Red blood cells are red blood cells formed after they are separated from plasma in the course of laboratory tests. It is harvested immediately after donation of blood by donors and is used to treat chronic, acute anemia and other diseases.
Record content:
- 1 Scope of erythrocyte mass, indications
- 2 Erythrocyte blood components
- 3 Types of red blood cells
- 4 Physiological properties
- 5 Pharmacokinetics
-
6 Mechanism of action
- 6.1 Substitution effect
- 6.2 Hemodynamic effect
- 6.3 Immunological effect
- 6.4 Hemostatic effect
- 6.5 Stimulating effect
- 7 Contraindications
-
8 Red blood cell transfusion
- 8.1 Getting erythromass
- 8.2 Erythromass transfusion procedure
- 9 Tolerability and side effects
- 10 Interaction
- 11 Cautions
- 12 Storage conditions and shelf life
- 13 Blood transfusion video
Scope of erythrocyte mass, indications
Erythrocyte mass (EM) is prescribed to prevent anemia, better oxygenation of the blood. It is a product of the primary fractionation of blood (separation into plasma and globular mass). The content of microclots in EO and whole blood is almost the same.
But the use of EM reduces the patient's immunity to plasma proteins, leukocytes and platelets from donated blood. EO has a high viscosity, which makes it difficult to transfuse it in an intensive mode, which is often necessary in case of profuse blood loss. Transfusion therapy is widely used in the treatment of pathologies and in the case of surgical interventions.
Erythrocyte mass is used to restore the body in cases of:
- surgical and traumatic shock, accompanied by blood loss;
- oxygen starvation with anemia;
- anemia after blood loss;
- the period of preparation of patients for major surgical interventions, if there is a low hemoglobin count;
- anemia of various etiologies as a result of repeated blood transfusions or pregnancy;
- homologous blood syndrome in order to prevent anaphylactic reactions.
Erythrocyte blood components
Red blood cells are hemoglobin-filled biconcave cells that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and tissues. They are produced in the red bone marrow in a process called erythropoiesis.
During this process, the precursors of erythrocytes derived from stem cells undergo a number of morphological changes, turning into mature erythrocytes.
These mature red blood cells enter the bloodstream, where they survive from 100 to 120 days, so their condition can be used to judge the health of a person over the past 3 months. After 120 days, old red blood cells are recirculated by macrophages of the spleen, liver, bone marrow and lymph nodes (reticuloendothelial system).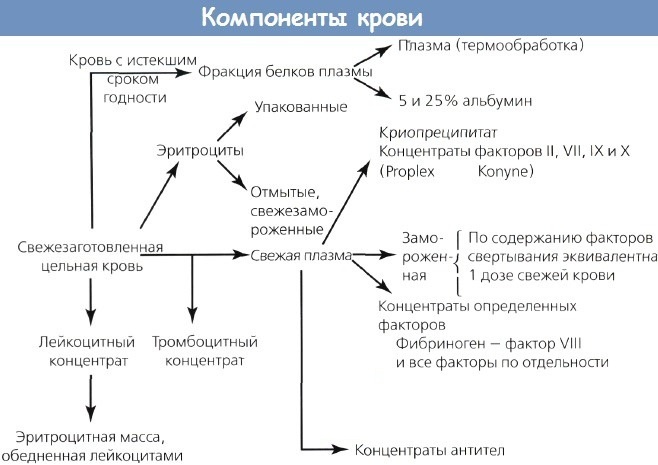
Erythrocytes have a constant diameter of 7-8 microns, an atypical structure. They resemble a donut in shape, which means that their periphery is thicker than the central part. The peculiarity of the structure facilitates gas exchange and transport. Red blood cells do not have a nucleus. They have two main structures - the cytoplasm and the cell membrane that surrounds it.
The cytoplasm is filled with hemoglobin, a protein that reversibly binds and transports oxygen and carbon dioxide. Each globin subunit contains an iron atom associated with a molecule called heme. Iron plays a major role in binding gases, so each hemoglobin can transport up to four molecules of oxygen or carbon dioxide.
Types of red blood cells
Erythrocyte mass is used to restore cells, carriers of oxygen molecules. It acts as the main component of blood, consists of 70-80% of erythrocytes, 20-30% of plasma with an admixture of leukocytes and platelets, hematocrit = 70-80%. In terms of the content of red blood cells, a single dose of erythrocyte mass (270 ± 20 ml) is equivalent to one dose (510 ml) of blood.
Types of erythrocyte-containing components:
| View | Characteristic |
| EM | A concentrate made from whole donated blood. Consists of:
To improve quality, it is allowed to add saline before transfusion. |
| Erythrocyte suspension | A concentrate prepared from whole donor blood, while a significant part of the plasma is removed and replaced with a biochemical solution. |
| Suspension leukoreduced | A red blood cell concentrate obtained from blood in which the donor's white cells have been removed. |
| Suspension with removed leukotrombosch | Concentrated erythrocytes made from whole donor blood with subsequent elimination of the maximum plasma and leukotrombocyte layer. |
| Washed erythrocytes | They are made from the mass of erythrocytes by washing them with sodium chloride. After which they represent an erythrocyte suspension, from which most of the plasma is removed. |
| Erythrocytes thawed and washed | As a result of thawing and washing, part of the extracellular potassium, sodium and glucose is removed from the mixture, and a minimum amount of plasma proteins remains. |

Each type of red blood cell mass contains a certain amount of hemoglobin, red blood cells, and has its own medical purpose.
Physiological properties
After 8-10 days of storage in the mass of erythrocytes, slight destruction (hemolysis) can be detected, which is not a contraindication for clinical use.
The longer the shelf life, the lower the oxygen transport function of erythrocytes. The erythrocyte components contain less whole blood and preservatives. Washed erythrocytes contain trace amounts of plasma protein components, platelets and leukocytes.
Pharmacokinetics
Components containing donor erythrocytes, after blood transfusion, function in the body from several days to several weeks, which is largely determined by the timing of the preparation of erythrocytes, the type of preservative and the conditions of their storage (native, thawed, washed).
In the body, destroyed donor erythrocytes are used by cells of the reticuloendothelial system of parenchymal organs.
Mechanism of action
Erythrocyte mass is the main component of blood. Its volume unit contains more red blood cells than whole blood. It is used in replacement therapy in order to replenish destroyed red blood cells under the influence of structural or enzymatic disorders.
What red blood cells do:
- In the capillaries of the lungs, hemoglobin binds inhaled oxygen, forming oxyhemoglobin. This substance gives arterial red blood cells a bright red color.
- The oxygen-rich red blood cells pass through the arteries until they reach the tissue capillaries.
- In tissue capillaries, oxygen is released from hemoglobin and diffuses into the tissue.
- At the same time, carbon dioxide from tissues binds to hemoglobin, forming deoxyhemoglobin. This substance gives red blood cells and venous blood a purple-blue color.
- Carbon dioxide-rich red blood cells travel through the venous blood to the heart and then to the lungs.
- In the pulmonary capillaries, carbon dioxide is released from hemoglobin in exchange for a new dose of oxygen.
Substitution effect
The substitution effect consists in reimbursing that part of the blood that was lost from the patient. EO, injected into the recipient, restores the properties, blood volume, and its gas transport function. Nutrients introduced with blood are included in a biochemical chain. The term of functioning of red cells in the patient's vascular bed is estimated from 30 days or more.
Hemodynamic effect
EO transfusion has many-sided effects on the cardiovascular system.
There is a revitalization of blood microcirculation:
- arteriovenous fistulas are reduced;
- arterioles and venules expand;
- capillary networks open.
As a result of these actions, the leakage of blood from the arterial system to the venous system is reduced.
Patients who have lost a lot of blood, with traumatic shock, as a result of transfusion, acquire a steady increase in the volume of circulating blood, venous flow to the right side of the heart. Their cardiac activity increases, the volume of blood circulation per minute increases.
On average, in patients, 30 hours after transfusion, lymph returns to the circulatory system, and as a result, an increase in the total volume of blood circulation.
For this reason, sometimes the high osmotic pressure of the injected blood products increases the volume of intravascular fluid, which leads to an overload of the circulatory system. Patients with renal and heart failure are especially sensitive to this factor.
For this reason, after transfusion, sometimes the increase in total circulating blood prevails over the volume of transfused blood.
Immunological effect
Erythrocyte mass is used to enhance the immunological properties of the body. Mature erythrocytes are able to fix immune complexes. They are more saturated with oxygen, which improves tissue nutrition, therefore, the body's ability to resist infections and viruses increases.
Hemostatic effect
With massive bleeding, a person loses a huge number of red blood cells. The main function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen to tissues.
The protein hemoglobin contained in erythrocytes serves as an oxygen carrier, therefore, a large blood loss is associated primarily with the loss of red blood cells and oxygen starvation of tissues. Therapy for blood loss consists not only of plasma transfusion, but also of erythrocyte mass.
Stimulating effect
Blood transfusion causes stress-like actions in the body. Corticosteroids in urine and blood increase, metabolism increases, respiration is stimulated, and gas exchange increases. The transfusion restores natural immunity: granulocytes are activated, and the production of antibodies increases in response to antigens.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the use of EM:
- massive bleeding (more than 40% of the total circulating blood);
- hypocoagulable states;
- thromboembolism of various origins;
- acquired non-hemolytic anemia.
Red blood cell transfusion
Erythrocyte mass is used to replenish the volume of circulating red blood cells and to maintain oxygen transport. It is obtained by separation from blood plasma.
Getting erythromass
Donated blood undergoes various physical and chemical changes in the process of preparation, processing and storage. Erythrocytes are obtained by centrifugation of whole donor blood.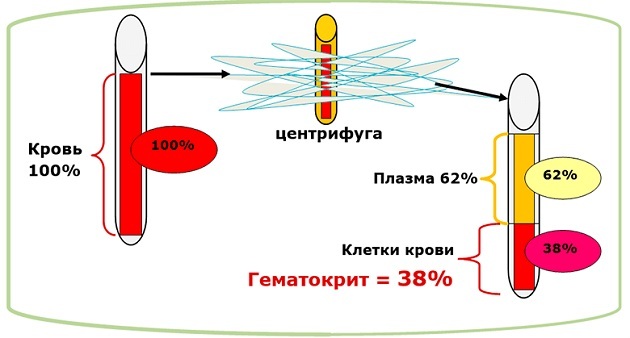
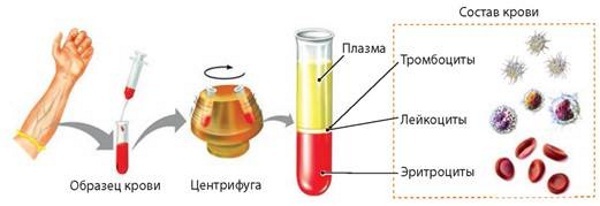
In subsequent processes, their additional processing is carried out:
- adding biochemical weighing solutions;
- Leukoreduction, which removes white cells to reduce the risk of immune complications
- X-ray or gamma radiation to reduce the risk of post-transfusion reactions;
- washing after gamma irradiation of erythrocytes, used to reduce plasma proteins;
- cryopreservation used to store red blood cells of rare phenotypes.
Erythromass transfusion procedure
In order to prevent blood incompatibility, numerous tests are preliminarily carried out:
- biological;
- according to the AVO system;
- on the group belonging of the donor and recipient erythrocytes.
Donor blood transfusion is more often carried out in the premises of the day hospital of the medical clinic. It uses standard disposable transfusion systems with ulnar vein needles. Blood products are administered in intensive care units or in a hospital ward through a central catheter.
The duration of the procedure is from 2 to 4 hours, since the volume of 1 dose of the mass of erythrocytes is 300-350 ml. During the procedure, 3-4 doses of the mass are poured.
The transfusion process is accompanied by a nurse who monitors the state of health after the procedure.
Tolerability and side effects
If the rules for the preparation, processing, storage and adequate use of donor red blood cells are followed, the risk of reactions and complications is minimized.
| Type of reactions and complications | Cause |
| Acute lung injury | Presence of donor anti-leukocyte antibodies in the recipient's blood |
| Shortness of breath due to blood transfusion | Not clarified |
| Allergic reaction (urticaria, anaphylactic shock) | The presence of antibodies to plasma proteins, the presence of primary immunodeficiency to immunoglobulin A in the recipient |
| Decreased blood pressure after transfusion | Vascular reaction due to the release of a peptide that dilates blood vessels (bradykinin) |
| Pyrogenic reaction, accompanied by an increase in body temperature | The transfused blood is infected |
| Acute intravascular hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells) | Incompatibility of donor blood according to the ABO system, fragility of erythrocytes |
| Delayed hemolysis | Destruction of transfused red blood cells supporting antigen within 10-14 days |

Washing red blood cells in an open system increases the risk of bacterial contamination of the recipient's blood. With multiple transfusions, there is a risk of iron overload, exacerbation of intravascular blood coagulation.
Before transfusion, the patient should be prepared, for which vitamin therapy is carried out, erythropoietin and iron preparations are prescribed.
Interaction
A low molecular weight dextran solution in a ratio of 1: 1 or 1: 0.5 reliably maintains the total circulating ability of blood, reduces the adhesion of particles that affect the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
It is not recommended to use glucose solutions and solutions containing calcium ions, as they cause blood to clot and form clots. The use of 8% gelatin as a preservative with citrate, chloride and sodium bicarbonate extends the life of washed red blood cells up to 72 hours.
Cautions
The ready-to-use suspension, thawed and washed, should have a red blood cell volume in the range of 70-80%. Due to the risk of bacterial contamination, the shelf life of washed EO before use can be no more than 24 hours at + 1-6 ° C.
The introduction of an excessive amount of EO can lead to hemoconcentration, which reduces blood coagulation and thereby impairs hemodynamics in general.
Storage conditions and shelf life
Blood and its components are stored at the temperature indicated on the labels of the containers or in the instructions for the preparations. The temperature range for storage in the refrigerator or freezer is also noted on the labels.
On average, the mass is stored for 24-72 hours (depending on the preservative solution) at a temperature of + 4 ° C.
The healthcare professional in charge of storage records the date, time of receipt and delivery of the product. The erythrocyte mass should not be at room temperature for more than 1 hour. This product must be discarded and returned as there is a risk of bacteria development.
The suitability of canned blood and EM is determined with sufficient illumination, since the slightest shaking the product leads to an erroneous conclusion due to the plasma staining pink from movement erythrocytes. The duration of erythrocyte mass transfusion is no more than 2-3 hours.
After the blood transfusion procedure, the tubes with the remnants of the recipient's and donor's hematopoietic products are stored in the refrigerator for no more than 2 days at a temperature of +4 + 8 ° C.
RBC transfusion should be based on the clinical condition of the patient. It should be used only for a specific purpose, if a side process occurs with the disease. in the form of anemia or urgent surgical intervention is necessary, suggesting a large loss blood.
Blood transfusion video
About blood transfusion: