Complete cooling of the body is a violation of the thermal balance, accompanied by a decrease in body temperature below normal.
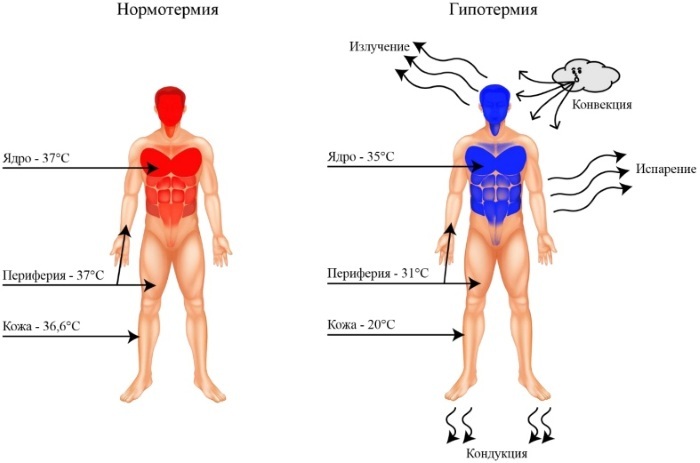
Hypothermia is physical condition in adults and children, which occurs due to a drop in body temperature below 34 ° C. In the process of hypothermia, the main organs are affected, first of all: the brain, heart, lungs.
Even a little cooling reduces the physical and mental abilities of a person. Severe hypothermia leads to unconsciousness and death. A large number of people in the world die from hypothermia every year.
During exposure to low temperatures, most of the heat, up to 90%, leaves through the skin, the rest is exhaled through the lungs. When immersed in cold water, heat loss occurs 25 times faster than when exposed to the same air temperature.
Body temperature is controlled by the hypothalamus. When this organ detects changes in body temperature, it triggers the necessary reactions to bring the temperature back to normal.
When exposed to low temperatures, shivering is a defense reaction to generate heat through muscle activity. In another heat-retaining reaction, vasoconstriction, the blood vessels are temporarily narrowed.
If the body temperature continues to fall, organs begin to fail, primarily the brain, lungs, kidneys, which ultimately leads to death.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Hypothermia Videos
Views
Hypothermia (causes in adults - impaired thermoregulation, low fat and carbohydrate content), as a state of an organism, it is subdivided into types:
-
Endogenous. The development of the condition is influenced by internal factors: diseases, prolonged immobilization.
- Exogenous. In this case, external factors influence the course of development: the cold season, improperly selected clothes, inactivity, the introduction of blockers.
Stages and degrees
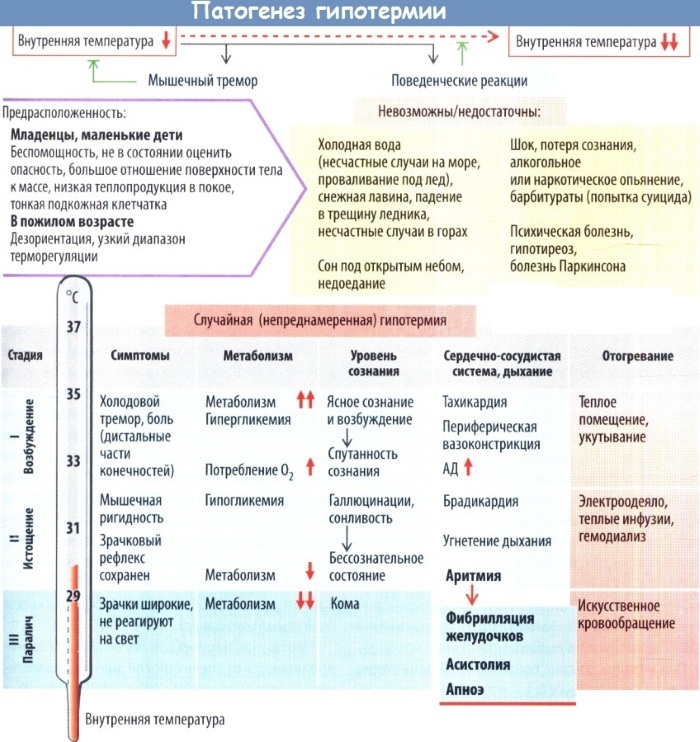
The body's reaction to complete hypothermia occurs in stages, with 4 stages of freezing distinguished.
- Stage I - compensatory. Clinically, general hypothermia presents with agitation, chills, and muscle tremors. The skin is pale, there is cyanosis of the lips and acrocyanosis, goosebumps. Blood pressure is increased, pulse and breathing become more frequent.
- Stage II adynamic (exhaustion). Marked with a defeat of consciousness, inhibition of all functions, a state of euphoria. A person is worried about a headache, dizziness, weakness appear. General hypothermia is characterized by asthenia, decreased muscle reflexes.
- Stage III - comparative. Appears lethargy, drowsiness, memory impairment, dysarthria, a false sensation of heat. The pupils are dilated. Possibly urinary and fecal incontinence. Blood pressure drops sharply, the pulse is 30-50 beats per minute. Respiratory rate is 8-10 breaths per minute.
-
Stage IV - comatose. Consciousness is absent, involuntary movements of the head, rotational movements of the eyes, tension of the muscles of the abdomen and limbs appear. The pupils are constricted, there is no reaction to light, the corneal reflex is absent, the eyeballs float. Arterial pressure is sharply reduced, the pulse is weak, up to 20 beats per minute, death quickly occurs from paralytic cardiac arrest and respiration, in which resuscitation is ineffective.
As the body cools, the body tries to prevent heat loss. The earliest signs occur when skin temperature (rather than body temperature) drops below average.
Hypothermia has 3 degrees of development:
- Lightweight. At this stage, blood circulation in the skin decreases and blood flows away from the cold surface of the body, which helps to maintain the internal temperature. A shiver appears in a person as a defense mechanism against the effects of cold.
- Moderate hypothermia. Mild hypothermia may develop if left untreated. Shivering stops when the body switches from using energy as a heat source to storing energy ahead of the oncoming cold.
-
Severe hypothermia. When the temperature drops to 28 ° C, the person loses consciousness and does not respond to most stimuli. Often, deep tendon reflexes are diminished or absent, which means the person stops responding to any attempts to wake up. Severe hypothermia is a serious medical emergency.

Hypothermia (causes in adults associated with impaired heat transfer) at the stage of the severe stage is accompanied by an increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
Symptoms
Symptoms progress from trembling and drowsiness to stunning, coma, and death:
- Severe tremors initially occur, but they stop when the body temperature drops below 31 ° C, which contributes to an even faster decrease in temperature.
- Progressive dysfunction of the central nervous system begins, people lose sensitivity in the affected areas.
- Drowsiness appears, numbness of the limbs, followed by stunning, sometimes hallucinations, resulting in a coma.
- There is a slowdown in breathing, the heartbeat slows down and stops.

Symptoms of hypothermia
With frostbite of individual skin areas, tingling occurs first, then skin whitening, followed by the appearance of blisters. At the 3rd stage of frostbite, darkening of the skin areas and death occur.
Reasons for the appearance
Risk factors that lead to hypothermia:
- Exhaustion. As a person gets tired, their sensitivity to cold decreases.
- Aged people. The body's ability to regulate temperature and feel cold decreases with age.
- Small children. At this age, heat is lost faster than in adults. Children can ignore the cold, forgetting about it, playing outside. Improperly selected clothing, getting wet from excessive sweating, also contributes to hypothermia.
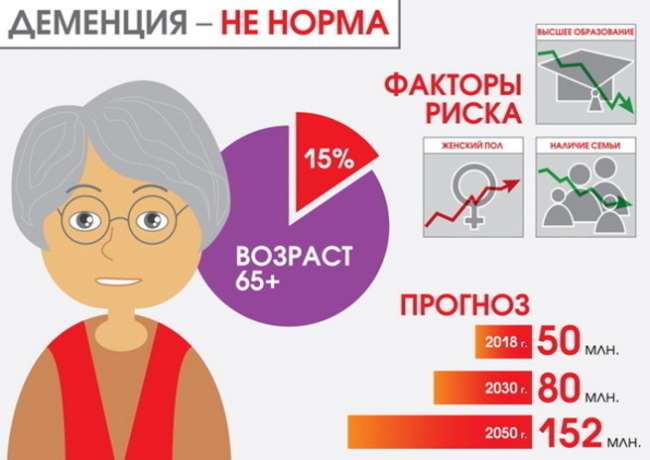
- People with mental illness, dementia, or dementia. People with mental disabilities may dress appropriately for cold weather. At the same time, they do not always realize that they are cold, and remain outside for a long time at low temperatures.
- Alcohol and drugs. Alcohol is especially dangerous because it creates the false impression that the internal organs are warming up. This actually causes the blood vessels to dilate and the skin loses more heat. In people who drink alcohol, the body's natural reaction, tremors, decreases.
- Certain medical conditions. Several health conditions affect the body's ability to regulate temperature. Examples include an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism), poor diet or anorexia nervosa, diabetes, stroke, severe arthritis, Parkinson's disease, and spinal cord injuries.
-
Medications. Hypothermia may be associated with medication: beta-blockers, clonidine, antipsychotics. Ethanol, hypnotics, also reduce the body's ability to respond to low ambient temperatures.

The risk group includes the elderly and children:
- Aged people. At this age, 65+, temperature sensitivity is often reduced. This is due to a reduced ability to regulate body temperature, inability to move quickly.
- Early childhood. In children, the ability to regulate the temperature regime of the body is poorly expressed, and the ratio of body weight and body surface area is high. This leads to an increase in the heat transfer process.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is by rectal thermometry. Electronic thermometers are preferred as standard mercury thermometers have a lower limit of 34 ° C. The causes of hypothermia in adults are being investigated through tests and research.
For this, the following are carried out:
- Laboratory tests that include a complete blood count,
- Determination of the concentration of glucose in plasma, electrolytes, nitrogen, urea, creatinine and blood gas composition.
- ECG. The assumption of hypothermia is confirmed by recording the Osborne wave on the ECG.
If the causes of hypothermia are unclear, the alcohol and drug levels in the blood are determined, and the function of the thyroid gland is checked. Hypothermia may have been influenced by sepsis, latent skeletal or traumatic brain injury.
When to see a doctor
Hypothermia can be detected by the following signs:
- increased, intense tremors;
- stiffness and numbness of hands, feet;
- clouding of consciousness;
- change in skin color to bright red;
- rapid heart rate.
All these signs together should be the reason for seeking medical attention.
Maintaining a normal body temperature is important to prevent freezing. If the temperature drops below 35 ° C, you should seek medical help from a physician if there are no symptoms of hypothermia.
Prophylaxis
Hypothermia (causes in adults often depend on non-compliance with the rules of self-defense) leads to the development of electrolyte disorders.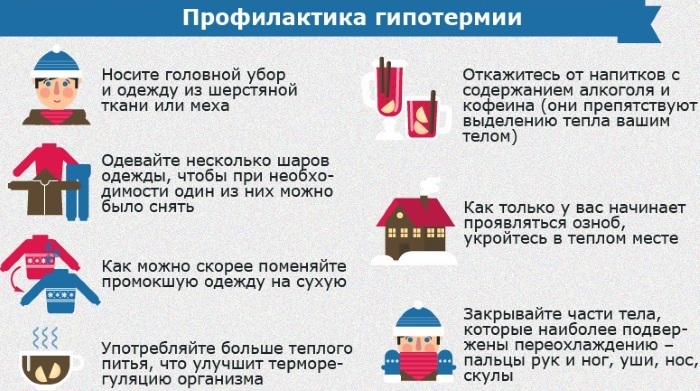
To prevent, preventive measures are proposed:
- Choose the right warm clothes. It is best to wear loose, layered clothing. There is always an air gap between the layers, which protects the body from freezing. On frosty days, cover all parts of the body.
- Do not drink alcohol before going outside during severe frosts.
- Try not to go outside on frosty, chilly days, wearing wet clothes.
- Be careful when exercising outdoors on cold days. Sweat helps cool and makes the body more susceptible to hypothermia.
- Avoid accidents in the winter on the river.
Treatment methods
Before receiving medical assistance, the following steps are taken:
- moving a person to a warm, dry place;
- taking off wet clothes;
- covering the body and head with blankets, leaving only the face open;
- respiration monitoring and cardiopulmonary resuscitation in case of respiratory arrest;
- ensuring skin-to-skin contact by removing clothing from the victim and the person who is saving him and joint shelter in a blanket to transfer heat, if possible due to circumstances;
- providing warm drinks, if the person is conscious, alcohol and caffeine are excluded.


It is imperative not to use direct heat, such as heating lamps or hot water, as this can damage your skin, cause an irregular heartbeat, and lead to cardiac arrest.
Do not rub with snow, oils, fats, immerse in a hot bath. Such actions lead to the death of the epithelial layer of the skin, prevent the restoration of blood circulation. You should not massage a person, as sudden movements can also cause cardiac arrest.
With a mild degree of frostbite, measures are taken:
- The patient is placed in a warm bath with a water temperature of 35 ° C. Gradually, the water is heated to 38-40 ° C (not higher) and maintained at this level until the person warms up. The warm-up procedure takes from 30 minutes to 2 hours with the obligatory constant monitoring of the victim's body temperature.
- For stable patients, an increase in core body temperature of 1 ° C per hour is permissible.
In the case of a moderate stage of frostbite:
- If hypothermia is moderate and thermoregulation is not impaired, warming with blankets and hot drinks is sufficient.
- Recovery of fluid volume is very important. Patients are injected with 0.9% sodium chloride solution intravenously (20 ml / kg of body weight for children).
In moderate to severe hypothermia, before starting warming of the extremities, it is necessary to stabilize the internal body temperature to prevent sudden cardiovascular collapse that develops when the peripheral vascular networks.
In severe cases, in the absence of diseases incompatible with life or injuries, intensive therapy is carried out until the body temperature reaches 32 ° C.
- Severe hypothermia is treated with saline and other fluids injected into a vein. Patients with a lower temperature, especially those with low blood pressure or cardiac arrest, need internal rewarming: inhalation, intravenous infusion, lavage, extracorporeal internal warming.
- Airway warming is also done through masks and nasal tubes. It helps to warm the stomach through the lavage of the cavity or the gastric pump, which pumps a warm solution of sea water into the stomach.
Medications
Medical treatment is carried out:
| Treatment | Appointments |
| For faster warm-up and desensitization | Introduced intravenously calcium chloride 10% - 5-10 ml. |
| To eliminate acidosis (pH restoration) | A solution of sodium bicarbonate 5% is introduced - 200-300 ml. |
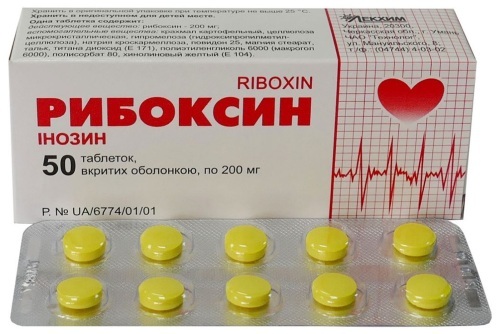
| With hypotension | Cardiovascular agents are used: lily of the valley glycoside (Korglikon), Inosine (Riboxin), Cocarboxylase, Caffeine. |
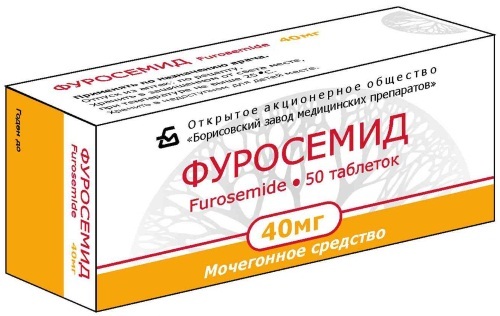
| With the development of edema of the brain and lungs | Corticosteroid hormones are used: Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, osmotic diuretics: Furosemide (Lasix), Mannitol. |
| As needed, for clinical indications, appoint: | analgesics and antihistamines, antiplatelet agents: Pentoxifylline Trental, Dipyridamole, vitamins C, B, PP, anticoagulants: sodium heparin 100-200 U / kg per day. |
After removing the patient from hypothermia, treatment is aimed at preventing possible complications: bronchitis, tracheobronchitis, pneumonia, nephritis.
Traditional methods
With a mild degree of frostbite, it is possible to use plant materials:
- Mustard oil and olive oil improve blood circulation, increase the speed of recovery of frostbite areas. The oil heated to 35˚C is applied in circular, lightly massaging movements to the affected areas of the body.
- Ginger has anti-inflammatory properties, reduces pain caused by frostbite, improves blood circulation in the body. Rub a little ginger, place on a cotton swab and rub into the skin for 5 minutes. The treatment should be repeated three times a day for best results. To make ginger tea, grate a small piece of ginger and add to the tea. Drinking the drink several times throughout the day is an effective way to increase blood circulation.
- Rich in antibacterial properties, aloe vera is a good natural remedy for frostbite. To do this, you need to extract fresh juice from the leaf of the plant, mix the gel with a small amount of water, stir until a homogeneous paste. Apply the paste to the affected areas, rubbing lightly in a circular motion.
Other methods
Hypothermia (causes in adults may be physiological or pathological) in some cases, it is treated using additional techniques:
- Surgical treatment of wounds by the method of ultrasonic cavitation.
- VAC-therapy of wounds (local use of vacuum dressings).
- Hydrosurgical treatment of wounds. In this case, a high-pressure stream of saline is used for surgical treatment of wounds.
Recovery procedures consist in physiotherapy:
- biogalvanization;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetotherapy.
Possible complications
Immediate medical attention is critical to prevent complications from frostbite.
Complications include:
- Frostbite or tissue death is the most common complication that occurs when body tissues freeze.

- Damage to nerves and blood vessels, resulting in loss of sensation.
- Gangrene or tissue necrosis.
- Hypothermia can also lead to death.
General cooling has a favorable prognosis; after treatment, people usually return to their activities. Deep frostbite with damage to large segments of the limbs leads to disability, disability.
The modern approach to the treatment of hypothermia in adults guarantees a positive result. Whatever the reason, doctors are currently restoring all neurological functions. The best prognosis is noted if the main medical measures were carried out in a timely manner.
Author: Belyaeva Anna
Hypothermia Videos
"About the most important thing" about the low temperature: