The state of moderate severity of the patient - This is a partial violation of the functions of internal organs, peripheral and central nervous systems, individual elements of the musculoskeletal system. A similar clinical picture can be caused by an acute or chronic disease, mechanical injury, damage to the body by chemical, electrical or thermal burns.
Patients with signs of a moderate condition should be hospitalized in an inpatient setting. hospital departments in order to prevent the progression of pathology and deterioration of general well-being.
Record content:
- 1 The severity of the patient's condition
-
2 What criteria are assessed to determine the patient's condition
- 2.1 States of consciousness
- 2.2 Vital functions
- 2.3 Conditions of focal neurological functions
-
3 Signs of a moderate condition in intensive care
- 3.1 The nature of motor activity
- 3.2 Respiratory process
- 3.3 The work of the organs
- 3.4 State of consciousness
- 3.5 Focal symptoms
- 4 Under what diseases and pathologies is the state of moderate severity observed?
-
5 Signs of a moderate to severe condition under different circumstances
- 5.1 With pneumonia
- 5.2 With a stroke
- 5.3 With a heart attack
- 5.4 At birth
- 6 What is the threat to life in a moderate condition?
- 7 What methods of therapy are used for moderate-severe condition
- 8 Patient condition video
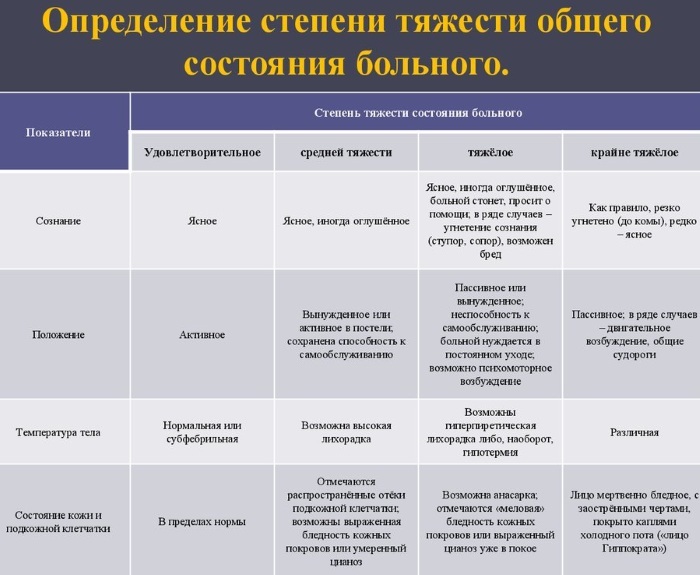
The severity of the patient's condition
The table below shows the 4 main degrees of severity of the patient's condition, regardless of the causal factors that caused the disruption of the body's working capacity.
| The severity of the patient's condition | Characteristics of pathology |
| Light (satisfactory condition) | The mild severity of the patient is characterized by his satisfactory condition with a favorable prognosis for the complete recovery of the body. Diagnostic examination in patients of this category reveals a slight decrease in the functions of one or another internal organ. The patient is able to move independently, to serve his personal needs, does not need outside help and care. At the discretion of the doctor, this patient can receive medication on an outpatient basis. |
| Average | The average severity of the patient's condition is characterized by rich symptoms of the underlying disease, which provoked an acute health disorder. Patients of this group are in a supine position, or they can move, but with great difficulty or with the help of strangers. The functional activity of individual organs and systems is partially absent. Without qualified medical care, patients of this category are faced with the progression of the pathological condition and the exacerbation of the existing symptoms. |
| Heavy | The severe severity of the patient's condition is characterized by complete dysfunction of several organs and systems, as well as confusion. In this case, the prognosis for recovery is not favorable. According to statistics, about 80% of patients in serious condition expect death. The recovery of such patients depends on the individual characteristics of their body, timely medical care and the professionalism of the attending physician. |
| Extremely serious condition | The extremely serious condition of the patient is characterized by the complete passivity of the internal organs and life support systems of the body. There is no physical activity and reflex reactions. In some cases, signs of seizures may appear. The patient is in a state of deep coma and is unable to breathe without the aid of a ventilator. |
A state of moderate severity, satisfactory health indicators, as well as severe symptoms are the general clinical picture, which is established by the attending physician during the examination of the patient. Based on the diagnostic results, a decision is made on the implementation of further therapeutic measures aimed at restoring the stable vital activity of the body.
What criteria are assessed to determine the patient's condition
In order to determine the severity of the condition, several criteria are used that allow obtaining comprehensive information about the health of a particular patient.
States of consciousness
Patients in a satisfactory condition retained clear consciousness without signs of impaired cognitive functions, confusion of the thinking process. The patient is completely adequate, quickly navigates in space, immediately answers the questions of the attending physician.
Patients in a state of moderate severity also retain clear consciousness, but in this case there is additional symptoms in the form of increased nervous excitement, anxiety without impairing the ability to self-control. The severe condition of the patient is characterized by the onset of stupor, the transition to a completely vegetative state with the manifestation of rare signs of self-awareness.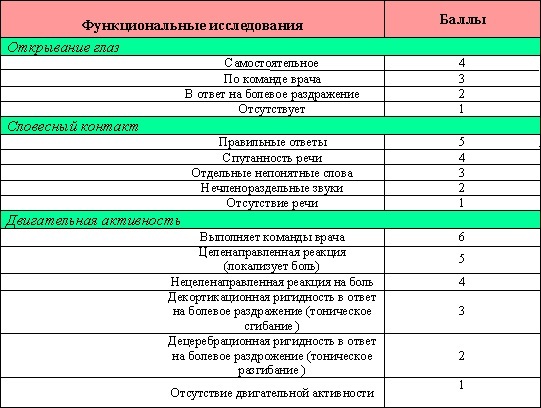
The patient is disoriented, there is increased psychomotor agitation. In the latter case, the occurrence of seizures and the manifestation of hypertonicity of the muscular system is not excluded.
Vital functions
One of the qualification criteria for assessing the patient's health is the identification of the state of the vital functions of his body. With satisfactory indicators, the work of internal organs and systems is fully compensated. There is no threat to the patient's life. The prognosis for a speedy recovery is positive and close to 100% result.
The state of moderate severity is characterized by the presence of decompensation of certain functions:
- hearts;
- kidney;
- liver;
- organs of the digestive tract;
- blood vessels.
But with all this, the fact of the presence of an immediate risk of death is not confirmed. In severe condition, decompensation of the functional activity of individual internal organs is capable of lead to death, or cause the acquisition of a deep and lifelong disability.
The prognosis for the restoration of stable functioning of the body is unsatisfactory.
Conditions of focal neurological functions
The preservation of the functions of the central and peripheral nervous system is an important sign of the positive dynamics of the patient's recovery. Patients who are in a satisfactory condition do not experience symptoms associated with dysfunction of the centers of the brain.
Patients of this category move independently in the environment, their coordination of movements is not impaired, and there is no damage to individual nerves of the autonomic system. Patients with moderate severity suffer from partial impairment of neurological functions.
A similar condition may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Strong headache;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- difficulty or loss of the ability to perform simple movements of the upper or lower limbs;
- tremors of the fingers or other parts of the body;
- dizziness;
- drop or increase in blood pressure;
- violation of body heat exchange, which is manifested by an abnormally high body temperature without signs of an inflammatory process;
- unstable psycho-emotional state;
- nausea and vomiting;
- sudden mood swings;
- asymmetry of the facial muscles.
The serious condition of the patient is characterized by the complete loss of certain neurological functions. Patients in this category may lose consciousness, fall into a coma, and experience difficulties in performing the act of breathing on their own. Patients in serious condition cannot move independently in the environment, as well as perform maintenance of basic needs.
In most cases, there is a severe impairment of the functions of the musculoskeletal system, which are of a neurological origin. For example, loss of speech, the ability to chew and swallow food, sensitivity of the lower extremities, the appearance of signs of urinary incontinence, involuntary defecation.
Signs of a moderate condition in intensive care
A state of moderate severity is a significant decrease in the body's performance, which has a number of characteristic signs. In the process of carrying out resuscitation measures, the attending physician evaluates the clinical symptoms, based on the results of which a decision is made on the use of further methods of treatment.
The nature of motor activity
In patients in a state of moderate severity, the following signs of motor activity are observed:
- the patient has lost the ability to move independently in the environment;
- the patient spends most of his time in bed, rising only in case of emergency with the help of strangers;
- retained self-service skills;
- the full implementation of hygiene procedures requires the help of medical personnel, loved ones or a nurse.
A patient who is admitted to intensive care in a state of moderate severity is transferred to the intensive care unit by transporting him on a gurney or in a wheelchair. Independent movement of patients of this category is impossible due to partial or complete decompensation of individual internal organs and body systems.
Respiratory process
A state of moderate severity is a violation of the functional activity of the muscles responsible for the synchronous filling of the bronchopulmonary tissue with a sufficient amount of air. Patients in a state of moderate severity can be admitted to intensive care with signs of acute decompensation of the respiratory system.
In this case, the key role is played by the type of disease or other causative factor that caused the pathological symptoms in a particular patient. The majority of patients in this category have rhythmic breathing with chest muscles contracting from 20 to 35 times in 1 min.
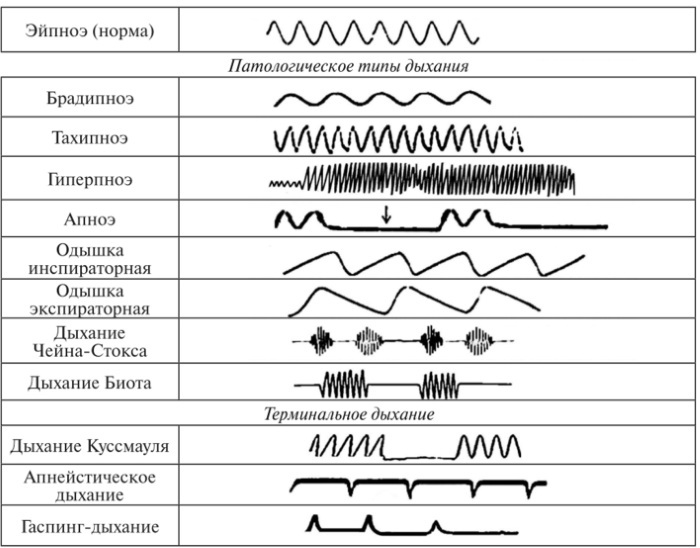
In conditions of further progression of decompensation of the functions of the lungs and bronchi, the patient is shown to carry out urgent resuscitation measures for his intubation and connection to the ventilator. In this case, the favorable prognosis for complete recovery is sharply reduced.
The work of the organs
In patients who enter the intensive care unit, being in a state of moderate severity, there is a decrease in the functional activity of the following organs:
- stomach and intestines - digestion proceeds very slowly, or is completely suspended due to the unsatisfactory condition of the patient (there may be signs of vomiting, diarrhea, opening of internal bleeding);
- a heart - symptoms of rhythm disturbance and unstable blood pressure are observed;
- lungs - the patient's breathing is rhythmic, but intermittent;
- kidneys - against the background of general psychoemotional arousal, there are more frequent urges to urinate;
- liver - the functions of this body are suppressed, but not significantly (the only exceptions are cases when the cause of the onset of a moderate condition is disease or damage to the liver fabrics);
- pancreas - the enzymatic activity of this organ is reduced, since the digestion process is suppressed.
Despite the unsatisfactory condition of the vital organs of the human body, the emergence of a threat to the patient's life is not observed. The risk of further progression of painful symptoms remains if the patient is not provided with qualified medical care.
State of consciousness
A state of moderate severity is a colossal load on the functions of all internal organs and life support systems of the body. In patients with similar symptoms, there are no significant disorders in terms of the work of individual centers of the brain.
Patients admitted to intensive care in a state of moderate severity, in 95% of cases, retain a clear consciousness. The only exceptions are those patients who are intoxicated with drugs or alcohol, or suffer from concomitant neuropsychiatric diseases.
The patient can independently express his thoughts and answer the doctor's questions. The cognitive function of the cerebral cortex is completely preserved without signs of impairment. Patients in a state of moderate severity may experience severe anxiety, panic, fear, increased agitation against the background of an injury or exacerbation of the underlying ailment.
At the same time, a person does not lose control over his emotions, which is a characteristic feature for patients of this category.
Focal symptoms
Depending on the type of underlying disease, damage to individual organs, tissues, or elements of the musculoskeletal system, may occur focal symptoms of a moderate condition, namely:
- complete loss of appetite;
- opening of internal bleeding;
- acute urinary retention;
- decreased filtration function of the kidneys;
- diarrhea that lasts more than 24 hours;
- intestinal obstruction;
- incessant vomiting;
- saturation of the bloodstream with vital oxygen only by 90%;
- severe dizziness, which makes it impossible to independently move around the room;
- paralysis of the muscles of the lower extremities;
- bone fracture without signs of displacement;
- multiple edema of epithelial tissues and subcutaneous tissue;
- an increase in body temperature to indicators from 37.6 to 38.5 degrees Celsius.

Focal symptoms of a moderate condition can be varied depending on the type of underlying disease. The patient is diagnosed by a doctor who is tasked with performing urgent resuscitation measures.
Under what diseases and pathologies is the state of moderate severity observed?
A moderate condition can be triggered by the following types diseases that are characterized by an acute or chronic form of the course:
- viral or bacterial pneumonia;
- flu with progressive symptoms but no signs of complication;
- food poisoning;
- intoxication with chemicals, biological poisons, salts of heavy metals;
- radiation sickness;
- diabetic angiopathy;
- brucellosis;
- dyskinesia of the esophagus;
- perforation of the uterus;
- gallbladder polyp;
- ulcerative lesion of the stomach;
- pyelonephritis in the acute stage;
- BPH;
- ovarian cyst;
- acute form of vaginitis;
- gallstone disease in the stage of movement of stones;
- internal bleeding, regardless of its nature of origin;
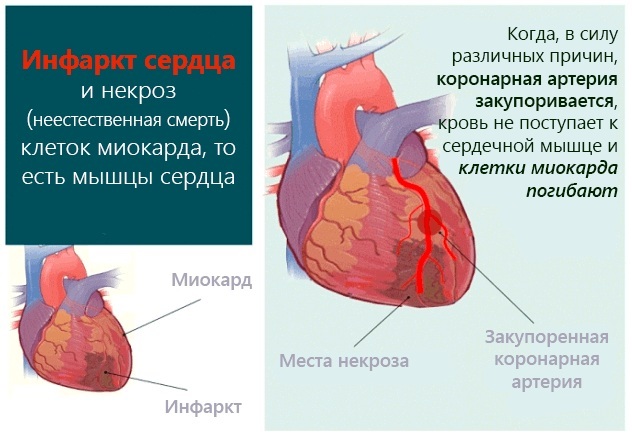
- myocardial infarction;
- traumatic brain injury;
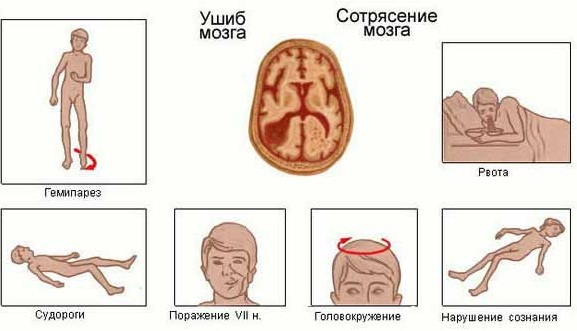
- cerebral stroke;
- polyps in the bladder cavity;
- endocarditis of infectious etiology.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the patient's body, a state of moderate severity can develop even against the background of a common cold or prolonged hypothermia of the body. Lack of timely treatment can lead to the rapid progression of pathological symptoms.
Signs of a moderate to severe condition under different circumstances
Each disease that is potentially life-threatening and capable of causing a state of moderate severity is characterized by a number of distinctive features.
With pneumonia
A moderate condition is a decrease in the functions of individual organs that are affected by a particular disease.
With pneumonia, patients experience the following symptoms:
- an increase in body temperature up to 38.5 °;
- frequent rhythmic breathing;
- sharp pain inside the chest;
- dry barking cough;
- intermittent feeling of lack of air, which quickly passes;
- physical weakness and general loss of strength;
- chills and fever;
- excessive sweating;
- headache.
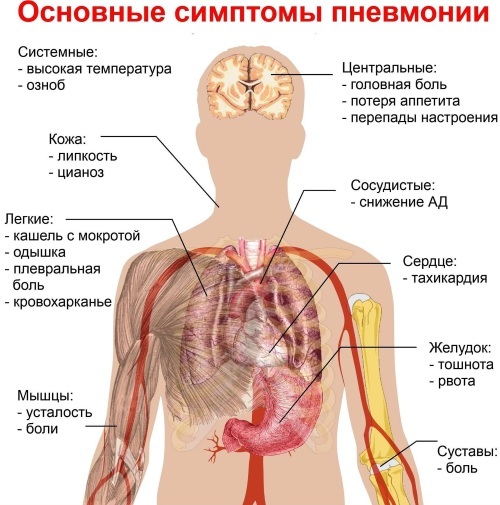 The main danger of pneumonia is that this disease, which is at the stage of moderate severity, can progress rapidly, causing more severe symptoms.
The main danger of pneumonia is that this disease, which is at the stage of moderate severity, can progress rapidly, causing more severe symptoms.
With a stroke
A cerebral stroke, which provoked the onset of a moderate condition, is expressed in the form of the following symptoms:
- loss of orientation in time and space;
- nausea and vomiting;
- Strong headache;
- increase in systolic blood pressure up to 179 tonometer units;
- feeling of dry mouth;
- speech impairment;
- decreased visual acuity and hearing;
- short-term loss of consciousness;
- violation of facial symmetry;
- paralysis of the lower or upper limbs;
- dizziness.
Symptoms of moderate severity in cerebral stroke can be quickly eliminated with medication. In the absence of urgent resuscitation actions, there remains a high risk of disability or further progression of the disease with the onset of death.
With a heart attack
A moderate condition caused by a heart attack is characterized by the following pathological signs:
- heart palpitations;
- pain in the retrosternal space, which is acute, and also persists for 15 minutes or more. up to 1 hour;
- a feeling of discomfort inside the chest;
- general weakness and loss of strength;
- dizziness;
- dry cough;
- shortness of breath, which occurs for no reason when a person is in a state of physical rest;
- pain in the abdomen, throat, left arm;
- a sudden feeling of acute shortage of air.
The above symptoms of a moderate to severe condition provoked by a heart attack require resuscitation measures that must be performed in relation to the patient during 15-20 minutes Otherwise, severe complications may develop.
At birth
A state of moderate severity in newborn children is recognized as such if the child was born with signs of functional decompensation of at least 1 organ.
At the same time, there is no risk of death of the baby, and the means of drug therapy and other methods of treatment allow doctors to restore the stable vital activity of the child's body. General symptoms of moderate to severe condition in newborns do not exist due to the difficulties in diagnosing patients in this category.
What is the threat to life in a moderate condition?
A distinctive feature of a state of moderate severity is that at this stage of the development of a disease or other pathology of the body, there is no direct threat to the patient's life. At the same time, there remains a significant risk of progression of painful symptoms with the transition of the disease to a severe form. In this case, the likelihood of death increases dramatically.
What methods of therapy are used for moderate-severe condition
In relation to patients who are in a state of moderate severity, the following methods of therapy are used:
- drugs in tablet and injectable form of administration;
- biologically active additives;
- physiotherapy procedures;
- surgical operations.
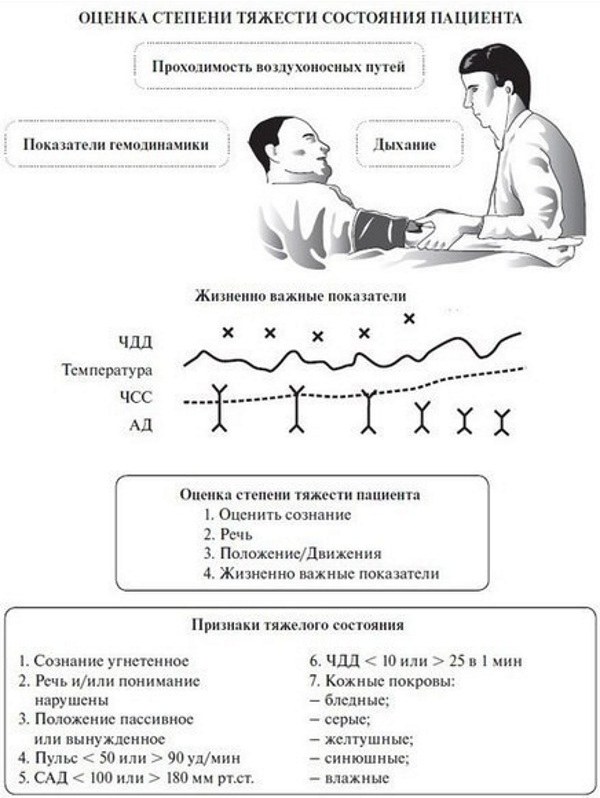
The treatment regimen is developed by the doctor on an individual basis for each patient with appropriate symptoms.
The state of moderate severity is characterized by moderate dysfunction of internal organs and limited mobility of the musculoskeletal system. Patients of this category retain clarity of consciousness, but at the same time they may be characterized by increased psychoemotional excitability.
The moderately severe condition of the patient is that stage of the development of the disease at which the possibility remains restoration of the functions of vital organs with the help of drug therapy or a method of surgical interference. Delay in starting treatment is fraught with the development of severe complications.
Patient condition video
Patient assessment: