Opioid or narcotic analgesics are chemicals that have the unconditional capacity to remove or reduce pain. The list of drugs includes drugs that lead to drug dependence (drug addiction).
Record content:
- 1 What is it
-
2 Classification of opioid analgesics
- 2.1 By chemical structure and origin
- 2.2 By the effect on opioid receptors
- 3 Mechanism of action
-
4 Effects
- 4.1 Central
- 4.2 Peripheral
- 5 Who are shown
- 6 Potential harm
- 7 Who are contraindicated
- 8 Addiction
- 9 Poisoning
- 10 Main characteristic
- 11 Opioid Analgesic Videos
What is it
The analgesic effect is revealed by substances with a different molecular structure and a way of implementing the mechanisms of action. Modern pain relievers are divided into 2 subgroups: drugs and non-narcotic analgesics.
Narcotic drugs are characterized by a strongly pronounced analgesic effect, but they can also cause side effects in the form of the development of addiction. Non-narcotic drugs have a less pronounced effect and are not addictive.
Opioids belong to the narcotic subgroup, they are characterized by a strong analgesic effect, which ensures their use for the purpose of relieving pain in various fields of medicine.
Opioids are most widely used in the treatment of the following pathologies:
- injuries;
- surgical interventions;
- injuries;
- oncological diseases;
- myocardial infarction.
A characteristic feature of the funds is the effect on the central nervous system in the form of calls to euphoria, changes in emotional mood, reactions to pain syndrome.
Patients receiving appropriate treatment note that the pain does not go away, just indifference to it appears. A significant disadvantage of opioids is the high likelihood of developing mental and physical dependence on them.
Classification of opioid analgesics
Opioid analgesics, whose list of drugs includes substances that cause drug addiction, are classified according to their origin, method of production and their effect on opiate receptors.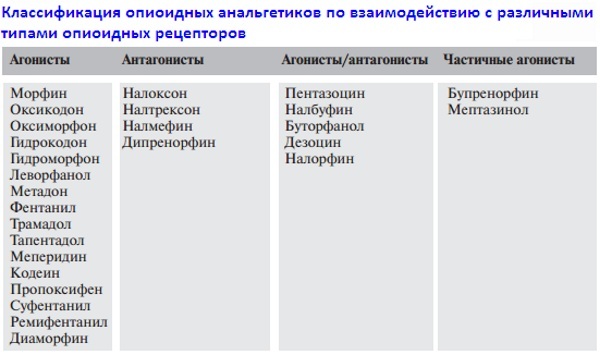
Scientists compare the degree of effectiveness of pain relievers with the classic representative of the series - morphine.
Depending on the analgesic capabilities, the substances are divided as follows:
- Sufentanil - 500 times stronger than morphine;
- Remifentanil - 200 times stronger than morphine;
- Fentanyl - 100 times stronger than morphine;
- Alfentanil - 30 times stronger than morphine.
By chemical structure and origin
By origin, drugs are divided into natural, semi-synthetic and synthetic compounds. The list of natural raw materials includes morphine and codeine. Artificial compounds are represented by trimeperidine, fentanyl.
Semi-synthetic narcotic analgesics:
- heroin;
- dihydromorphone;
- morphinone;
- etorphine;
- buprenorphine.
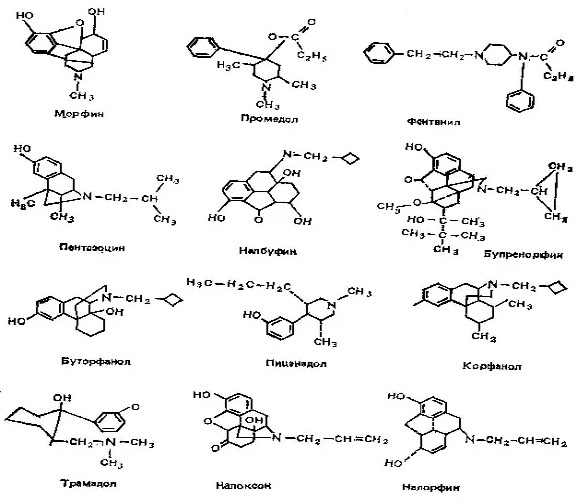
Chemical formulas of opioid analgesics
In the process of manufacturing analgesics in pharmacology, it is possible to obtain substances that are morphine antagonists (antidotes): naloxone, naltrexone.
By the effect on opioid receptors
The degree of analgesic efficacy and the manifestation of side effects of analgesics depends on the properties of their molecular structure and chemical-physical characteristics of substances that are able to come into contact with receptors involved in drug reactions.
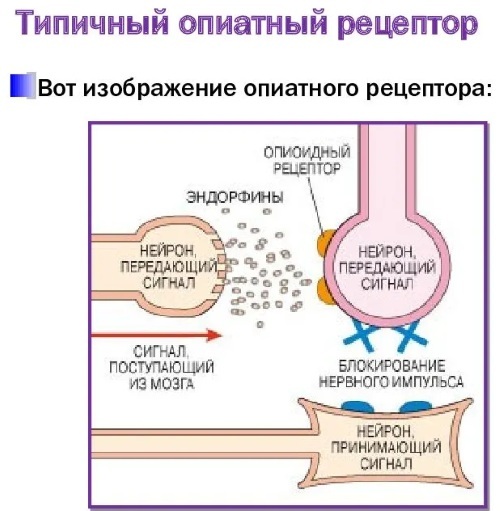
In the 70s. of the last century, scientists discovered specific receptors that regulate pain (opioid), as well as neuropeptides with morphine-like action. Sensory nerve endings (receptors) are localized mainly in the brain, but also in small quantities located in various organs and tissues.
In the central nervous system, receptors are located in those places where the transfer and transformation process of pain impulses takes place. There are different degrees of influence of neuropeptides on opiate sensory endings. Scientists divide 5 subpopulations that perform different functions.
All pain relievers are categorized according to characteristics functioning with opioid sensitive endings into subgroups:
- agonists acting on all receptors (morphine, trimeperidine, tramadol, fentanyl);
- agonists-antagonists, activating some and blocking other groups of receptors (nalbuphine, butorphanol);
- partial agonists that activate the first group of the subpopulation (buprenorphine);
- antagonists that turn off all types of receptors (naloxone, naltrexone).
Mechanism of action
Opioid analgesics (the list of drugs is insignificant) have a mechanism of action that is based on oppression thalamic areas of the brain responsible for pain sensitivity and conduction of impulses to the membranes of the central nervous system.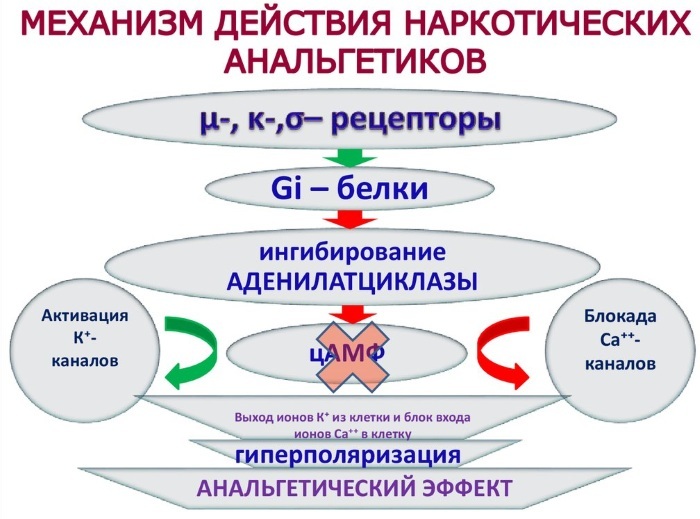
The effect of drugs must be considered using the principles of functioning of neural networks in the brain, which provide an analgesic effect through the properties of different types of receptors. They are still not fully understood in all areas of the central nervous system.
However, opioids are known to cause the following changes in patients:
- anesthesia;
- drowsiness;
- changes in mood and psychological state.
One of the characteristic features of the series is that its use does not cause loss of consciousness. If the patient does not experience pain and is injected with morphine at the usual dose, then this can cause discomfort in the person.
Scientists have shown that the ability to relieve pain is selective, as only pain receptors are blocked. However, other sensory modalities remain intact.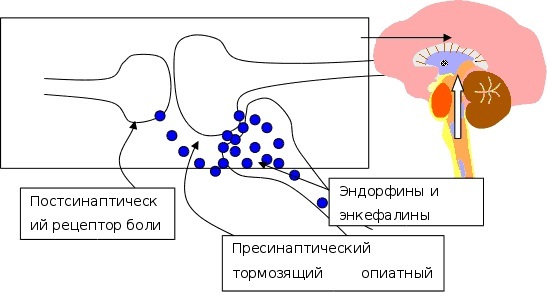
Anesthesiologists distinguish between 2 types of pain:
- Sensations are caused by stimulation of nociceptive receptors with the transmission of impulses through neural networks.
- A syndrome that occurs through damage to nerve fibers (neuropathic pain).
The first type is more easily treatable with opioids. The second usually reacts poorly to narcotic analgesics and requires an upward dose adjustment.
Effects
The analgesic effect of opiate analgesics is due to their interaction with different types of receptors. All effects are due to the mechanism of action of these drugs.
Potential areas of impact include:
- muscle rigidity;
- postoperative tremors;
- nausea and vomiting;
- respiratory and cardiovascular effects;
- tolerance or addiction.
Central
Opioid analgesics, whose drug list contains substances with a high likelihood of developing side effects, have central effects from use.
The directed action of narcotic substances includes:
- anesthesia;
- euphoria;
- sedative effect;
- respiratory depression;
- suppression of cough;
- miosis (constriction of the pupils);
- stiffness of the muscles of the body (stiffness of movement);
- nausea and vomiting;
- addiction (drug addiction).

Codeine inhibits the cough center by reducing the excitability of the respiratory system to carbon dioxide and reflex influences. The effect on the vomiting center is manifested in two ways: on the one hand, inhibition is observed, on the other, stimulation on the trigger zone of the center. In practice, this means that 20-40% of patients experience nausea and vomiting, followed by a rapid suppression of the reflex.
Sedation is expressed by clouding of consciousness, which is accompanied by a violation of intellectual abilities. The stiffness of the skeletal muscles leads to a decrease in the tone of the respiratory muscles, which carries an additional burden on the lung function. The constriction of the pupils is associated with the action of morphine on the optic motor nerves.
Addiction to drugs manifests itself in the form of a decrease in the effect of the drug with its prolonged use. As a result, patients become dose dependent. If a person is prescribed high doses of drugs, then the addiction develops faster.
Patients with chronic pain develop tolerance more slowly. It manifests itself as a feeling of bliss and indifference to others, loss of fear and anxiety. Feelings cause the desire to take the drug again and form a psychological dependence, which is the first stage of drug addiction.
Peripheral
The peripheral effects of opiates include abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs. The conditions are explained by the fact that the active substances are able to increase the tone of smooth muscle organs. Peripheral effects are associated with the interaction of drugs with specific receptors.
As a result of the influence of drugs, the intestinal tone increases and its peristalsis slows down, as well as the rate of passage of food masses. Further, the degree of absorption of water from the digestive system increases, which leads to constipation.
The development of conditions is promoted by general weakness and slight physical activity of patients. Usually, doctors prescribe laxatives to such people.
Morphine is able to increase the tone of the bile ducts, thereby disrupting the secretion of bile and enzymes in the intestine. Increased tension in the ureters and bladder leads to urinary problems.
Who are shown
Narcotic analgesics serve as a last resort for pain relief when other drugs do not work. Doctors make their appointment last.
The indications for the use of opioid drugs are the following:
- acute pain syndrome with injuries, burns, surgical procedures;
- chronic severe pain associated with tumor processes in oncological practice;
- acute phase of myocardial infarction;
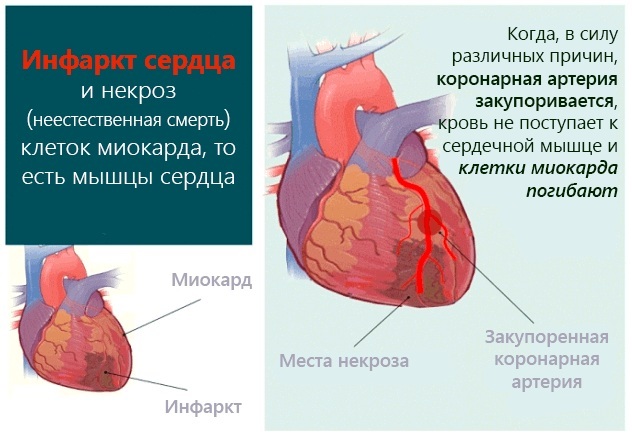
- pulmonary edema with shortness of breath;
- pain relief of postpartum activities;
- in the postoperative period as anesthesia;
- renal and hepatic colic.
Potential harm
Opioid analgesics (the list of drugs is divided depending on the mechanism of action) have a number of side effects from use, which include the following conditions:
- depression of respiratory function;
- an increase in blood pressure;
- delay in urination;
- allergic reactions in the form of urticaria in the nasal area;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- the appearance of a feeling of anxiety;
- trembling limbs;
- hyperactivity;
- manifestation of a gag reflex with nausea;
- constipation.
Who are contraindicated
Contraindications to the use of narcotic analgesics are the following aspects:
- bronchial asthma;
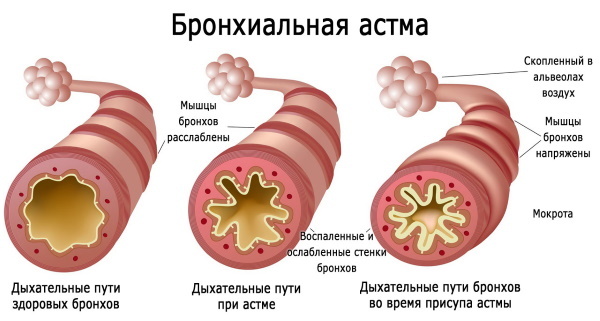
- a state of oppression of the respiratory center;
- trauma and damage to the brain, accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure;
- the period of pregnancy and labor, since the funds are able to lower the tone of the uterus and increase the period of childbirth, and also affect the respiratory center of the child;
- children under 2 years of age due to the presence of a high sensitivity of the respiratory system to opioids;
- advanced age due to slow absorption of morphine.
Addiction
Drug dependence manifests itself in the form of a progressive decrease in the effect of morphine with prolonged use of drugs. The effect is dose-dependent.
With the initial use of a high dosage, tolerance develops faster than with normal use, and there is a need for an increase in the amount of drugs. Scientists have found that patients with chronic pain syndrome develop tolerance more slowly.
The degree of severity of dependence on morphine in relation to different effects is manifested differently. A stronger relationship is observed in relation to pain relief, euphoria, sedation, nausea and vomiting, and respiratory depression. A slight tolerance is manifested in relation to miosis and constipation.
Scientists have found that dependence in relation to euphoria and the respiratory effect decreases faster already during several days after the withdrawal of funds, and resistance to the muscle effect can persist for up to several months.
It has been proven that the effects of euphoria and tolerance that appear with the use of drugs (especially with intravenous administration) are interrelated. Euphoria forms psychological dependence upon drug withdrawal.
At this stage, negative emotional experiences appear, but if you continue to use opiates, then addiction develops, which is expressed by the desire for their search and reception, with the development of difficult to control character.
Physical dependence appears along with the formation of tolerance to opioid drugs. As soon as a decrease in the effect of the administration of drugs begins to be observed, drug addiction is immediately ascertained.
A characteristic sign of physical dependence is withdrawal or withdrawal symptoms, which are expressed by the following symptoms:
- agitation, restlessness, feelings of anxiety and hostility;
- insomnia;
- fever;
- lacrimal rhinitis;
- headache sensation;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- tachycardia.
If the patient needs to discontinue the drug, then this should be done gradually, reducing the dose by about 20% per day. In such cases, withdrawal symptoms are less common.
Poisoning
The list of drugs for opioid analgesics contains drugs that are characterized by a high risk of poisoning. As a result of an overdose of drugs, acute intoxication occurs, which is characteristic the following signs, laid out in chronological order of appearance:
- After 20-30 minutes. after taking the funds, dizziness, vomiting, drowsiness, impotence, a change in psychological states from euphoria to stupor with constriction of the pupils may occur.
- Further, the analgesic effect rapidly occurs with the transition to a coma.
- During sleep, there is a decrease in the respiratory rate up to 2-3 times per minute, the appearance of arrhythmia, the development of pulmonary edema, cyanosis is possible.
- After there is a sharp drop in blood pressure (in childhood before seizures).
- It is possible that an unfavorable outcome (death) occurs, which occurs within 6-18 hours through paralysis of the respiratory system and its failure.
In the course of a favorable course of poisoning, there is a transition from coma to sleep lasting up to 1.5 days followed by the manifestation of withdrawal symptoms (feelings of fatigue, weakness, headache, vomiting).
In case of acute manifestation of opioid poisoning, the following algorithm of actions must be observed:
- Carry out measures to restore breathing (connecting the patient to a ventilator with positive pressure during inspiration). The most critical period is the first 10-12 hours.
- It is necessary to administer the antidote (naloxone) to the patient intravenously.
- Next, the gastric lavage is performed using a probe and absorbents.
- Throughout the entire period of recovery from the state, constant continuous monitoring of the patient should be organized to prevent a repeated decrease in respiratory activity.
- Then doctors anesthesiologists prescribe symptomatic treatment aimed at restoring the patient's cardiovascular activity.
Main characteristic
A list of commonly used opioid drugs with a description is summarized in the table.
| Name | View | Description |
| Buprenorphine | Agonist | The substance is 20-30 times more effective than morphine. Areas of application are postoperative treatment, labor pain relief, myocardial pain, oncology. Side effects include drowsiness, nausea, and vomiting. In case of overdose, requires the administration of high doses of naloxone. |
| Butorphanol | Agonist antagonist | The drug is used in the treatment of postoperative pain. The disadvantage is the rapid development of addiction and severe drowsiness. |
| Nalbuphin | Agonist antagonist | The drug has a low narcogenic potential, but causes drowsiness. It is used in postoperative treatment and in cancer pathologies. |
| Morphine | Agonist | The substance serves as the gold standard for opioid analgesics, which has strong analgesic activity. It has all the typical side effects of the series. |
| Prosidol | Agonist | The remedy is weaker than morphine. It can be used for severe pain syndromes in cancer patients. Has a local anesthetic effect. |
| Codeine | Agonist | A widely used opiate with a low rate of physical dependence. Has side effects that are similar to morphine, but not as severe. The drug is used in the presence of moderate pain. |
| Fentanyl | Agonist | The most potent opioid analgesic, which is 90 times more active than morphine. It initially inhibits respiration to a high degree, but it does not last long. The agent is used to treat moderate pain, belong to a number of weak agonists. The drug is characterized by a higher narcological safety in comparison with other opiates. Dizziness and nausea are common side effects. |
Opioid analgesics are drugs that occupy the last step in the classification of pain relievers. Despite the presence of a high likelihood of side effects, addiction, their list serves today as an absolutely uncontested way of treating chronic or severe pain.
Opioid Analgesic Videos
Basic pharmacology of opioid analgesics: