The influence of hormones on the functioning of the body is difficult to overestimate. From their content, which does not go beyond the norm, depends not only on the state of physical health, but also on the psychological state. Often, the definition of indicators is performed to diagnose diseases that are not even associated with the endocrine function, since the body's response to any disorder begins with hormones.
Properties of hormones
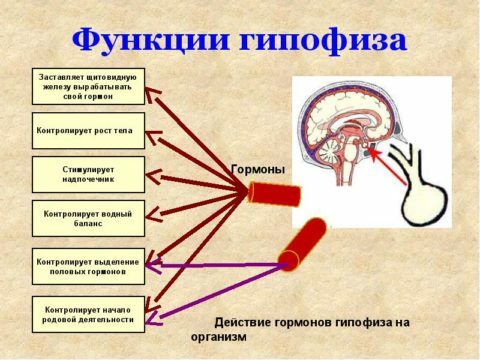
TTG is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the pituitary gland. TTG serves as a stimulant for the secretion of the hormones of the gland. Its detection and analysis are conducted to identify chronic diseases that occur asymptomatically, including mental illness.
The main function is the regulation of the energy exchange. In addition, it regulates the work of the genitourinary and digestive systems and the transmission of nerve impulses.
Free thyroxine or T4 is a precursor of triiodothyronine. The production takes place directly in the thyroid gland cells. Its main task is to regulate the rate of energy exchange, increase energy production and oxygen absorption by cells in the body.
Norms
Normal TSH in the blood lies in the interval 0.4-4 mIU / l. Free thyroxine has a norm in the range of 0.8-1.8 pg / ml or 10-23 pmol / l. The peculiarity of free thyroxin is the change in its parameters depending on the time of day and year, as well as the dependence on sex.
At day, the T4 concentration reaches a maximum from eight in the morning to half a day - at this time it is usual to take a blood test to determine the maximum production. The minimum value of the hormone reaches in the evening, around midnight.
Throughout the year, the maximum value of T4 reaches in the autumn-winter period, the minimum - in the summer. The content of free thyroxine in the blood of women is usually lower than that of men. The level of content in both sexes is almost constant up to 40 years - after reaching this age the concentration gradually decreases.
Causes of abnormalities
A rise may indicate diseases associated with hyperfunction of the gland. Otherwise, the destruction of the gland tissue leads to an increase.
Causes not related to pathology may be concealed in the non-standardized intake of hormone preparations based on thyroid hormones.
Diseases of the gland causing an increase in free thyroxine content are, most often:
- toxic goiter,
- thyroiditis,
- choriocarcinoma,
- nephrotic syndrome,
- liver disease in chronic course,
- obesity, thyrotoxicosis,
- goiter.
The cause of the deviation from the norm in the larger side may also be self-directed or overdose of hormonal drugs. This syndrome is called medical thyrotoxicosis. Sometimes drugs based on free thyroxin are taken deliberately to reduce weight, while the dosage exceeds acceptable standards, especially in an organism that does not need additional hormone intake. In other cases, the doctor prescribes the wrong concentration of the hormone or improperly adjusts the strategy of taking the drug.
Hyperthyroidism and its symptoms
The most common cause of increased free thyroxine concentration is hyperthyroidism. In medical practice, this phenomenon is not called a disease, therefore hyperthyroidism is considered a clinical syndrome. The most striking clinical picture that blood tests can provide is an increase in T4 against a background of normal or reduced TSH content.

The main symptoms accompanying hyperthyroidism are manifested in the psychoemotional state of the patient. Most often it's a quick temper, excitability, irritability, hypersensitivity, difficulties with falling asleep, timidity. Physically, the symptoms are manifested in a sharp decrease in weight against a background of increased appetite, diarrhea, sweating.
Other symptoms:
- sudden deterioration of well-being in hot weather,
- tremor of extremities,
- arrhythmia and tachycardia,
- frequent desires for defecation,
- malfunctions in menstruation, amenorrhea,
- exophthalmos, same eyelash, edema of eyelids,
- lacrimation, inability to concentrate vision,
- prolapse andfragility of hair, foliation and soft nails.
Causes of development of
disorders The causes of abnormality are divided into two types. The first type of cause is associated with pronounced hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. This means that the production of hormones multiplies many times, despite the fact that there is no need for them in the body. The phenomenon of hyperfunction is observed in adenomas of the gland and pituitary gland, toxic goiter.
The second type of cause is associated with the destruction of thyroid cells, as a result of which the previously synthesized hormone is released into the blood. This is the main reason if postpartum or autoimmune thyroiditis is diagnosed.
Recently, the cause is a primary malfunction in the immune system. If a joint effect of the provocateurs of the disorder is carried out, the activation of the cells of the immune system begins. These cells, they are antibodies, and lead to the destruction of the cells of the organ. In other words, the immune system fails, resulting in the synthesis of cells that destroy the thyroid tissue. These cells include antibodies to TPO, TG and TTG.
Clinical picture of
If hyperfunction is manifested due to diffuse-toxic goiter, the antibodies interact with thyroid-mediated receptors, thus replacing the effect of natural TSH.As a result, synthesis and secretion of hormones increase, leading to hyperthyroidism. The clinical picture has a pronounced progression and symptoms.
In the case of chronic, autoimmune, postpartum thyroiditis, antibodies do not affect the activity of hormone synthesis, but simply destroy thyroid-structural units of the thyroid gland. If this occurs, there is an increase in T4 in the blood and a decrease or stability of the TSH level. In this case, the syndrome does not have a long-lasting character and a pronounced clinical picture, and its effect ceases within six months.
Degrees of severity
In hyperthyroidism, three degrees of severity are distinguishable depending on the concentration of T4 and the ratio with TSH.
The mild symptom symptom is indicated as subclinical and is determined if T4 is in the normal range and the TSH is slightly elevated. This form of flow is easily tolerated, with little or no symptoms.
The mean severity of the course is already indicated by the disease and in medicine is called manifest hyperthyroidism. It is diagnosed if T3 and T4 are higher than normal, and TSH is lower. The greater the deviation of thyroxin from the norm, the more violations in the endocrine system of the body.
Heavy form is called thyrotoxicosis and is diagnosed at a high thyroxine level if the TSH is in the normal range or is lowered. This form of chronic hyperthyroidism has a pronounced symptomatology and clinical picture. The root cause of thyrotoxicosis is diffuse toxic goiter.
Diagnosis and analysis of

For the diagnosis of hyperthyroidism, the patient is referred to a blood test to determine the total and free thyroxine content, as well as TSH.The antibody titer is determined to determine the causes of the occurrence, confirm the autoimmune character of the disease, and evaluate possible relapses. When confirming the alleged diagnosis, the patient is referred for ultrasound to determine the diseases that led to the destruction of the gland cells.
Indication for analysis is the suspicion of hyperthyroidism, a decrease or increase in the level of TSH, a pregnancy test, a diffuse toxic goiter. In the latter case, the study is conducted several times to confirm the picture of the course of the disease - once in ten days.
Preparation for blood donation
To exclude extraneous factors affecting these analyzes, it is recommended to perform an empty stomach test, while it is forbidden to drink tea, only pure water without dyes and gas.
The last meal should be at least eight hours ago, and for a day you must adhere to dietary intake, eliminating fried, fatty, alcohol. Avoid prolonged physical activity.
Non-hormonal medications should be withdrawn no later than two weeks before blood sampling or their administration is prescribed for the period after the study. If this is not possible, in the direction the endocrinologist is required to indicate which drug and in what concentration is taken by the patient.
It is recommended to exclude medicinal preparations of hormonal nature 7 days prior to blood sampling. Iodine containing preparations should be excluded no later than three days before the analysis.
It is not recommended to conduct the test in one day after ultrasound or rectal examination, X-ray and fluorography.
An increase in the result may be caused by the use of estrogen, thyroid medications. Underestimation of results can be caused by corticosteroids, reserpine, sulfonamides, penicillin, excess thyreostatics, androgens.
Research and fence are carried out only when directed from an endocrinologist, therapist, surgeon, gynecologist, pediatrician and psychotherapist.
If confirmation of the diagnosis of thyrotoxicosis is confirmed and further observation of the disease pattern, TSH is not interpreted in the results of the analysis or is interpreted at the physician's request in the direction. A more important diagnostic value in this case is a free and common thyroxine.
Treatment and therapy
To adjust the T4 level, hormonal drugs that block the action of excess thyroxine in the body and replace it are prescribed. In severe forms, the drug takes up to a year. Treatment begins with taking a large dose of the drug to normalize the content of thyroxin, then the concentration gradually decreases to the supporting values. The cancellation can be appointed or nominated at long-term stable indication of a thyroxine in one interval.
In some of the most severe cases, the patient is offered surgery to remove nodes or the same procedure with laser surgery.