Bleeding (most common and the correct concept of the term) is the outpouring of blood outside the blood vessels or the heart into the environment or a hollow organ. There are several types that are distinguished according to certain characteristics.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Symptoms
- 3 Reasons for the appearance
- 4 Diagnostics
- 5 When to see a doctor
-
6 How to stop treatment
- 6.1 First aid
- 6.2 Medications
- 6.3 Folk methods
- 6.4 Other methods
- 7 Possible complications
- 8 Bleeding Videos
Views
Bleeding, the concept and types of which depend on certain signs, can be divided into types.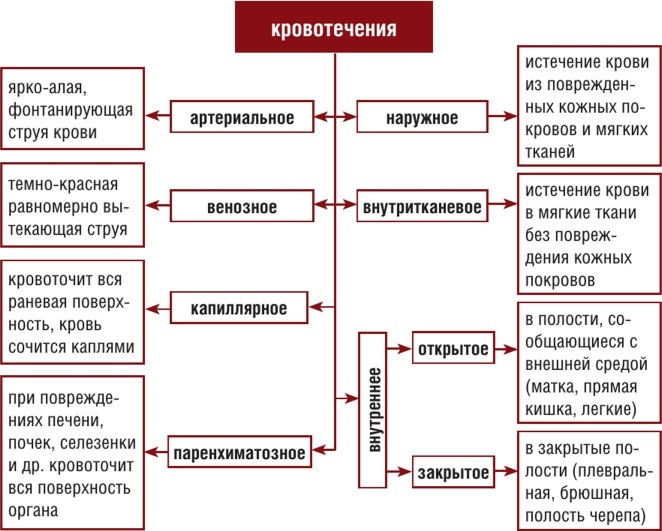
Bleeding classification:
| The sign by which bleeding is classified | Types (types) of bleeding | Brief description of the process, characteristic features |
| The place where blood is poured | Hidden | Latent bleeding is characterized by hemorrhage in parts of the body that are not associated with the environment. Most often, this process takes place in the cavity 12 of the duodenum or stomach. Bleeding can only be determined using laboratory diagnostic methods. |
| Internal | Internal bleeding is characterized by hemorrhage not into the environment (as in an external process), but into the cavity of another organs or gaps between tissues. Hemorrhage can occur in the brain, uterus, stomach. Internal bleeding is very dangerous, since it is impossible to immediately identify the affected organ and carry out medical procedures. | |
| Outdoor | External bleeding is easy to determine by visual examination of the patient. Also, in some cases, you can easily stop the blood. The outpouring takes place into the external environment. | |
| Severity of bleeding | Lung | Light bleeding is characterized by a loss of 10-15% of the total circulating blood volume. Blood loss with such a hemorrhage is no more than 0.5 liters. |
| Average | This type of hemorrhage is characterized by a loss of 0.5 to 1 liter of biological fluid. This blood volume is about 16-20% of the BCC. | |
| Heavy | Loss of more than 1 liter (no more than 1.5 liters) of blood. Also, a severe form of hemorrhage is characterized by a loss of more than 20% of the volume of circulating biological fluid. | |
| Massive | Massive bleeding is characterized by a loss of 30-40% of the BCC. | |
| Deadly | The peculiarity of fatal hemorrhage is the loss of about 2000-2500 ml of biological fluid. | |
| Absolutely deadly | More than 3 liters or a loss of 60% (or more) of the total circulating blood volume characterizes absolute fatal bleeding. | |
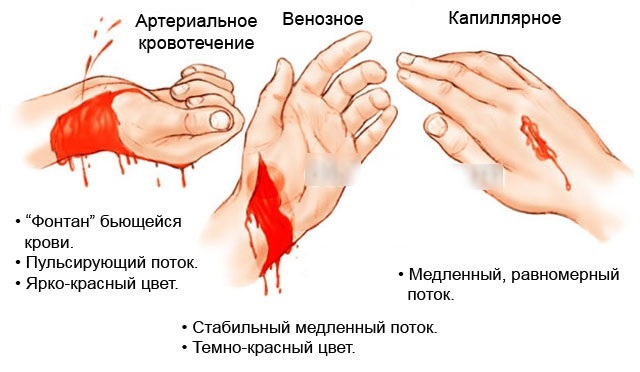
| Damaged vessel type | Venous | Venous bleeding is characterized by continuous flow of biological fluid from the wound (slight pulsation is possible). The process can be deadly, depending on how large the veins are exposed. Venous blood of a darker and more saturated shade. |
| Arterial | The most dangerous type of hemorrhage is arterial. In a short period of time, you can lose a large volume of blood, which will lead to death. The blood that comes out in the process of damage to the arteries is of a scarlet hue. Also, a distinctive feature is the mechanism of blood release - the biological fluid beats with a fountain. Despite the danger of this phenomenon, the hemorrhage can be stopped. There are several ways to stop the blood from such an injury. |
|
| Capillary | The main feature of capillary bleeding is the ability to quickly and easily stop the blood on its own. With capillary bleeding, it is difficult to distinguish bleeding vessels with the naked eye, since they are very small. Capillary fluid shade is a mixture of arterial and venous bleeding. Hemorrhage can only be dangerous for people with bleeding disorders. |
|
| Parenchymal | It is almost impossible to stop such bleeding on your own. Parenchymal hemorrhage is associated with a malfunction of the parenchymal organs or severe damage to the chest or abdominal cavities. The biological fluid flows out over the entire surface of the wound. Blood appears in two shades - arterial and venous. |
|
| Mixed | Mixed hemorrhage is characterized by damage to both arteries and veins, capillaries. You can take the first measures to help the victim yourself. The measures taken to stop the blood depend on the most dangerous types of bleeding. | |
| Time of bleeding | Primary | With primary bleeding, the process occurs immediately after damage to the vascular system. |
| Secondary (or early secondary) | Secondary hemorrhage is characterized by the appearance of biological fluid no more than 3 days after injury. Bleeding occurs as a result of the rejection of blood clots caused by an increase in blood pressure. | |
| Late secondary | Late secondary bleeding may appear several days or weeks after injury. | |
| Origin of the process | Traumatic | Traumatic bleeding is the release of biological fluid as a result of mechanical damage to blood vessels. |
| Pathological | Pathological bleeding is characterized by vascular damage as a result of pathological processes of the cardiovascular system. |
Also, experienced specialists can distinguish several types of bleeding, depending on the technique of first aid. Bleeding, the concept and types of which depend on the place of hemorrhage, into the internal environment is the most dangerous for the body.
There is a separate classification for internal bleeding:
- Gastrointestinal bleeding. One of the most common forms of internal bleeding. This spread is due to numerous diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often, bleeding can occur with an acute ulcer and erosion of the stomach. The most frequent manifestation of bleeding in the cavity of the gastrointestinal tract is vomiting of blood.
- Pulmonary hemorrhage is characterized by coughing up blood. It is also possible that there is an abundant release of body fluid when coughing. Hemorrhage can be the result of tuberculosis, bronchial tumors.
- Bleeding into the abdominal and pleural cavity. This phenomenon can be the result of a closed injury, during which the parenchymal organs are damaged. Such bleeding can be a consequence of minor trauma, which can only be determined by the manifested anemia.
- Intrapleural bleeding. Determine this subtype of hemorrhage by breathing a person. The rib cage may rise unevenly. Noises also appear in the process of gas exchange.
 There is also a separate subspecies - intra-abdominal bleeding. Determine it by finger examination.
There is also a separate subspecies - intra-abdominal bleeding. Determine it by finger examination.
Symptoms
Symptoms of bleeding, like the concept of the term, are associated with the types and types of hemorrhage. Local and general symptoms of this phenomenon are distinguished.
Common symptoms of hemorrhage include:
- tiredness and drowsiness;
- weakness;
- thirst;
- lightening of the skin due to decreased vascular tone (lips turn pale most noticeably);
- anemia;
- dizziness, frequent fainting is possible.
Also, among the main symptoms, one can single out the direct process of leaving the circles from the vascular bed.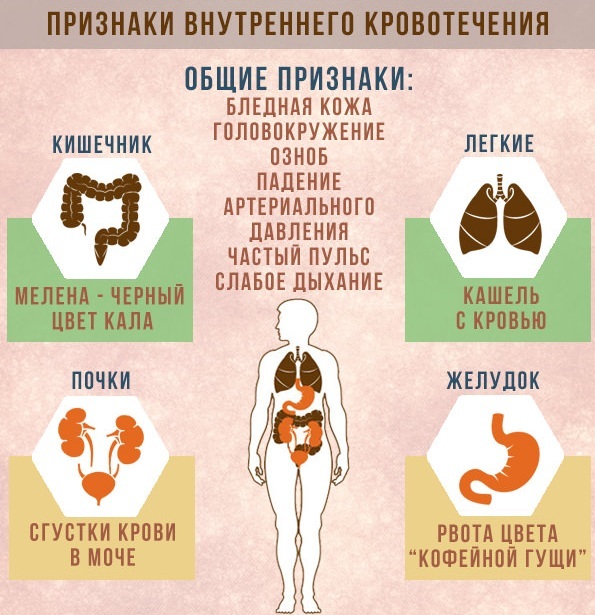
Local symptoms of bleeding include:
- with pleural bleeding, in addition to general symptoms, shortness of breath appears. Also, breathing becomes confused, the sound when inhaling and exhaling is shortened. Weakening of gas exchange is possible;
- the main symptom of bleeding into the region of the skull are symptoms of acute or chronic compression of brain tissue;
- joint bleeding - an uncomplicated and non-lethal process. The joints are small in volume, so there is no acute anemia. With joint bleeding, the general symptoms of hemorrhage appear.
- bleeding in the abdominal cavity - unpleasant and painful processes. Symptoms of this subspecies are associated with irritated organs of the gastrointestinal tract - nausea and vomiting. Muscle tension in the injured area can also be noted.
-
interstitial hematoma. The intensity of the symptoms in hematoma depends on the location and size of the hematoma. Symptoms include swelling in the damaged area, tissue induration, and severe pain. It is also possible to increase the volume of damaged tissue.
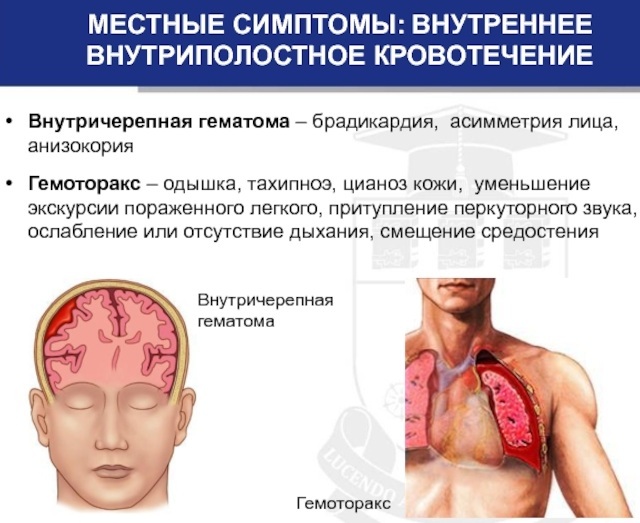
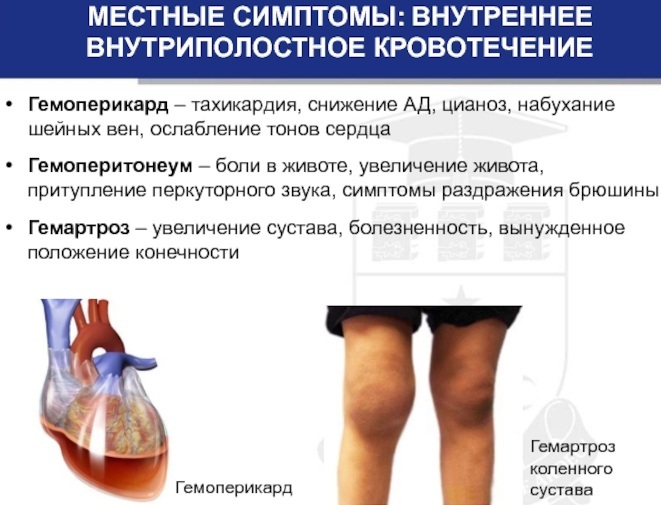
Hematomas can be the cause and starting point for the development of gangrene.
Reasons for the appearance
Bleeding, the concept and types, as well as the reasons for the appearance of which depend on factors affecting the body, - it is the release of biological fluid (blood) through the vascular bed into the environment, or into the body cavity.
The reasons for the appearance of hemorrhage are:
| Type of bleeding | Reason for appearance |
| Outdoor | External bleeding occurs as a result of a violation of the integrity of the skin, veins or arteries. Depending on the affected vessels, several types of bleeding are also distinguished. Blood can spill onto the surface of the body from wounds, ulcers, and skin tumors. |
| Interstitial | The reason for the appearance of interstitial bleeding is bruises or fractures, various types of injuries. Also, an important factor in the development of interstitial hemorrhage can be pathologies of the cardiovascular system associated with vascular permeability and blood coagulability. |
| Intracavitary | Intracavitary bleeding is closely associated with trauma to the parenchymal organ. Also, the disease can develop due to the pathology of the damaged organ. |
| Pulmonary | Pulmonary hemorrhage is the most dangerous, since during the process of hemorrhage, biological fluid can completely fill the lung. If the lungs are damaged, there is a lack of air, breathing problems. Pulmonary hemorrhage can be the result of advanced forms of diseases of the respiratory system. Also, congenital defects and pathologies affect the appearance of hemorrhage. |
| Gastrointestinal | The cause of gastrointestinal hemorrhage is ulcers, colitis, tumors. Also, vomiting of blood can cause foods that are contraindicated in a certain disease.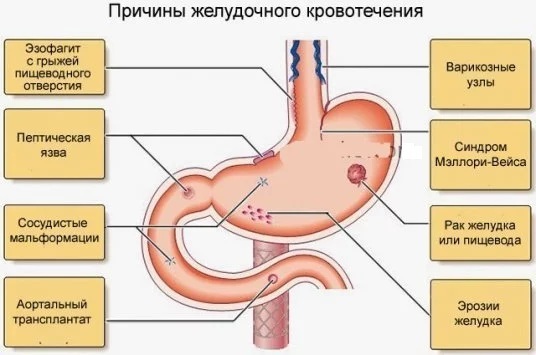
|
| Afibrinogenic | The cause of this hemorrhage is heavy and long-term operations on the abdominal and chest cavity. For a long time, a lot of fibrinogen is expended. |
| Postoperative | Postoperative hemorrhage = secondary. They arise when a thrombus is pushed out. |
They also distinguish the classification of bleeding according to the affected vessel. The cause of such hemorrhage is a direct vascular injury, or a disease of the vascular system.
Diagnostics
It is quite simple to diagnose external bleeding - this requires only a visual examination of the victim. By the nature of the wound and blood, one can easily determine the type of hemorrhage and provide assistance.
Internal bleeding can be diagnosed in the following ways:
- Endoscopy. Allows you to identify pulmonary and gastrointestinal hemorrhage. During the procedure, a tube is inserted into the patient's cavity. An endoscope is used to examine the area to be diagnosed. The comfort of this process depends on the specialist. Endoscopy is a fairly inexpensive procedure. You can find clinics that provide services for 350 rubles.
- Ultrasound procedure. Ultrasound is the most popular and safest way to diagnose a disease. With the help of a special device, the presence of pathology in the painful cavity is determined. The price of an ultrasound scan depends on the area being diagnosed.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging. The procedure is carried out in a separate room using a tomograph. The cost of tomography varies from 1,500 to 8,000 rubles.
- Determination of the number of red blood cells. To determine the number of red blood cells, it is necessary to donate blood for analysis. The price of this analysis is from 200 rubles and above.
Also, bleeding can be diagnosed, and most importantly, its localization can be based on pronounced symptoms. Among such manifestations are vomiting of "coffee grounds", blood impurities in the stool, hemoptysis.
When to see a doctor
Bleeding, the concept and types of which depend on the signs of the phenomenon, can be dangerous and even fatal to the body.
In what cases it is necessary to see a doctor:
- with periodic changes in blood pressure (sharp jumps);
- hemoptysis due to illness or injury;
- vomiting of coffee grounds;
- for a long time, the usual hematoma does not subside, or it is very painful;
- if, with external bleeding, the wound is deep, touches an artery or vein, you should immediately seek help. In addition to blood loss, infection can occur.
- pallor of the skin against the background of anemia.
- swelling in the abdominal area;
- there are blood impurities in the stool.
It is important to monitor your health, as with internal bleeding, there is a high risk of death from blood loss.
How to stop treatment
Severe bleeding cannot be treated at home. In case of profuse hemorrhage, hemorrhage in the natural cavities of the body, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance, before the arrival of which it is only necessary to maintain the patient's condition.
First aid
It is quite simple to provide first aid for external bleeding. It is only important to follow all the “steps” and use sterile means to clean the wound.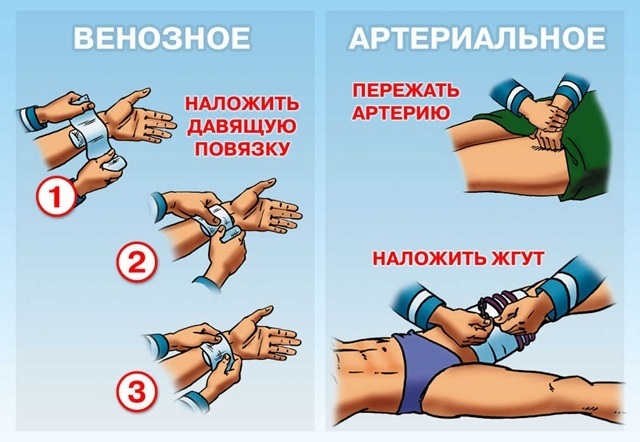
With capillary bleeding, you only need to rinse and treat the wound with skin disinfectants. If the abrasion is small, then a plaster or wound glue is enough. A large wound surface can be bandaged.
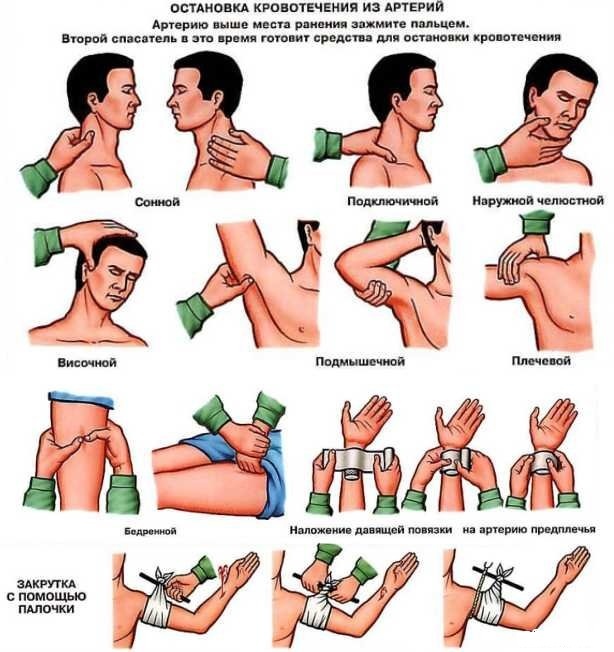
With arterial bleeding, a tourniquet must be applied. A tourniquet should be applied above the wound site to prevent blood flow to the cut site. If there is no special harness, then a belt or other improvised elements can be used. It is also necessary to take into account the time of application of the tourniquet and transfer the information to medical professionals.
For venous bleeding, a pressure bandage should be used. A pressure bandage creates a constant pressure on the vessel, preventing blood from flowing out. To create a pressure bandage, you need gauze / bandage / gauze napkins and gauze bandage. From the gauze, you need to twist a tight roller, which must be applied to the damaged area. It is necessary to tightly fix the roller on the limb with a bandage.
Help with internal bleeding must be provided very carefully so as not to worsen the situation of the victim. At the first sign, it is necessary to immediately deliver the patient to a medical facility.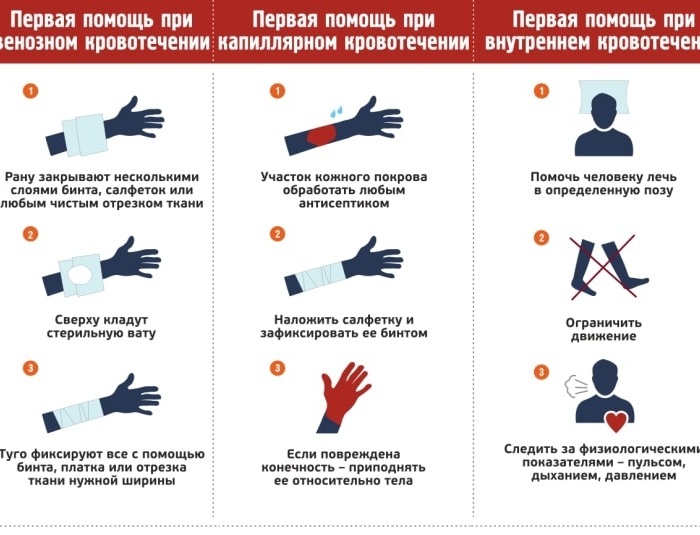
First aid algorithm:
- Provide rest to the victim.
- If there are signs of pulmonary hemorrhage, it is necessary to give the floor a sitting position. In other cases, it must be laid on a flat surface.
- Apply cold to the painful area.
It is forbidden to apply heat to the painful area, give laxatives and heart medications.
Medications
For external bleeding, any disinfectant and aseptic agent can be used to clean the wound site.
With internal bleeding, drugs can be administered to stop the bleeding:
- Aminocaproic acid. Introduced intravenously. The volume of the drug should be calculated based on the patient's age. The maximum dose of the drug is 18 g per m2. It is excreted from the body quickly.
-
Vikasol. The drug is produced in tablets and ampoules. It is also necessary to inject a solution depending on the age of the victim.

Vikasol
If it is close to a medical facility, and the patient's condition is not critical, it is best to stop using medications to avoid side effects.
Folk methods
It is impossible to use traditional medicine as the only and main method of treatment - this can lead to complications and death. Alternative methods can relieve symptoms and become an auxiliary method of treating hemorrhage.
With the help of folk methods, uterine bleeding can be stopped. To do this, boil the zest of 7 oranges in 1.5 liters of water, so that 0.5 liters of pure broth remains as a result. You need to use such a decoction 20 ml 3 times a day.
To stop pulmonary, gastric and intestinal bleeding, it is recommended to use herbal infusions. The most effective are the plants "cat's paw" and "medicinal letter". You need to use infusions every hour until the hemorrhage stops.
Other methods
In addition to the classical methods of stopping blood, other methods can be used.
The use of such methods is relevant in field, stressful situations: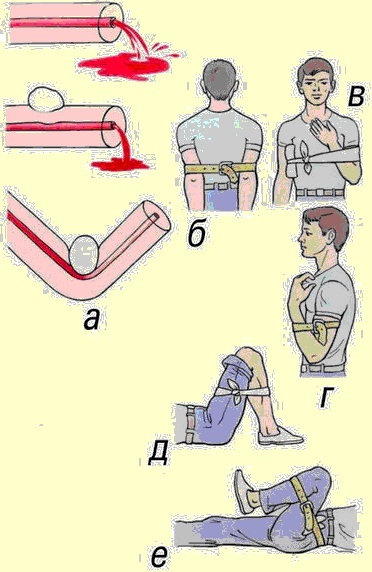
- Tamponade of the wound. Used for gunshot or stab wounds. To do this, you need to place the dressing on the tip of the palm tree and insert it into the hole. Thus, it is necessary to fill the wound with a dressing material, changing hands, without removing the finger from the hole. The tamponade must be fixed with a bandage.
- Finger pressure on a bleeding vessel. It is used when it is impossible to apply a tourniquet or pressure bandage. You need to press on the wound tightly and hard to stop the bleeding.
- Limb flexion in the joint provides obstructed blood flow to the damaged vessel. Works in cases where the wound area is at the end of the limb. The limb must be fixed in a bent position. You can also simply fix the limb in an elevated state.
To correctly apply the method of stopping bleeding, it is necessary to correctly determine the localization of the wound and the type of hemorrhage.
Possible complications
In case of untimely, incorrect or “home” treatment, as well as complete In the absence of medical attention, the following complications may appear:
- Acute anemia. Anemia develops against the background of loss of more than 1 liter of biological fluid.
- Air embolism. It appears when large trunk cells are injured, due to which air can enter the heart.
- Compression of organs and tissues. Complication in most cases is fatal and requires surgical intervention.
At the first sign of bleeding, seek medical attention.
The concept of bleeding directly depends on the type of phenomenon. Bleeding can be internal and external, different in severity, as well as localization of the affected vessel.
Bleeding Videos
Types of bleeding:



