Four-headed the thigh muscle is located in the outer part of the thigh, from the photo of which you can accurately determine its location in the leg, and is included in the thigh muscle group.
This muscle will perform flexion and extension functions, which allows it to participate in the movements of the knee and hip joint. Any disturbance in the work of the quadriceps muscle of the thigh causes discomfort, affects the work of the entire muscle group and the ability to walk.
Record content:
- 1 Characteristic
- 2 Functions and properties
- 3 Anatomy and structure
-
4 Possible diseases and pathologies
-
4.1 Stretching
- 4.1.1 Classification
- 4.1.2 Symptoms and Signs
- 4.1.3 Causes
-
4.1.4 Treatment methods
- 4.1.4.1 Rest
- 4.1.4.2 Cold compress
- 4.1.4.3 Fixation bandage
- 4.1.4.4 Medications
-
4.2 Inflammation
- 4.2.1 Classification
- 4.2.2 Symptoms and Signs
- 4.2.3 Causes
-
4.2.4 Treatment methods
- 4.2.4.1 Rest
- 4.2.4.2 Taking anti-inflammatory drugs
- 4.2.4.3 The use of pain medications
- 4.2.4.4 Skin treatment
-
4.3 The gap
- 4.3.1 Classification
- 4.3.2 Symptoms and Signs
- 4.3.3 Causes
- 4.3.4 Treatment methods
-
4.1 Stretching
- 5 Thigh Muscles Videos
Characteristic
The quadriceps muscle of the thigh, the photo of which can be correlated with its location on the body, is called musculus quadriceps femoris. This muscle is part of the thigh muscle group and is located on the front of it, partially occupying the lateral surface of the upper leg. This muscle is the main flexor muscle of the knee and hip joint.
The muscle, which is large in size on one side, is attached to the patella in the tibial region, and on the other side, at the base of the pelvis from different sides. The muscle begins at the top in the form of 4 independent plexuses of muscle tissue or 4 different muscles, which are combined into a single dense plexus and a rigid tendon on the knee.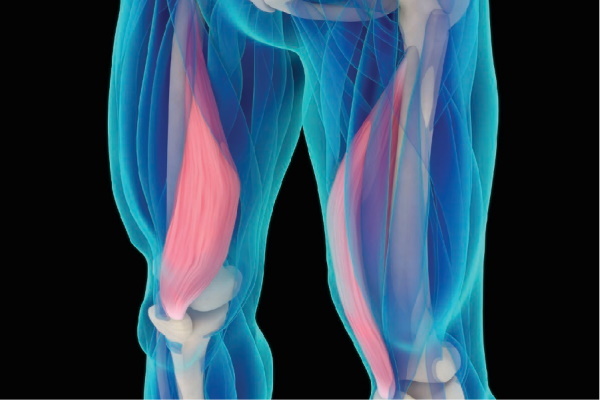
This muscle is considered one of the largest and most powerful muscles in the body. Most of the load during movement falls on it, especially when playing sports. She also participates in fixing the body and helps to stand upright.
The quadriceps femoris is considered one of the longest in the body and, due to its complex structure and location, is most often injured. In the absence of treatment and prolonged immobility, it can gradually atrophy.
Functions and properties
The quadriceps muscle of the thigh, a photo and description of which makes it possible to assess the scale of the occupied area, completely covers the front and partially the lateral part of the thigh. It has 4 main thin muscular processes on top, which occupy different positions in the upper thigh.
Closer to the bottom, muscle fibers are connected to form a single large muscle and tendon, which provide movement to the knee joint. Due to its dense structure, the tendon of this muscle completely covers the patella and blocks it from possible friction and injury.
The quadriceps femoris has several main functions and is responsible for:
- extension of the lower leg in any position of the body, including with weight and in an upright position;
- takes part in hip flexion;
- helps maintain a static body position;
- complements other muscles when performing movements.
Anatomy and structure
The quadriceps muscle of the thigh, which can be found on the net in a schematic image and in the form of a photo, has a complex structure.
In the upper part, it combines 4 independent muscles, namely:
- lateral broad muscle of the thigh;
This muscle is located in the inner thigh and is attached between the base of the vastus rectus muscle and the muscle that tenses the fascia lata. The same muscles cover it from the front and from the top. The basis for the attachment of this muscle is considered to be the rough line of the thigh of the lateral lip and the greater trochanter.
The muscle has a structure of fibers located vertically with a slight slope. From a thin formation, muscle tissue is transformed into a dense and wide plexus and forms the inner supporting part of the kneecap, performing a partially supporting function.
- the intermediate broad muscle of the thigh;
This muscle sits under the rectus femoris muscle to provide support. This muscle is the weakest and shortest among the other heads. It originates on the outer surface of the thigh bone. This muscle also has a vertical oblique structure inside and passes into a large tendon at the knee.
- vastus medialis muscle;
The muscle is located inside the front of the thigh, mostly in the lower region of the thigh. The muscle begins with a tendon on the medial lip of the rough line on the femur, gradually dropping down.
Closer downward, the muscle becomes more and more compacted and passes into the dense tendon of the rectus femoris, connecting to the patellar ligament. Internally, the muscle has an oblique structure with a downward and forward bending, providing complex knee movement.
- Straight.
The longest part of the quadriceps femoris is the rectus femoris. It has 2 dense attachment heads: straight and curved. This muscle is located right in the middle of the thigh and occupies its entire outer part. At the base of the rectus femoris muscle is a large tendon, which is firmly attached to the anterior spine, as well as the supracranial groove of the ilium.
On the outside, the muscle is covered by a muscle that exerts tension on the main fascia of the thigh. The rectus femoris is placed vertically and goes down into the dense tendon of the quadriceps femoris. Such a complex structure of the quadriceps femoris muscle provides active movement and protection of the bone from friction.
The quadriceps muscle of the thigh, the photo of which must be compared with the skeletal system, is supplied with blood and nutrients through the femoral artery, which runs next to the muscle and penetrates it capillaries.

The femoral nerve provides the muscle with nerve endings, thanks to which its well-coordinated work is supported. The main antagonist of the quadriceps femoris muscle is the biceps femoris and semitendinosus.
Possible diseases and pathologies
The quadriceps muscle of the thigh, a photo of which is taken in different projections for the convenience of perceiving information, has a unique structure and is mirrored in the other limb. This muscle completely occupies the entire front and, in a smaller part, the lateral part of the thigh. At the top, the muscle has 4 main heads, which are fixed on different parts of the thigh.
Dense and thin muscle fibers gradually intertwine into a rigid tendon that provides movement to the knee joint. Such a complex structure and location makes this muscle the strongest and one of the most vulnerable. With increased loads and constant sports, this muscle suffers most often.
In most cases, she is injured due to:
- stretching;
- inflammation;
- break.
Stretching
Stretching is an overstrain of muscle tissue, which abruptly changes its position and shape. Due to the overload of muscle fibers, their density and functionality are significantly reduced. There is a deformation of soft tissues with various changes in location. This phenomenon can appear during a physical reboot or after a bruise.
Classification
Stretching muscle tissue always has 2 main stages of development:
- the initial stage of the disease includes damage to muscle tissue with the appearance of sharp pain and redness of the skin;
- the acute stage of the development of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of deformities on the surface of the thigh. The tissues gradually swell, bruising and dull pain appear in a calm position.
Depending on the degree of damage, stretching is divided into:
- A mild form of damage, which is characterized by the presence of pain syndrome without additional tissue edema. With such damage, the range of motion can be maintained.

- The middle form is a more severe type of injury, in which, in addition to pain, swelling and cyanosis appear in the thigh. Leg movements become stiff and painful.
- Severe stretching is associated with partial rupture of muscle fibers. In this case, the soft tissue around the injury is deformed. Hematomas and redness appear on the skin. Knee and hip movements are reduced to a minimum.
Symptoms and Signs
Immediately after injury in the form of a sprain in the hip, sharp pain occurs, which intensifies with movement. Pain syndrome may or may not be accompanied by additional symptoms.
The main symptoms of biceps muscle strain are:
- hip pain;
- redness and then blue discoloration of the skin at the site of injury;
- swelling and swelling of soft tissues;
- reduction in the amplitude of limb mobility;
- the appearance of a "click" in the injured muscle during movement.
In this state, a person cannot fully use the capabilities of a limb, often loses the ability to rely on it. When walking, there is a sharp severe pain with any movement as a result of compression of soft tissues.
Causes
Injury to the quadriceps femoris muscle can occur for various reasons.
These include:
- increased physical activity in the absence of the necessary stretching of muscle tissue;
- lifting weights;
- a sharp change in body position;
- prolonged immobility (more than 1 month);
- injuries (blows, bruises, falls).
Treatment methods
Stretching of the quadriceps femoris muscle is treated comprehensively by:
Rest
Immediately after injury, it is important to provide maximum rest to the muscles of the thigh of the injured limb. Any movement after injury can cause not only pain, but also increase the recovery period due to displacement and inflammation of muscle fibers.
Cold compress
The cold helps soothe damaged tissues.  It relieves swelling and redness, and also helps to restore the damaged area. The hot water bottle with ice is wrapped in a towel to limit direct contact with the cold and applied to the injury site for 20 minutes. every 2-3 hours. in the first days after damage.
It relieves swelling and redness, and also helps to restore the damaged area. The hot water bottle with ice is wrapped in a towel to limit direct contact with the cold and applied to the injury site for 20 minutes. every 2-3 hours. in the first days after damage.
Fixation bandage
Recovery is facilitated by the most tight fixation of the injury site, which supports the muscles and prevents them from overstraining. For fixation, in this case, an elastic bandage or a special orthopedic bandage is used, which is applied to the thigh and tightly fixed. It is important to tie the bandage as tightly as possible, but at the same time not to squeeze the soft tissues.
Medications
Drug therapy includes:
- taking pain relievers (nise, ketarol), which help to quickly remove pain in the thigh muscle, and also have anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, diclofenac), which also remove puffiness and promote tissue repair;
- treatment with ointments (heparin ointment, declofinac gel), which help restore blood microcirculation and heal sprains.
Inflammation
Inflammation is muscle tissue deformation, enlargement, and swelling. Inside the muscle, the process of blood supply is disrupted, redness of the adjacent skin of the thigh may occur.
Inflammation of the quadriceps femoris muscle can be triggered by an injury or be the result of another disease. The inflammatory process can appear in a part of the muscle or completely disable it, causing a lot of discomfort.
Classification
Inflammation in a muscle can be classified into:
- tendinitis, or inflammation of muscle tissue;
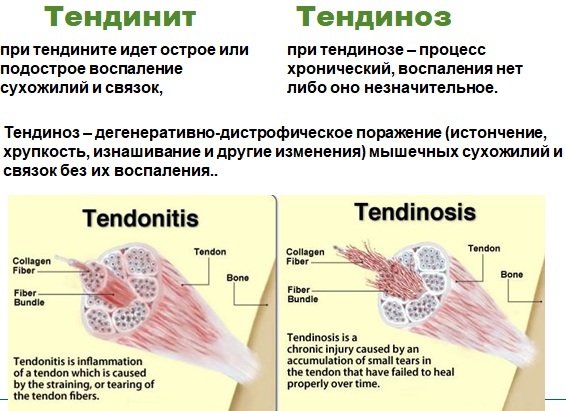
Tendinosis and tendon tendonitis - myositis (inflammation of the cartilage tissue).
Tendinitis and myositis have the same developmental stages:
- The initial stage of inflammation takes up to 1 day, during which there is an increase and swelling of certain areas of the muscle. Pain may be completely absent and limb mobility remains.
- At the acute stage of the development of the disease, muscle tissue is largely damaged and swollen. On the outside of the skin, redness and swelling appear at the site of injury. Pain syndrome develops, which can increase during movement.
Symptoms and Signs
The main signs of muscle inflammation include:
- dull pain, which can increase significantly during movement or pressure;
- swelling of soft tissues;
- redness of the skin at the site of injury;
- in rare cases, an increase in body temperature.
Causes
Inflammatory processes in the quadriceps muscle of the thigh have a complex developmental process, which can be triggered by a number of reasons:
- trauma (bruise, strong blow, or fall);
- a transferred infectious disease, when the infection enters the muscle tissue along with the blood and can gradually spread to neighboring tissues;
- long-term stay without movement (fracture);
- an allergic reaction to drugs, food;
- inflammatory processes in the bone and diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- a sharp drop in immunity quickly reduces the protective functions of the body. Such a weakening can provoke the onset of the inflammatory process;
- increased physical activity (sports, weight lifting and physical strain).
Treatment methods
Myositis and tendinitis have similar treatments, which include:
Rest
Ensuring that the muscular load on the thighs is reduced and that they are optimally resting helps accelerate the healing of inflamed tissues. This is especially recommended for inflammation in the quadriceps muscle of the thigh, which has developed after injury.
Taking anti-inflammatory drugs
To relieve the inflammatory process from damaged tissues, ibuprofen or diclofenac is prescribed.  The drugs help restore tissue to normal and promote muscle healing. However, for active exposure, it is recommended to take them in courses.
The drugs help restore tissue to normal and promote muscle healing. However, for active exposure, it is recommended to take them in courses.
The use of pain medications
Pain relievers (ketarol, nurofen, analgin) help to remove the painful effect during the healing period, which can last for a long time. Pain may be intermittent, so pain relievers are prescribed as needed.
Skin treatment
Local treatment of the skin with special preparations (fastum gel, diclofenac, valtaren emulgel) helps relieve swelling and inflammation, as well as anesthetize the affected skin area. Systematic skin treatment helps to stop tissue microcirculation and improve muscle condition.
The gap
The rupture of the quadriceps femoris muscle due to its density and location is in most cases partial. In the event of a rupture, muscle fibers are disconnected at the site of injury with disruption of muscle function completely or partly, forming an area with impaired blood circulation, supply of nutrients and attachment of nerve endings.
Classification
The rupture of the quadriceps muscle, depending on the shape and type of damage, can be:
- Internal, in which the deep layers of muscle tissue are damaged. Such damage has a pronounced symptomatic manifestation and a long recovery period.
- External rupture of ligaments occurs with a superficial loss of the integrity of muscle tissue, including in the presence of damage to the skin. Most often, such damage occurs as a result of trauma and is accompanied by a violation of blood microcirculation.
Symptoms and Signs
Muscle tissue rupture is manifested by:
- severe pain syndrome;
- loss of mobility of the knee joint and part of the hip;
- swelling at the site of injury;
- the appearance of a hematoma and severe redness at the site of tissue rupture.
Causes
The reasons for the appearance of a muscle rupture can be:
- injuries resulting from impact, fall;
- a sharp stretching of the muscle;
- increased physical activity or weight lifting.
Treatment methods
A ruptured quadriceps femoris muscle is a complex disease that requires urgent and competent treatment, including:
- ensuring complete immobility of the limb and thigh with the imposition of a plaster cast if necessary;
- surgical intervention, which is carried out in case of large damage to muscle fibers. In this case, the muscle tissue is connected manually. The operation is time consuming and is performed under local anesthesia.
- physiotherapy, which include magnetotherapy and electrophoresis with novocaine. Such procedures are prescribed in a complex of 10 and several courses in a row.
The quadriceps muscle of the thigh performs a limited range of important functions in movement, therefore, any damage to it incapacitates the entire musculoskeletal system. Possible causes of the disease can be determined by photos on the network and descriptions, but only a specialist can prescribe competent treatment and the necessary examination.
Ignoring hip pain when moving can cause complications. Only correct diagnosis, rest and a course of therapeutic measures will allow you to quickly restore the condition of the thigh muscles and make it possible to move freely.
Thigh Muscles Videos
Thigh muscles. Femoral canal: