- 6 Gilbert's syndrome and pregnancy
- 7 Possible complications
-
8 Diagnostic measures
- 8.1 Laboratory Methods
- 8.2 Instrumental methods
- 9 Drug therapy
- 10 Procedures and operations
- 11 Diet and lifestyle
- 12 ethnoscience
- 13 Disease prognosis
- 14 Video about Gilbert's syndrome
Reasons for development
Gilbert's syndrome is a liver disease caused by inherited disorders. The abnormalities are that the body does not properly process bilirubin, a yellowish waste product produced by the breakdown of old red blood cells.
Unconjugated bilirubin or bile water-insoluble pigment circulates in the liquid part of the blood, plasma, associated with protein, albumin. In a healthy body, this bilirubin is absorbed by the liver cells and, with the help of the UGT1A1 enzyme, is converted into water-soluble bilirubin (conjugated). It is removed through feces along with bile.
People with the syndrome have a hereditary abnormality that causes a decrease in the production of an enzyme involved in the processing of bilirubin.
Gilbert's syndrome (symptoms and treatment depend on the form of the disorder) develops after inheriting the UGT1A1 gene from the father, mother, or both parents in an autosomal recessive manner.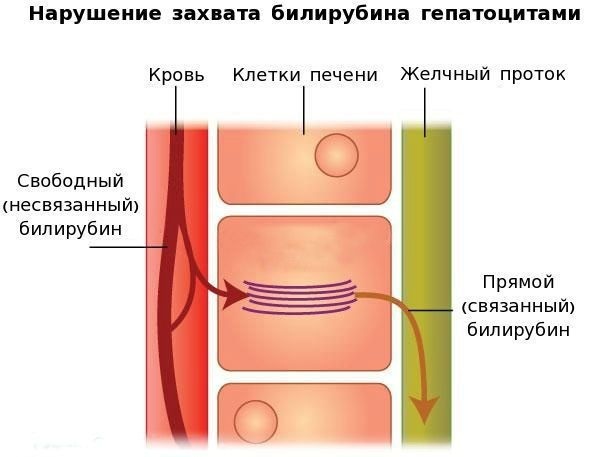
A healthy gene encodes an enzyme (protein) that is involved in the breakdown of bilirubin in the liver. When a defective gene is inherited, the normal enzyme cannot be produced in the body. A mutation in the UGT1A1 gene causes the body to produce less bilirubin-UGT, an enzyme that breaks down bilirubin.
When old, worn out red blood cells are cleared from the body to be replaced with new, healthy cells, bilirubin is broken down in the liver and excreted through the stool. But people with Gilbert's syndrome do not have the protein responsible for breaking down bilirubin. Thus, bilirubin cannot be removed from the bloodstream, so its concentration in the blood remains high.
Autosomal recessive conditions are signs or disorders that occur when two copies of an abnormal gene have been inherited from a non-sexual chromosome. If both parents have an autosomal recessive condition, there is a 100% chance of passing on the mutant genes to their children.
However, if only one mutant copy of the gene is inherited, the individual will be the carrier of the condition but will be asymptomatic. Children born to two carriers have a 25% chance of being homozygous dominant (no change), 50% chance of being heterozygous (carrier) and 25% chance of being homozygous recessive (affected) dominant.
Symptoms
Gilbert's syndrome is less commonly diagnosed in women but more commonly in men. The disorder affects about 3-7% of people.
It can be diagnosed in infants at birth, but more often remains undetected until adolescence. The syndrome manifests itself when the body is under stress, such as from prolonged periods of fasting, illness, dehydration, vigorous exercise, or during menstruation.
Symptoms are usually subtle and sometimes not.
At the moment of appearance, they are expressed:
- tiredness;
- nausea and diarrhea;
- loss of appetite;
- irritable bowel syndrome caused by bloating, constipation, stomach cramps;
- yellowing of the eye sclera and skin (jaundice);
- the emerging problem of concentration (brain fog);
- slight discomfort in the abdomen;
- a general feeling of ill health.

What affects the increase in the level of bilirubin and the intensification of symptoms:
- lack of water in the body;
- period of menorrhea;
- emotional stress or physical stress;
- having an infection or illness;
- exposure to cold;
- lack of sleep;
- starvation;
- recovery after surgery;
- excessive alcohol consumption.
40% of people do not have any signs of the syndrome, they are found in the case of blood tests showing a high level of unconjugated bilirubin.
Well-being during the period of remission of pathology
The conditional symptoms characteristic of the syndrome are absent during the period of remission. One third of affected patients have no symptoms during an exacerbation.
Classification
Gilbert's syndrome, the symptoms and treatment of which are not dangerous and difficult, has other alternative definitions:
- Familial benign unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
- Constitutional liver dysfunction.

- Familial non-hemolytic non-obstructive jaundice.
- Chronic hyperbilirubinemia of mild degree.
- Unconjugated benign bilirubinemia.
- Meilengracht's disease.
Hyperbilirubinemia in newborns
Benign hyperbilirubinemia in infants is a temporary and normal increase in bilirubin levels, which is observed in almost all newborns, which is also called "physiological" jaundice.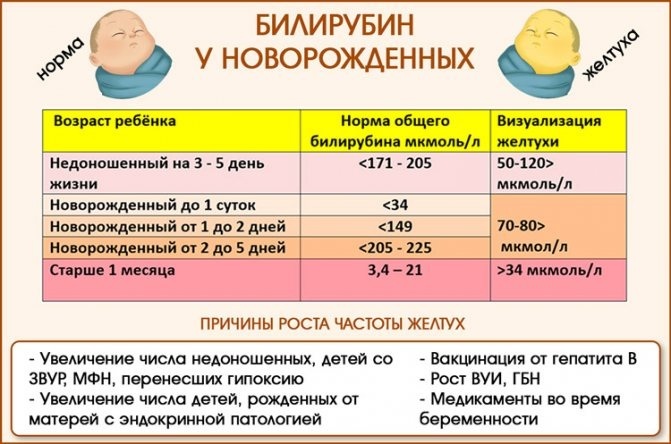
The need for treatment depends on the bilirubin level and the underlying cause.
Gilbert's syndrome and pregnancy
Gilbert's syndrome does not pose a threat to a woman and her child. The greatest danger associated with this disorder is the inability to take many medications. Symptoms do not affect the severity of the pathology, and treatment is reduced to taking choleretic drugs, hepatoprotectors and multivitamins. Doctors often prescribe activated charcoal to help reduce symptoms.
When planning pregnancy, parents who are carriers of familial non-hemolytic jaundice should consult with geneticists.
Possible complications
Complications result from the liver's inability to process bilirubin due to the presence of a defective enzyme.
People with this condition may not be able to take certain medications because it is difficult for the liver to detoxify the medications. These are irinotecan (a chemotherapy drug) and protease inhibitors that are used to treat HIV. Other possible complications include the development of stones in the gallbladder and ducts.
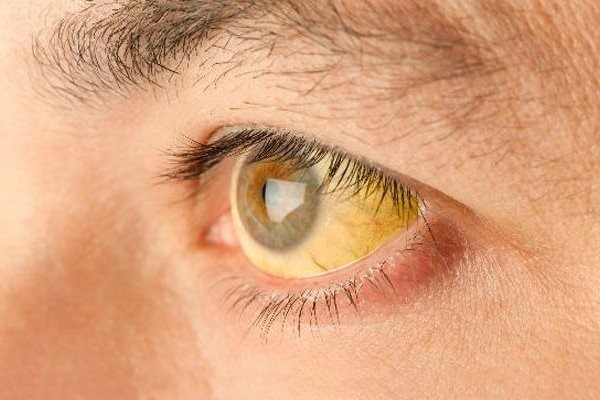
The syndrome is not fatal and does not impair quality of life. But it has some negative consequences. Over the years, people with jaundice may develop psychosomatic disorders.
In rare cases, with the disorder, pigment stones form in the bile ducts or the bladder itself. This occurs when an excessive amount of indirect bilirubin precipitates. In this case, no changes are observed in the liver. But if you take medications uncontrollably, do not limit yourself to alcohol, junk food, then hepatitis may develop.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosing a genetic disorder can often be challenging. Healthcare professionals typically take medical history, symptoms, physical examinations, and laboratory tests before making a diagnosis.
Numerous tests are performed in order to rule out diseases that may be causing an increase in bilirubin levels. Often the syndrome occurs along with other diseases of the liver and blood, and their symptoms are similar.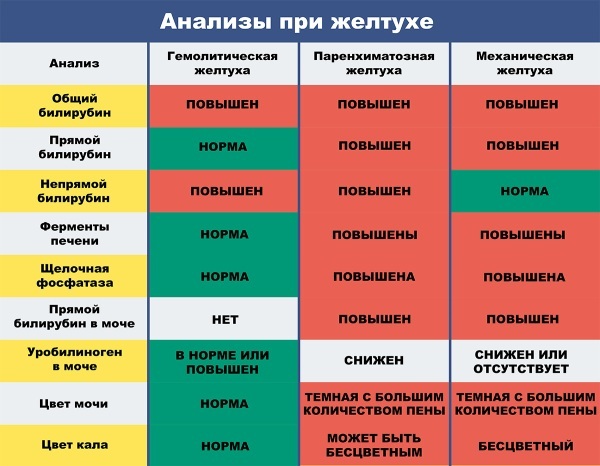
To make the correct diagnosis, the doctor uses a genetic test to check for a gene mutation. In some cases, medications such as niacin and rifampicin cause an increase in bilirubin and interfere with a correct diagnosis.
Laboratory Methods
The fastest method to detect the syndrome: direct DNA diagnosis. In this case, the number of TA repeats is determined in the UGT1A1 gene. For research, venous blood is taken as a biomaterial.
In addition, you need to do:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- determine the levels of total bilirubin in the blood;
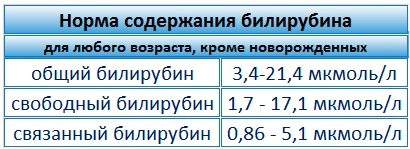
- direct bilirubin levels.
Instrumental methods
After consulting a therapist, you should undergo diagnostics:
- Ultrasound of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity. This is done to determine diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma, the thickness of its walls, and to identify stones in the bile ducts and bladder.
- To exclude the diagnosis of cirrhosis and hepatitis, a percutaneous liver biopsy should be performed.
Drug therapy
Gilbert's syndrome (symptoms and treatment usually do not require medical attention) is a disease associated with an inherited disorder of bilirubin metabolism, so levels can fluctuate, sometimes causing episodes jaundice. However, jaundice is usually mild and will go away on its own.
In some cases, doctors prescribe:
| A drug | Action |
| Phenobarbital (in case of increased bilirubin up to 50 μmmol / L) treatment course 2-4 weeks |
Reduces the level of bilirubin, reduces the signs of jaundice in newborns with hemolytic disease. |
| Zixorin the course of treatment is 1-2 weeks, a break between courses is up to 4 weeks |
Lowers the level of bilirubin in the blood |
| Activated carbon | It adsorbs bilirubin in the intestine, accelerating its destruction in tissues, excretion from the body. |
Hepatoprotectors | |
| Ursofalk | Choleretic agent, destroys cholesterol stones. |
| Ursosan | It has a choleretic immunomodulatory effect. |
| Essentiale | Protects and restores liver function. |
| Choleretics | |
| Holagol | Complex preparation for choleretic and antispasmodic effects. |
| Holosas | Improves metabolic processes in the liver. |
| Allohol | The drug is made on a natural basis, has a choleretic effect. |
It is useful to take multivitamin complexes during an exacerbation, especially those containing B vitamins. In order to reduce the level of free bilirubin, drugs are prescribed.
Procedures and operations
In the case of the development of chronic hepatitis, when the liver cannot be cured, an operation for its transplant is prescribed. In case of gallstone disease, which has developed in violators of the regime and diet, an operation is prescribed to remove stones.
The method of phototherapy is also used - this is an artificial reduction of a high concentration of bilirubin. A procedure in which free bilirubin is destroyed is performed using blue light irradiation. This method is more often seen as preparation for liver transplantation.
At high doses of bilirubin, bloodletting, exchange blood transfusions, plasmaphoresis are performed.
Diet and lifestyle
Gilbert's syndrome, for which there is no danger of symptoms and treatment, is treated at home with bed rest, a healthy diet, and plenty of fluids.
- Get enough sleep. Night sleep should be at least 7-8 hours.

With Gilbert's syndrome, diet table 5 is prescribed - Long-term intense exercise should be avoided. Your workout should include 30 minutes of light exercise every day.
- The body must receive a lot of moisture. This is especially important during exercise, hot weather and illness.
- Use relaxation techniques to deal with stress. Listen to music, meditate, do yoga.
- Eat a balanced diet. Eat regularly, do not skip meal times, do not follow any dietary plans that recommend fasting, or eat only a small amount of calories.
- Follow a healthy diet. Avoid low-calorie diets. Stick to your normal diet.
- Limit alcohol intake. If you have liver problems, it is best to avoid alcohol.
- Avoid taking medications that are contraindicated in the syndrome, especially drugs used in the treatment of cancer.
It is recommended to include in the diet proteins, fatty fish, as they help to remove fat-soluble bilirubin.
Foods such as walnuts, avocados, cauliflower, eggs, broccoli, blueberries, kale contain a mixture natural sulfur compounds, and also contain glutathione, which is a strong antioxidant and protects liver. All of the above foods help break down toxins in the body.
There is no special diet to follow for the syndrome, but there are foods that contain nutrients that are good for the liver.
| Nutrients | Products |
| vitamin K | green leafy vegetables and alfalfa sprouts |
| Arginine helps the liver to detoxify ammonia, which is a toxic byproduct of protein metabolism | beans, peas, lentils, oats, walnuts, wheat germ and seeds. |
| Antioxidants | fresh juices from celery, carrots, beets, pears, apples, and green drinks such as cereal and barley juices, as well as fresh fruits, especially citrus and kiwi. |
| Selenium | The antioxidant selenium is found in Brazil nuts, brewer's yeast, seaweed, brown rice, lemon balm, seafood, wheat flour, whole grains, garlic, and onions. |
| Methionine is necessary for the body to cleanse, remove toxins, harmful substances |
Legumes, fish, eggs, garlic, onions, seeds and meat. |
| Essential fatty acids | seafood, sardines, salmon, mackerel, tuna, whole grain foods, wheat germ, green vegetables such as green beans, spinach, green peas, eggplant. |
| Natural sulfur compounds | Compounds are found in eggs, garlic, green onions, leeks, shallots, and cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts. |

Some foods that contain high concentrations of plant hormones are very beneficial for the liver.
These include phytoestrogens found in natural foods:
- ginger root;
- chilli;
- garlic;
- Chinese water spinach;
- bok choy or bok choy;
- turmeric;
- curry;
- Chinese mushrooms: shiitake, oyster mushroom, straw mushroom, field grass.
Eat plenty of raw orange, yellow, purple and red fruits and vegetables, and dark green leafy vegetables. The diet should contain 30-40% raw fruits and vegetables. It is good if they are present at every meal, as they contain live enzymes, vitamin C, natural antibiotics and phytonutrients.
Tomatoes, especially the yellow varieties, contain the antioxidant lycopene, which is the most potent of all dietary carotenoids.
Beets are dark purple in color and contain the antioxidant anthocyanidin. Beet components have been proven to have antiviral and antitumor effects.
Other foods that also exhibit these properties, albeit to a lesser extent, are red and green peppers, red onion peels, paprika, and cranberries. These foods contain healthful phytonutrients such as carotenoids, capsanthin, and anthocyanins, which are beneficial for the liver.
ethnoscience
Natural products will help get rid of the disease:
-
Turmeric helps in increasing glutathione levels, improves detoxification. It can be added to finished products.

- Milk thistle can be of great benefit to the liver. Taking 150 mg of the plant twice a day can help protect against chronic liver disease. It contains silymarin, which affects detoxification. In case of hepatitis, liver diseases, a decoction is made from the dry powder of the plant and drunk 4–5 times during the day.
- Dandelion herbal tea helps to improve liver function.
- Royal jelly Is a processed bee substance containing biostimulants necessary to restore metabolic processes in the liver. It is used only by sucking under the tongue, or adding to the curd.
- Spirulina, containing antioxidants, omega-3, 6, 9 polyunsaturated acids. It is applied in the form of drops.
- Evening primrose oil. Pharmacy product produced in the form of capsules. Accepted 1 pc. 3 to 5 times / day.
- Blackcurrant seed oil. Contains active amino acids, is taken orally with food intake.
- Borage oil (borago) contains gamma-linoleic acid, which has a positive effect on the function of the adrenal glands and liver. It is taken as a course for 3-6 months.
- Lecithin also contains oils that are beneficial to the liver. The food supplement improves liver pigment function. Can be used from childhood.
- Grapefruit juice contains antioxidants, vitamin C, folic acid, potassium, lipin. Clinical studies show that grapefruit helps in the detoxification process.
- Grape seed extract significantly improves liver function in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Coffee. Drinking three or more cups of coffee a day reduces the risk of cirrhosis in people with chronic liver disease and may help reduce the risk of liver cancer.
- Daily intake of 1000 mg of high quality fish oil supplements a day will improve liver function.
Disease prognosis
Gilbert's syndrome is a genetic disorder that has a good prognosis in most cases. People with it usually live healthy lives with a normally functioning liver.
Complications associated with Gilbert's syndrome can be prevented by avoiding stressful conditions, periods of fasting, and ensuring a healthy diet high in calories.
High levels of bilirubin in the blood usually recover on their own, unless they are associated with other medical conditions.
With Gilbert's syndrome, it is better to avoid taking medications, but to follow preventive rules and lead a healthy lifestyle. Many of the symptoms of the disease can be overcome by consuming medicinal foods that contain powerful medicinal properties.
Video about Gilbert's syndrome
How to live with Gilbert's syndrome: