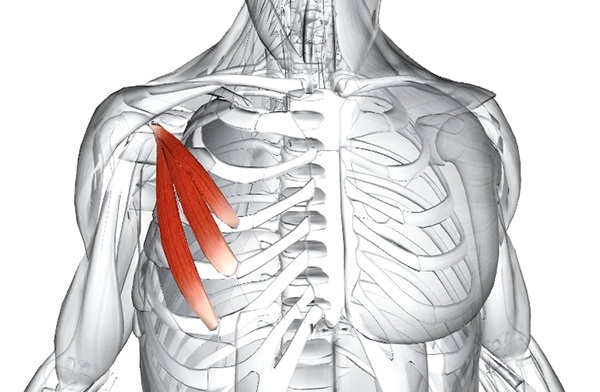
Small chest Is a small, thick muscle located in the upper chest. The anatomical arrangement of the organ contributes to the raising of the ribs, the movement of the scapula.
Record content:
- 1 Characteristic
- 2 Functions and properties
- 3 Anatomy and structure
-
4 Possible diseases and pathologies
-
4.1 Wright's syndrome
- 4.1.1 Classification
- 4.1.2 Symptoms and Signs
- 4.1.3 Causes
- 4.1.4 Treatment methods
-
4.1 Wright's syndrome
-
5 The main set of exercises
- 5.1 Push-ups and their modifications
- 5.2 Bench press with dumbbells
- 5.3 Stretching the shoulder girdle
- 5.4 Breast stretching with a roller
- 6 Pectoralis minor video
Characteristic
The pectoralis minor muscle has a triangular shape and is located under the pectoralis major muscle, both form the anterior wall of the armpit. It is a relatively small organ responsible for fixing the scapula, preventing its displacement. In a state of immobility, the scapula muscle contributes to the respiratory movement of the chest.
Functions and properties
The pectoralis minor (anatomy reveals the principle of muscle mechanics) has several functions. Its main action is to move the blade forward and downward. The scapula is one of the bones of the shoulder joint.
By moving the bone forward and downward, the muscle helps maintain mobility in the shoulder, which is one of the most labile joints in the body. When the muscle contracts, the scapula moves down, forward and inward to the ribs. In addition, it helps stabilize the shoulder and prevents the scapula from being pulled back - for example, when walking on crutches.
The minor muscle lifts the ribs, which helps the chest to expand during inhalation, increasing the lung capacity (as if a person took a deep breath before diving).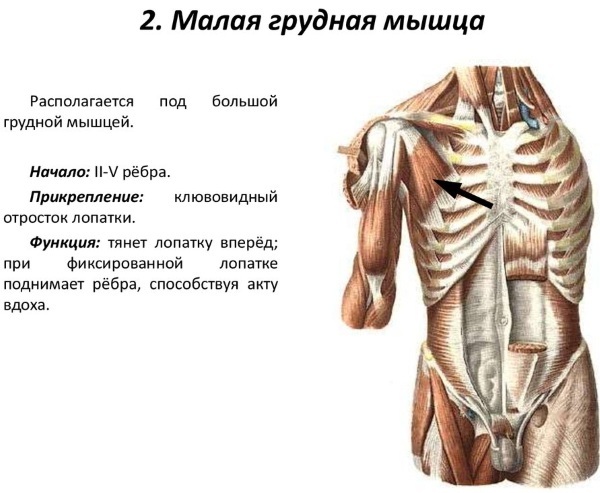
The lifting of the ribs with the help of the muscle occurs at the moment when the chest girdle is fixed or raised.
- When the scapula is fixed, the minor muscle can be considered as an auxiliary respiratory muscle for deep and forced inhalation, as it helps to raise the 4th and 5th ribs during inhalation, contributing to the expansion of the thoracic cavity.
- When the ribs are immobilized, the muscle pushes the scapula forward.
- Compression of the scapula is usually carried out by gravity, however, when additional force is required, this action is assisted by the serratus anterior muscle.
Anatomy and structure
The pectoralis minor (the anatomy is descriptively presented on the site) is a paired thin triangular muscle, located in the upper part of the chest, which originates from the coracoid process of the scapula and reaches the upper edges. The base of the muscle is formed by fleshy pads extending from 3-5 ribs, close to the costal cartilage. At the point of attachment, at the coracoid scapular process, the muscle flattens and becomes a tendon.
Although the pectoralis minor is an important organ in the chest, the pectoralis major is stronger and larger. Both muscles have the same innervation but act in different ways. The small one is for the movement of the scapula, and the large one is for flexion and adduction of the shoulder.
| Muscle | Origin | Insert | Action | Innervation |
| Pectoralis minor | The anterior surface of 3-5 ribs, lateral to the costal cartilage. | Medial edge and upper surface of the coracoid process of the scapula. | Stabilization, stretching of the scapula. Downward rotation of the joint. Stretching the scapula. |
Medial pectoral nerve. |
The main nerve supply to the muscle comes from the medial pectoral nerves, but can be innervated by the lateral pectoral nerve through a communicating branch known as the ansa pectoralis.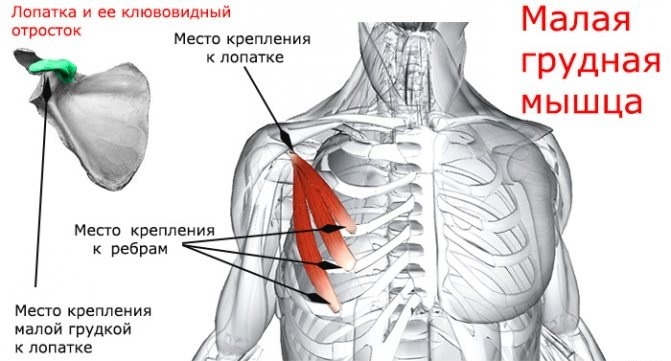
The pectoral muscles are metabolically active tissues that require high blood saturation in order to function properly and remain strong.
From an anatomical point of view, the vascular supply of the minor muscle comes from several sources:
- The thoracoacromial artery (a branch of the second part of the axillary artery) gives two feeding branches - the thoracic and deltoid.
- The superior thoracic artery (a branch of the first part of the axillary artery).
- Lateral thoracic artery (a branch of the axillary artery).
The blood vessels are located behind the pectoralis minor and are called the subclavian. The associated bundle of nerves is called the brachial plexus.
Possible diseases and pathologies
Improper sitting position, which negatively affects the posture of the upper body, negatively affects the functioning of the pectoralis minor. Poses in which there are extended periods of stretching of the scapula cause the scapula to contract, keeping the bone in an undesirable position.
What affects the development of pathologies:
- Chest injury.
- Large or minor fracture, deformation of the upper ribs.
- Long-term use of crutches.
- Hyperventilation or heavy breathing.
- Long-term mental stress.
- Wearing a heavy backpack or other weights for a long time.
- Holding the head for a long time in a position with a lowered chest, typical for people working at a computer.
- Previous or irregular heart pain as a result of a heart attack or angina pectoris.
The pectoralis minor (the anatomy of which is constantly being studied) can show signs of disorders and abnormalities.
Therapy depends on the severity of the pain and the area of injury, but the treatment process is often conservative:
- Rest. A patient with major or minor muscle pain should avoid strenuous activities that worsen the condition and increase the pain. Rest allows you to repair any minor damage due to your own immune system.
- Physiotherapy. This is the most important part of pectoral pain therapy. In most cases, doctors will prescribe physical therapy. Stretching, light resistance, and strength training are helpful during the recovery period.
- Anesthesia. For immediate relief, reduce inflammation, relieve swelling, ice packs are applied. In some situations, mild analgesics are used.
- Surgery.
Wright's syndrome
The term "syndrome" is used in medicine and surgery to refer to a group of abnormalities that constantly occur together. Since the pectoralis minor muscle connects the scapula to the chest and at the same time is close to the nerves and blood vessels, the term "pectoralis minor syndrome" means:
- abnormal scapula mechanics;
- abnormalities affecting adjacent nerves and blood vessels.
Minor chest abnormalities can lead to compression of nerves and blood vessels, as well as pain in the scapula.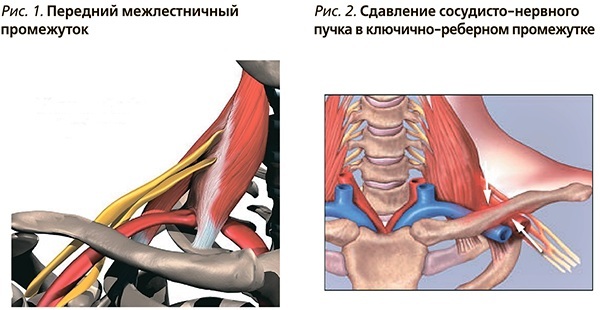
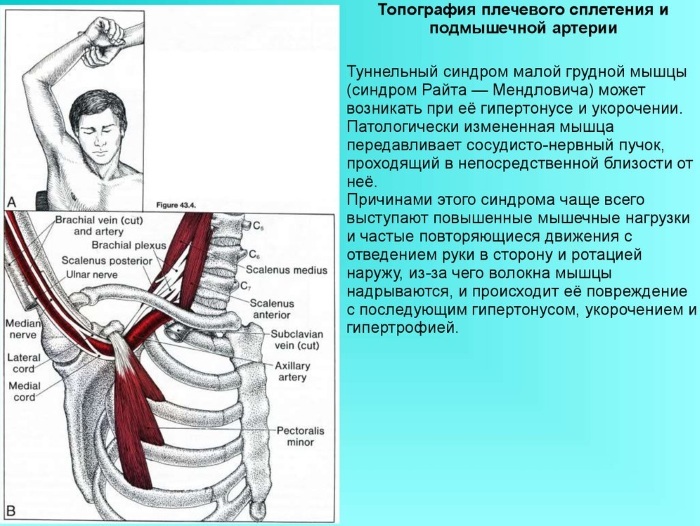
Pectoralis minor syndrome is the compression of the brachial plexus between the uncinate process on the top of the scapula and the contracted minor muscle. This is due to the tight muscle, which squeezes the neurovascular structures between it and the chest.
The tight and shortened muscle also causes the rounded scapula to straighten. Weakened scapular retractors (the muscles that pull the scapula towards the back) contribute to this position as they lack the strength to resist the pull of tight pectoral muscles.
Wright's syndrome or tunnel develops with hypertonicity and muscle shortening. With the maximum abduction of the shoulder, the pectoral muscle presses the vascular and nerve bundles to the coracoid process of the scapula.
Sometimes there is squeezing of the subclavian artery, veins that pass under the place of attachment of the pectoral muscle to the coronoid process.
Microtrauma, repeated many times, causes vasospasm and maintains irritation of the brachial plexus trunks.
Classification
There are four forms of thoracic outlet (outlet) syndrome:
- Anterior scalene syndrome.
- Costal-clavicular syndrome.
- Pectoralis minor syndrome.
- Cervical rib syndrome.
The upper opening of the chest (opening) connects the neck and chest. This area is considered the "exit" where the arteries carry blood from the chest to the arm to nourish the tissues of the upper limb, and motor neurons carry motor innervation from the chest to the arm to control muscle contraction in the upper limbs.
However, this condition is sometimes called thoracic entry syndrome because the veins in this area carry blood, and sensory neurons transmit innervation to the chest from the arm. This concept is used for any compression in this area, whether compressed structures are exiting or entering.
Symptoms and Signs
Common characteristics of the syndrome include:
- the head is constantly or often in the forward position;
- increased cervical lordosis;
- increased thoracic kyphosis;
- Raised, elongated, or rounded shoulders when the muscles are in a continuous state of stretching;
- the visible portion of the scapula protrudes instead of lying flat (scapula wing).
 The deformed muscles associated with the syndrome place stress on the surrounding muscles, tendons, bones and joints, as a result of which most people develop symptoms:
The deformed muscles associated with the syndrome place stress on the surrounding muscles, tendons, bones and joints, as a result of which most people develop symptoms:
- headache;
- pain and tightness in the chest, neck;
- pain in the upper back, especially in the shoulders;
- soreness in the jaws, shoulder blades;
- fatigue;
- limited range of motion of the neck and shoulders;
- numbness, tingling in the forearms;
- squeezing the chest girdle;
- a feeling of pain emanating from the inside of the elbow;
- pain that occurs inside the hand and extends to the middle, ring and pinky fingers;
- numbness of the forearm, hand and fingers;
- Difficulty sitting, driving a car, stretching the arm forward and up.
Causes
The shortening of a small muscle or tonic tension is most often the cause of neurovascular disorders occurring due to compression of the neurovascular bundle. Various movements can cause the syndrome, but in most cases it develops due to improper posture when the head is pulled forward for a long time.
The reasons influencing the abnormality:
- Muscle injury. After healing, it became shorter, scarred and lost its elasticity.
- Developed hypertrophy, which is especially typical for athletes.
- Congenital organ anomaly.
- Long-term use of the hand during repetitive work, for example, by carpenters, construction workers. This is also the case for office workers who slouch at the computer for a long time. Keeping the arms in front with the elbows bent, they thereby narrow the space where the arteries and nerves pass. Over time, an incorrect position leads to increased muscle hypertonia, shortening of the muscle, in the process of adapting to the new position of the scapula.
Treatment methods
Stretching the chest is one of the main treatments because it reduces spasms of the pectoralis minor muscles.
Treatment methods:
- Massage, manual therapy. The procedures work on the muscles, destroying the scar tissue between muscle layers, muscle fibers, tendons and fascial restrictions of the neurovascular bundle.
- Laser treatment. Accelerates the healing and regeneration of nerves from damage caused by chronic compression.
- Paraffin treatment. It is used for severe persistent pain.
In some cases, novocaine blockade is used. In the absence of a result after conservative treatment, an operation is recommended - the intersection of the tendons of the pectoralis minor muscle.
The main set of exercises
The pectoralis minor, whose anatomy explains the principle of dynamic muscle structure, needs support as it heals and regains functionality. To do this, you should perform exercises, at first easy, and then move on to more complex ones.
Recommended light muscle toning exercises:
- static chest push-ups;
- external rotation of the shoulder;
- flexion of the shoulder;
- bringing the resistance band using an expander tape.
A physical therapist will also advise on when to start vigorous exercise. Overtraining should be avoided and attention should be paid to correct exercise so as not to provoke rupture of muscle fibers in the chest.
Push-ups and their modifications
To carry out the exercises, 2 sturdy chairs are needed (it is best to weigh them down with books so that they cannot fall), located at a distance of slightly more than shoulder width apart. The backs of the chairs should be facing each other. Several squats should be done before exercise.
- Stand between the chairs, put your hands on the armrests and start lifting off the floor. Then slowly lower the body
- Repeat lifting and lowering several times.
The following types of push-ups:
-
Knee push-up. The exercise is performed with support on the knees. At the same time, the shoulders should be kept above the palms, the chest should be lowered exactly in the middle. Make sure the knees are bent, not the waist.
- "Scorpion". Push-ups are performed as described above, but as the body is lifted, one leg is raised and bends at the knee. In this case, the foot should be turned towards the head. The hips and upper body turn slightly with it.
- Sliding. Place a towel under each hand. When lowering the body, the arms move apart along with the towels. When lifting, the arms are brought together.
- Isometric chest press. This exercise can even be done in the office. In a standing or sitting position, the arms are bent, the palms are joined in front of the chest, the elbows are directed outward. Hands are pressed tightly together for about 15 seconds, then the tension is slowly released. This process is repeated several times.
Bench press with dumbbells
The exercise is similar to the bench press, but it uses a training bench.
- Take 2 dumbbells in your hands and hold them down with your palms, sit on a bench.
- Raise the dumbbells, put them on your hips, then lean back and move your knees up, throw them on your chest.
- Bend your lower back, take a breath, rest your feet on the floor.
- Exhaling air, raise the dumbbells, straighten your arms. The dumbbells should be brought together.
- Slightly holding the dumbbells at the top, start lowering them slowly to their original position.
For dumbbell presses, you can vary the incline of the bench. The steeper the rise of the bench, the more the upper pectorals are used.
Stretching the shoulder girdle
The shoulder stretch relaxes the pectoralis minor and pectoralis major muscles, which can help relieve shoulder pain and chest discomfort.
- Stand up straight with your hands on the wall.
- Bend your hips and knees slightly and place your feet about 10 cm from the wall.
- Bend your arms at a 90˚ angle, palms facing forward, and arms parallel to your head.
- Keeping your back, arms and hands against the wall, raise your arms as far as possible, and then slowly lower them back to their original position.
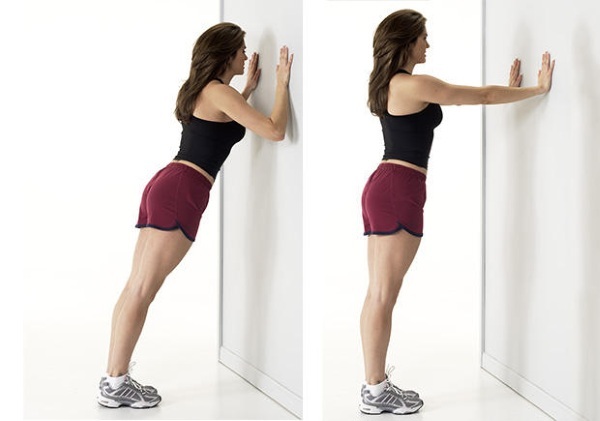

Do 20 sets daily to keep your muscles relaxed and flexible.
Breast stretching with a roller
When the chest muscles become too tense, they can pull the shoulders forward, leading to potential shoulder injuries and poor posture. Exercising on a foam roller stretches the chest muscles, helping them return to normal function.
- Lie longitudinally on a foam roller with your tailbone at one end and your head at the other.
- Bend your knees with your feet flat on the floor.
- Straighten your arms and take them at an angle of 90˚ from the body, palms up. Place your hands on the floor and relax your chest and shoulder muscles.
- try to make a "snow angel" with your hands, slowly raising them above your head.
- Perform the exercise for 30-60 seconds.
To enhance the action, you can try to perform a combination of static stretching and "snow angel" for 2-3 minutes.
Chest pain cannot be ignored, as it can lead to a more difficult situation if you do not take action in time. In many cases, the symptoms of pain in the pectoralis minor muscle are similar to angina pectoris. Only a doctor familiar with the anatomy of muscle structures can differentiate them.
Pectoralis minor video
Pectoralis minor:



