Acetylcholine can act on the bodyby stimulating the response or blocking it and, thus, to carry out an excitatory or inhibitory effect.
The organic compound ester of choline and acetic acid, which transmits nerve impulses, is the main neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system, parts of the autonomic nervous system that regulates smooth muscle contraction, dilation of blood vessels, regulates secretion, slows down heartbeat.
Record content:
- 1 What is Acetylcholine
- 2 Functions of acetylcholine
- 3 The beneficial properties of acetylcholine
- 4 Why is there a deficit
- 5 Excess acetylcholine
- 6 Risks and side effects
- 7 How to increase the level of acetylcholine in the body
- 8 Sources of acetylcholine and dosage
- 9 Food
- 10 Examples of additives
- 11 Video about acetylzoline
What is Acetylcholine
In recent years, nootropics, also known as mental stimulants, have become popular. Acetyl choline is a neurotransmitter that is involved in brain functions such as memory, thinking, and learning.
There are no dietary supplements containing acetylcholine, but supplements that indirectly increase acetylcholine levels are becoming increasingly popular. Acetylcholine imbalance is associated with several medical conditions. People with Alzheimer's and Parkinson's have low levels of acetylcholine.
Functions of acetylcholine
In the body, acetylcholine has several important functions, it is involved in muscle movement, thinking, memory mechanism and other brain functions.
- In the peripheral nervous system: Acetylcholine is formed at the ends of cholinergic (acetylcholine-producing) neurons. When a nerve impulse reaches the end of a motor neuron, acetylcholine is released into the neuromuscular junction. There, it binds to a receptor molecule in the muscle fiber. If sequential nerve impulses accumulate at a high enough frequency, this leads to the contraction of muscle cells.
- Acetylcholine (the effect on the body is carried out in the autonomic nervous system) behaves in a similar way, emerging from the terminal of one neuron and binding to receptors on membranes other cells. Its activity affects a number of systems, including the cardiovascular system, where it acts as a vasodilator, reduces heart rate and cardiac muscle contraction. In the gastrointestinal tract, it enhances gastric motility and increases the amplitude of digestive contractions. In the urinary tract, its activity decreases the capacity of the bladder and increases the pressure during voluntary urination. It also affects the respiratory system and stimulates secretion by all glands that receive impulses from the parasympathetic nerve.
- Acetylcholine is known to play an important role in the development of memory and learning. It has been shown to be involved in the emergence and development of several major neurodegenerative diseases in which memory is impaired, such as dementia and Alzheimer's syndrome. Memory impairment is correlated with a decrease in the amount and activity of acetylcholine, especially in certain areas of the brain that are key to memory formation, such as the hippocampus.
- Acetylcholine, along with other neurotransmitters and hormones, stimulates awakening. The activity of acetylcholine neurons increases during wakefulness and decreases during certain sleep phases.
- Acetylcholine is involved in processes such as concentration and mindfulness. In one study, conducted on 60 patients 40-60 years old, it was shown that taking cytidine diphosphate choline for 28 days significantly improved their ability to concentrate.
- Acetylcholine (the effect on the body is significant in the hormonal system) affects the synthesis and release of various hormones. For example, the level of the neurotransmitter has been shown to correspond to the secretion of the hormones prolactin and growth hormone by the pituitary gland. The mechanism of regulation is not fully understood, it is assumed that regulation is carried out through the hypothalamus, a part of the brain involved in hormonal regulation.
- Acetylcholine affects inflammation. The cells of the immune system release anti-inflammatory proteins (cytokines) in response to infection or injury. Cytokines trigger a chain of reactions that mobilize inflammatory cells in the area of inflammation to suppress it. Acetylcholine has a so-called "inhibitory" effect on this immune response. This protects the body from tissue destruction if the inflammatory response spreads to the kidneys, liver, lungs, or other important organs.
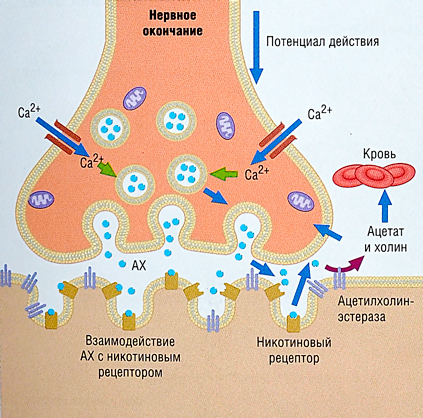
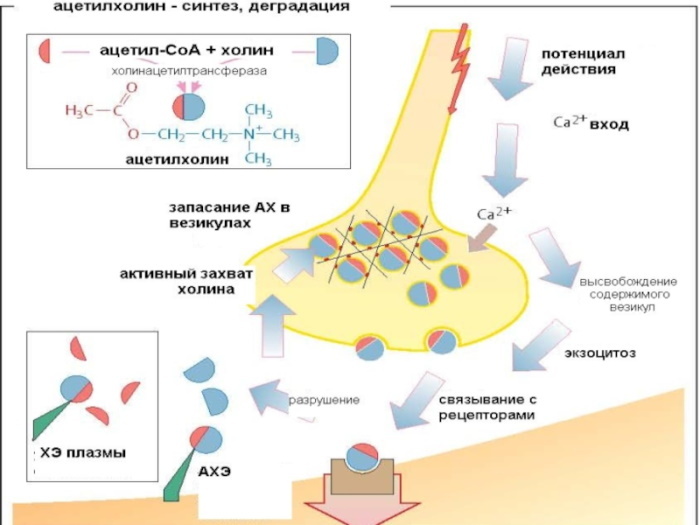
In addition to participating in anti-inflammatory reactions, acetylcholine interacts with the immune system and influences the immune response to infections. For example, it prevents microorganisms from forming films in infections caused by the fungus Candida albicans.
- Acetylcholine is involved in pain perception mechanisms. Therefore, through the regulation of this neurotransmitter in the body, pain symptoms can be alleviated. For example, in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, donepezil is used to increase the level of acetylcholine. At the same time, it acts as a pain reliever. The effect is dose dependent and can be used to treat migraine symptoms.
The beneficial properties of acetylcholine
Increases in acetylcholine levels have been linked to possible health benefits:
- Improving memory and brain function. In people with memory problems, choline, a precursor of acetylcholine, improves memory. Lifetime choline supplementation significantly improves memory and reduces the formation of beta-amyloid plaques - formations that are associated with the development of the disease Alzheimer's. The studies were carried out on 2195 patients aged 70-74 years. It has been shown that the higher the blood choline level, the better the patient's memory and learning ability.
Supplements that inhibit the breakdown of acithelcholine, such as bacopa, ginkgo biloba, and huperzine A, improve memory and brain function. Research into these supplements and their links to mental performance is fairly recent. More research is needed in this area.
- Improving mental performance. Supplements containing the precursor acetylcholine can help with certain mental health conditions. Studies with over 5,900 participants have shown that low blood choline levels are associated with a high risk of anxiety disorders. Although no link has been found between choline levels and depression.
In another study, which involved 50 people with depression syndrome, it was observed that patients taking 200 mg of choline daily in for several weeks in parallel with citalopram (a drug for depression), had less pronounced symptoms of depression than patients taking only medicine.
There is also evidence that bacopa and ginkgo biloba reduce symptoms of anxiety disorders, but these findings warrant more research.
Choline preparations are used to treat symptoms in patients with bipolar disorder. But there is not enough research in this area to recommend these supplements for such purposes.
- Maintaining pregnancy. Approximately 90-95% of pregnant women consume less than the required daily amount of choline. Choline supplementation during pregnancy supports the normal development of the embryo and improves the development of the embryo's brain.
Studies have shown that supplementation of 480 or 930 mg of choline during the third trimester of pregnancy significantly improved the baby's brain activity and memory. In pregnant women with alcohol dependence, after taking 2 g of choline daily from mid-pregnancy to birth, the effect of alcohol on the development of the child's brain significantly decreased.
It has been noted that taking choline during pregnancy reduces the risk of fetal neural tube disorders, but these data also warrant more extensive research.
- Other beneficial properties. Choline deficiency can be associated with liver disease. Therefore, choline supplementation may be associated with a reduced risk of liver disease and liver cancer.
- Heart disease. There is evidence that choline supplementation may reduce the risk of developing heart disease and angina. But the data is still insufficient, more extensive research is required.
 Dietary supplements that act on the acetylcholine system do not just temporarily increase the level of acetylcholine, they improve the functioning of the acetylcholine receptors. The peculiarity of these receptors is that when they are stimulated, they become more sensitive. Fewer choline supplements are required over time to get the same results.
Dietary supplements that act on the acetylcholine system do not just temporarily increase the level of acetylcholine, they improve the functioning of the acetylcholine receptors. The peculiarity of these receptors is that when they are stimulated, they become more sensitive. Fewer choline supplements are required over time to get the same results.
Another feature of choline supplementation is that it can be taken as needed, as soon as it occurs. the need to increase mental activity, for example, during exams or performing difficult work projects. When supplements are taken, the improvement in mental performance is felt immediately, usually within half an hour.
Why is there a deficit
There are several reasons for a decrease in acetylcholine levels. One of the possible reasons is the presence of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors, for example, in a disease such as severe pseudoparalytic myasthenia gravis. There is also evidence that autoimmune responses to acetylcholine receptors occur in schizophrenia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Insulin resistance and diabetes affect the synthesis of acetylcholine. But the 2 main causes of acetylcholine deficiency are inadequate diet and medication.
A low fat diet and vegetarian diet are the main causes of acetylcholine deficiency. Acetylcholine is synthesized from choline, a B vitamin nutrient. 90% of people do not get enough choline from food. The richest food in choline is egg yolk, organic meat. But any fatty animal food contains choline.
In plant foods, only a few plant species contain choline, and it is almost impossible to get enough choline from vegetarian food alone.
So, one egg contains 150 mg of choline. The same amount of acetylcholine can be obtained from plant foods by eating 2 servings of tofu, 3 potatoes, 1.5-2 servings of broccoli, or 6 servings of brown rice. Therefore, a diet that does not include fatty meats or eggs leads to a lack of choline.
The second major cause of choline deficiency is the use of anticholinergics that block the action of acetylcholine.
These tools include:
- antacids;
- antibiotics;
- antihistamines;
- antihypertensive drugs;
- antidepressants.
 Acetylcholine, which has an important effect on the body, is found in anticholinergic drugs, most of which are prescription drugs. A number of drugs are sold over the counter, such as the antihistamine benadryl and the acid-lowering agent pepsid AC. Uncontrolled use of these anticholinergics in the elderly increases the risk of dementia.
Acetylcholine, which has an important effect on the body, is found in anticholinergic drugs, most of which are prescription drugs. A number of drugs are sold over the counter, such as the antihistamine benadryl and the acid-lowering agent pepsid AC. Uncontrolled use of these anticholinergics in the elderly increases the risk of dementia.
To increase acetylcholine, you need to eat a diet that contains fats, limit your intake of anticholinergics, or take choline supplements.
Excess acetylcholine
In most cases, an imbalance in the level of a neurotransmitter means a deficiency, not an excess. But sometimes there is an excess of acetylcholine, especially if you take active measures to increase its level.
A rise in acetylcholine levels can be caused by exposure to organophosphate pesticides, insecticides, or toxic nerve agents.
These chemical compounds increase the level of acetylcholine in the nervous system and cause symptoms such as:
- pulmonary obstruction syndrome;
- sweating;
- weakness;
- headaches;
- fainting;
- diarrhea and nausea;
- change in mental status;
- muscle cramps;
- cramping;
- paralysis;
- cessation of breathing.
Exposure to chemicals that affect the balance of acetylcholine can be through the skin, respiratory or digestive system. The most likely route for these compounds to enter the body is through the ingestion of pesticides through vegetables and fruits, as well as as a result of contact with agents that are used in everyday life to destroy insects.
An imbalance in acetylcholine levels aggravates Parkinson's disease. Normally, the body has a balance of acetylcholine and dopamine, another neurotransmitter that controls muscle contraction. Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder in which involuntary movements, tremors, and disturbances in mood and thinking develop.
The exact cause of the development of the disease is not known. But it has been shown that in patients with this syndrome, the level of dopamine decreases, and because of this, the level of acetylcholine increases. In this case, the muscles become too "agitated", symptoms such as twitching movements and tremors appear.
Some drugs used to treat Parkinson's disease block the action of acetylcholine. Dopamine levels return to normal and symptoms disappear. These drugs are called anticholinergics. Other symptoms of Parkinson's disease, such as memory complications, may also be related to acetylcholine levels.
Risks and side effects
As with any dietary supplement, you must inform your healthcare professional if you are taking choline. Choline supplements such as alpha GPC and citicoline are safe in most cases and rarely cause adverse reactions.
In case of an overdose of choline, side effects such as:
- low blood pressure;
- increased sweating;
- unpleasant "fishy" body odor;
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- liver disease.
The maximum dosage of choline that will not cause adverse effects is 3,500 mg per day. This amount can only be obtained by taking nutritional supplements.
Taking supplements containing bacopa, ginkgo biloba, and huperzine A can lead to side effects such as nausea, stomach pain, diarrhea, and headache. These supplements can interact with other medications, so contact your healthcare professional before taking them.
How to increase the level of acetylcholine in the body
To improve brain function, nutritional supplements are becoming increasingly popular that increase levels of acetylcholine, the so-called nootropic drugs, natural or synthesized substances that improve mental activity.
Acetylcholine cannot be obtained using dietary supplements. There are supplements that increase the synthesis of acetylcholine in the body, such as choline. In addition, you can take substances that inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine.
To increase the production of acetylcholine, indirectly consume certain foods containing choline.
Sources of acetylcholine and dosage
Acetylcholine, whose effects on the body are discussed above, has a precursor called choline, so taking drugs containing choline is the best way to increase acetylcholine levels. Plus, these supplements have fewer side effects.
They are available in capsule and powder form. It is recommended to take 600-1200 mg per day, which is equivalent to 2 capsules twice a day. This amount has an effect and is well tolerated by the body.
Acetylcholine levels can be increased by taking dietary supplements containing the following ingredients:
- alpha glyceryl phosphoryl choline (alpha-GPC, choline alfoscerate);
- cytidine diphosphate choline (CDP choline);
- choline bitartate.
Alpha-GPC and Cytidine Diphosphate Choline contain more choline and are more easily absorbed.
Another way to indirectly increase acetylcholine levels is to take supplements that inhibit enzymes, destroying acetylcholine:
- Ginkgo biloba leaf extract;
- Bacopa (Bacopa monnieri);
- Asian centalla (Centalla asiatica);
- common ginseng;
- huperzine A.
The question of how effective supplements that inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine are compared to supplements containing choline are not fully understood. Although Huperzine A, Heperzia serrata extract is so effective that it is used as a remedy for Alzheimer's in some regions.
Also, vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) is a necessary coenzyme for the synthesis of acytlcholine from choline. Therefore, taking this vitamin along with choline will help increase acetylcholine levels.
Food
Choline content in different foods:
| Products | % of the daily value of choline |
| 25 g beef liver | 65 |
| 1 boiled egg | 27 |
| 85 g beef tenderloin | 21 |
| 85 g toasted soybeans | 19 |
| 85 g boiled chicken breast | 13 |
| 85 g cod | 13 |
| 75 g oyster mushrooms | 11 |
| 128 g canned green beans | 8 |
| 185 g quinoa | 8 |
| 240 ml 1% milk | 8 |
| 245 g yogurt | 7 |
| 78 g boiled broccoli | 6 |
| 78 g cooked Brussels sprouts | 6 |
Examples of additives
There is a wide variety of choline supplements available in pharmacies and online stores:
| Brand name | Description | price, rub. |
| Jarrow Formulas, Citicoline, CDP Choline | Contains 250 mg of citicoline, 120 capsules, it is recommended to take 1 capsule 2 times a day. It is not recommended to take the supplement during pregnancy, planning pregnancy, breastfeeding, or taking medication. |
2770 |
| Country Life, Choline 100 tablets |
Contains choline bitartrate 293 mg per tablet. It is recommended to take 1 tablet a day. |
1013 |
| Solgar, Choline 350 mg | 100 capsules, 1 capsule contains 350 mg choline bitartrate. The recommended daily dose is 1 to 3 capsules per day. | 983.5 |
| Jarrow Formulas, Alpha GPC | 60 Vegetable Capsules Containing 300 mg Alpha-GPC | 1920 |
| Canonpharma production, Holitilin | Produced in Russia, 14 capsules, 1 capsule contains 400 mg of alpha-GPC. | 562 |
| Sotex, Tsereton | Produced in Russia, 14 capsules, 400 mg alpha-GPC. | 544 |
Acetylcholine is a very important neurotransmitter. With an imbalance of its level in the body, neurological disorders occur, characteristic of Alzheimer's syndrome or Parkinson's disease.
Eating a healthy diet and taking nutritional supplements can help you get the choline you need, which is enzymatically converted to acetylcholine. Consult your healthcare professional before taking choline supplements to avoid unwanted side effects.
Video about acetylzoline
About acetylcholine:




