Gonadotropic hormones are vital because they are responsible for the functioning of the sex glands in the human body. In case of failures in the development of this group hormones can develop sexual dysfunction.
Record content:
- 1 What are gonadotropic hormones?
-
2 Secretion of gonadotropic hormones
- 2.1 Regulation of secretion
- 2.2 Mechanism of action
-
3 Follicle stimulating hormone
- 3.1 The role of FSH in women
- 3.2 The role of FSH in the male body
-
4 Luteinizing hormone
- 4.1 LH functions in women
- 4.2 LH functions in men
- 5 Chorionic gonadotropin
- 6 Physiological effects of gonadotropic hormones
- 7 Norms of gonadotropic hormones in women and men
-
8 How is the level of gonadotropic hormones determined?
- 8.1 Reasons for downgrading
- 8.2 Reasons for the increase
-
9 Diagnostic use of gonadotropic hormones
- 9.1 Pregnancy test
- 9.2 Determining the timing of ovulation
- 9.3 Diagnosis of reproductive disorders
-
10 Therapeutic use of gonadotropic hormones
- 10.1 Female infertility
- 10.2 Male infertility
- 10.3 Cryptorchidism
- 11 Video about gonadotropic hormones
What are gonadotropic hormones?
Gonadotropic hormones are a group of hormones produced by the anterior pituitary gland and the placenta. Substances are necessary for the correct and complete development of the reproductive system and the whole organism as a whole.
Secretion of gonadotropic hormones
Gonadotropic hormones are actively involved in the synthesis and production of other hormones. In this case, these substances are produced and regulated by the hypothalamic, pituitary and gonadal systems.
Regulation of secretion
Regulation of the secretion of LH and FSH is carried out by the central nervous system through the hypothalamus according to the feedback principle. The increased content of sex hormones in the body suppresses the production of these substances.
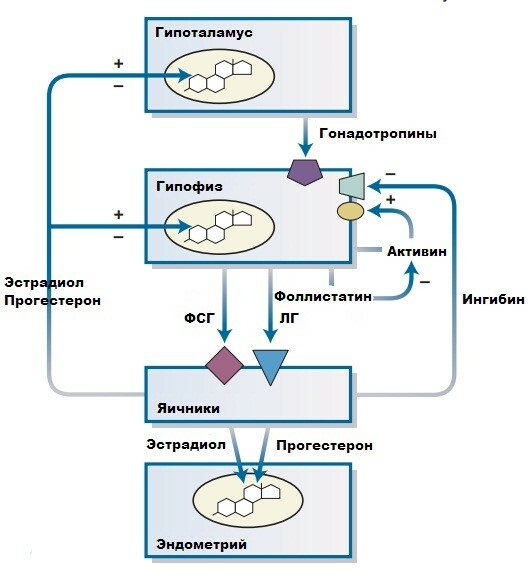
Castration or other atrophic changes in the ovaries (during menopause) cause increased production of LH and FSH. In men, in the absence of sperm production, FSH levels increase. With normal or rapid spermatogenesis, FSH production decreases.
Mechanism of action
Luteinizing and chorionic hormone interacts with the LH receptor. Follicle-stimulating hormone binds to its receptor.
Due to the interaction with G-proteins, these receptors are able to recognize substances. Proteins start the processes associated with the action of adenylate cyclase. In this case, there is an increase in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP).
The high ligand content leads to the activation of protein kinase C and promotes an increase in blood calcium. Most of the reactions can be reproduced using analogous cAMP substances. However, the effect of various protein kinases has not yet been studied.
Follicle stimulating hormone
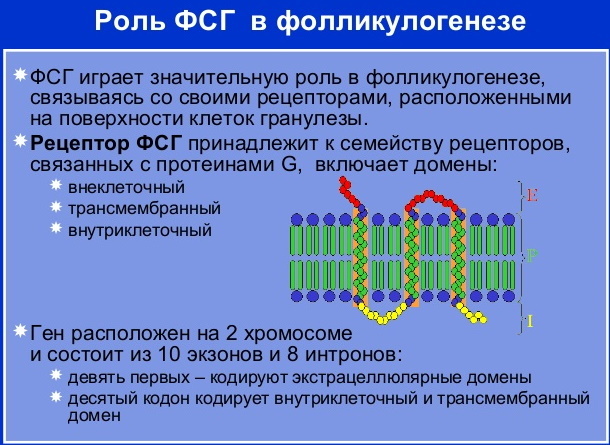
Gonadotropic hormones are a series of hormones produced by the placenta and the anterior pituitary gland. This subclass also includes follicle-stimulating hormone. This substance is synthesized by basophilic cells of the pituitary gland. He is responsible for the functionality of the sex glands in women and men. The production of FSH is regulated by a hormone produced by the hypothalamus.
The role of FSH in women
In the female body, the hormone is responsible for the work of the ovaries. Moreover, its level directly depends on the phase of menstruation. Insufficient or increased production of FSH leads to problems associated with conception, ovulation, or fertilization.
Role of the hormone:
- development and maturation of the egg in the ovary;
- synthesis of estradiol;
- conversion of the male sex hormone (testosterone) to estradiol;
- starting the ovulatory process.
 Thanks to this action, changes occur in the female body that lead to an adequate production of progesterone.
Thanks to this action, changes occur in the female body that lead to an adequate production of progesterone.
The role of FSH in the male body
In a man's body, this hormone is responsible for the normal functioning of the seminiferous tubules and leads to the development of sperm.
Role of FSH:
- synthesis of testosterone;
- transportation of the male sex hormone to the epididymis;
- responsible for the production of androgen binding protein;
- improves regeneration and protects cells from negative effects.
Testosterone is responsible for the level of FSH in the male body.
Luteinizing hormone
Lutropin belongs to the group of peptide hormones and is responsible for the normal functioning of the entire reproductive system, both in women and in men. The effect of this hormone occurs when interacting with FSH.
LH functions in women
The hormone LH is responsible for the normal menstrual cycle. An increase in the level is observed during ovulation and continues for 2 days.
Functions:
- synthesis of estradiol;
- leads to ovulation (with close interaction with FSH);
- promotes the transformation of the follicle into the corpus luteum;
- responsible for the formation of progesterone produced by the corpus luteum;
- participates in the synthesis of androgens.
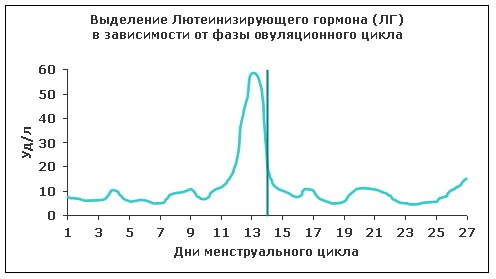
Any abnormalities in the LH level lead to disturbances in the functioning of the reproductive system.
LH functions in men
This hormone has a direct effect on Leydig cells and is responsible for the production of testosterone. LH has a stimulating effect on the endocrine capacity of the testes.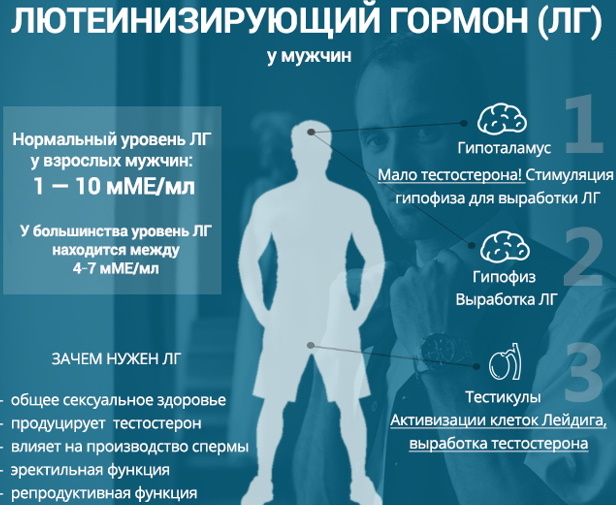
Moreover, its level in the blood directly depends on the concentration of testosterone - the higher the LH content, the more the male sex hormone is produced. Luteinizing hormone is involved in regulating the synthesis of luliberin.
Chorionic gonadotropin
Gonadotropic hormones are several main hormones, the production and action of which are vital not only for the person himself, but also for the normal intrauterine development of the fetus. This substance includes hCG.
Chorionic gonadotropin is a specific hormone produced during pregnancy by the membrane of the fetus. Its level begins to increase gradually, starting from the first day of conception. The maximum concentration of hCG occurs by 11-12 weeks of pregnancy and lasts until the birth itself.
Due to its structural similarity with LH and FSH, this hormone affects the corpus luteum, allowing it to persist in pregnant women throughout the 1st trimester. After that, this function is performed by the placenta.
Functions:
- stimulation of the ovaries, due to which the production of weak androgens and estrogen is activated;
- starts processes that prevent the rejection of the fetus, as a foreign element of the body;
- ensures the normal functioning of the placenta.
 The hormone serves as tumor markers or pregnancy development.
The hormone serves as tumor markers or pregnancy development.
Physiological effects of gonadotropic hormones
In men, these substances act mainly on the production of testosterone, increasing its content in the body. Testosterone, in turn, is responsible for normal sexual development, sex drive, and the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
In women, the effect of gonadotropic hormones on the body is more complex. These substances are responsible for the development and maturation of follicles, which is necessary for the conception of a child. If the production of HG is impaired, the reproductive function is impaired and leads to infertility.
Norms of gonadotropic hormones in women and men
There are certain norms for the content of gonadotropins in the female and male body.
| Gonadotropic hormone | Norm (for women) | Norm (for men) |
| Total testosterone | – | 6.68-30.5 nmol / l |
| Dihydrotestosterone | – | 250-990 pg / ml |
| SHGS | From 17 to 50 years old - 2.48-10.45 μg / ml Over 50 years old - 1.34-6.55 mcg / ml |
From 17 to 65 years old - 1.38-4.60 mcg / ml |
| DHEA sulfate | 1.8-10.3 μg / ml | 7.6-17.4 μg / ml |
| FSH | 1.01-6.4 μg / l | 1.37-13.58 μg / l |
| LH | 0.9-9.93 μg / L | 1.14-8.75 μg / l |
| Prolactin | 40-530 mcg / l | 53-360 μg / l |
| Progesterone | 1.8-7.0 μg / l | 1.5-6.4 μg / l |
| Estradiol | 91-861 μg / l | 40-161 mcg / l |
Any deviations from the norm indicate the presence of internal pathologies.
How is the level of gonadotropic hormones determined?
The level of gonadotropic hormones is determined using special tests (immunochemiluminescent analysis). To do this, the patient is taken blood from a vein, after which the material is sent to the laboratory for further study.
Reasons for downgrading
Gonadotropic hormones can drop in the blood for a variety of different reasons. This process can be associated with internal diseases or negative effects of external factors.
The most common hormone deficiency disorder is infertility.
Causes:
- disorders in the luteal phase;
- tobacco smoking;
- the formation of cysts in the ovarian area;
- overweight;
- lack of a menstrual cycle;
- Simmonds syndrome;
- drug abuse;
- underdevelopment (dwarfism);
- heart attack or necrotic lesion of the pituitary gland caused by childbirth;
- Denny-Morphan disease;
- an increase in prolactin in the body;
- functional disorders in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus;
- pregnancy;
- stop menstruation.
Heredity can also play an important role in the development of pathology.
Reasons for the increase
Reasons for increasing the hormone:
- frequent stressful situations;

- excessive physical activity;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases, especially chronic forms;
- diseases transferred in childhood;
- toxic damage to the body, which has a negative effect on the brain;
- neoplasms in the pituitary gland;
- severe pathologies occurring in the pituitary gland or thyroid gland;
- excessive and frequent starvation;
- excessive food intake;
- traumatic brain injury;
- Skien's disease;
- drugs that have a negative effect on the central nervous system.
In rare cases, the concentration of hormones can be reduced in the presence of congenital pathologies that are hereditary.
Diagnostic use of gonadotropic hormones
Gonadotropic hormones are a subclass of tropic hormones that are responsible for regulating the functioning of the gonads. These substances can be widely used in medical practice, including some types of research.
Pregnancy test
This type of research is used to determine the timing of pregnancy. The technique is informative and highly effective. In only 2% of cases, the diagnosis can give false results.
For research, venous blood is taken, after which it is sent to the laboratory to study its properties using enzyme immunoassay. HCG is used as a marker.
Types of analyzes:
- General. This type of research is used in early pregnancy. In the 2nd trimester, the diagnosis is carried out as part of the screening.
- Free b-hCG. This type of analysis is carried out in order to determine the chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. Indications for screening are hereditary diseases, Down syndrome and radiation injury.
Deciphering the results obtained should be dealt with by the attending physician.
Determining the timing of ovulation
The study is aimed at determining the concentration of luteinizing hormone. The formation of this substance directly depends on the ovulation cycle.
The analysis for the content of LH is carried out daily, starting from the 11th day of the cycle, in cases of planning pregnancy, as well as when planning the time of sexual intercourse.
Normal ovulation rates range from 10.5 to 77 mIU / ml. At the same time, the maximum LH content in the blood before ovulation is in the range from 12 to 24 hours. Ovulation itself begins 36 hours after the release of the hormone into the blood.
By the quantitative content of the hormone in the urine, you can determine the time of ovulation.
Diagnosis of reproductive disorders
In reproductive disorders, studies of hormones such as prolactin, testosterone, LH and FSH are prescribed.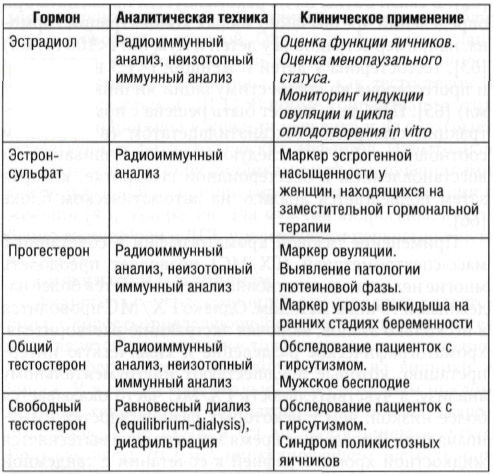
In most cases, men are assigned a general testosterone test. Indications for diagnosis are sexual dysfunctions, hypogonadis, and clinical manifestations of pathospermia.
The determination of the content of FSH is carried out with signs of varicocele and hypogonadism. With erectile dysfunction in men, it is recommended to pass an analysis for the quantitative content of prolactin.
With delayed sexual development, a test with hCG is prescribed. A low testosterone response to the hormone may indicate a functional disorder of the Leydig cells. Normal indicators indicate damage to the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
For reproductive disorders in women, a test is performed for the content of progesterone and estrogen. On the 3rd day of menstruation, a diagnosis is carried out, which determines the quantitative content of FSH. The method allows you to determine the level of fertility. With a low concentration of the hormone, the chances of artificial insemination are extremely low or absent.
Diagnostic methods consist in the study of venous blood and the introduction of artificial gonadotropic hormones.
Therapeutic use of gonadotropic hormones
Gonadotropic hormones are specific substances in the human body that can be used as an adjuvant therapy for various disorders associated with their production and synthesis.
Female infertility
The main indication for the appointment of hCG in the treatment of female infertility is chronic anovulation resulting from the secondary development of testicular failure.
In chronic forms of anovulation, in the overwhelming majority, the use of FSH leads to positive results. Treatment with the substance is carried out in the first 6-7 days of menstruation. In this case, the daily dosage is 75 IU. During the entire period of therapy, it is necessary to undergo systematic studies (ultrasound), since the risks of developing ovarian hyperstimulation are high.
The use of FSH allows the follicles to mature. To complete the process, hCG is prescribed in the supplement, after which an artificial insemination procedure is performed.
Possible side reactions:
- violations of water and electrolyte balance;
- a decrease in the volume of circulating blood;
- the formation of intra-abdominal bleeding;
- various forms of thromboembolism;
- functional disorders of the liver;
- respiratory distress syndrome in adults.
With the development of side effects or the risks of developing multiple pregnancies during therapy, chorionic gonadotropin is not prescribed. Treatment in this case is carried out only with the use of FSH.
Male infertility
In case of male infertility, the use of gonadotropic hormones is advisable only if there is a lack of them. At the beginning of treatment, androgens are used, after which HG is prescribed to increase fertility.
The dosage of CG is from 1000 to 5000 IU intramuscularly 3 times a week. In case of normal reactions, they switch to a different dosing regimen: 2000 IU 2 times a week. Menotropin, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormone are prescribed as an additional drug.
The duration of treatment can vary from six months to 2 years. Chorionic gonadotropin is used as maintenance therapy.
Among the side effects, the most common is gynecomastia, which is believed to be formed against the background of a sharp increase in estrogen.
Cryptorchidism
This disease is undescended testicles. In this case, spermatogenesis is impaired and, as a result, the risks of neoplasms in the testicular area increase significantly.
In the absence of anatomical defects and anomalies, the pathology can be treated with chorionic gonadotropin.
Dosage: 500 IU / m2 intramuscularly. The hormone is administered every other day.
In cases of lack of effect, surgical intervention (orchipexia) is prescribed.
Treatment of diseases with gonadotropic hormones is carried out only under the strict supervision of a specialist, since adverse reactions are likely to develop. At the same time, systematic studies are required to determine the quantitative content of GH in the patient's blood.
Video about gonadotropic hormones
Tropic hormones of the pituitary gland:



