In total, there are up to 850 different muscles in the human body - organs that can contract and relax under the influence of nerve impulses. When counting, they are taken into account as the largest of them, like gluteal or tailorand micromuscles.
Record content:
- 1 general information
- 2 The most powerful
- 3 Femoral area
- 4 Calf area
- 5 Head area
- 6 Language
- 7 A heart
- 8 Reproductive system
- 9 Human Muscle Videos
general information
Each muscle, even the smallest, is attached to the bones of the ear, is a separately functioning organ and is controlled by specific nerve endings. Depending on the classification, the number of muscles in the human body can vary - if small muscles are included in the composition of larger muscle complexes, then their number is 640.
If you count all muscle tissue as muscles (for example, individual cells of smooth muscle tissue), then you can count about a billion muscles. Scientists have proposed classifying all types of muscle tissue and attributing cells to individual structures, and those, in turn, to complexes of structures.
Anatomically, the muscles are divided not only by their location in the body (chewing, gluteal) and the direction of muscle fibers (directed straight, transversely), but also by the structure of the joints (single-joint muscles, double-joint muscles), as well as along the trajectory of movement (flexion and extensor, pronator insteps) and taking into account the function they perform (agonists or antagonists).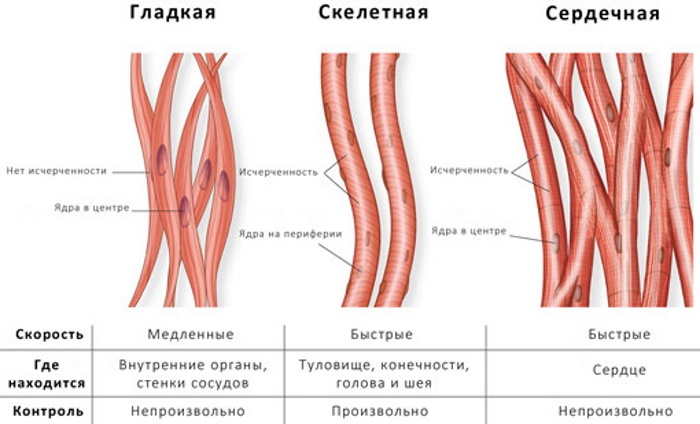
In total, there are 3 types of muscles in the human body:
- Skeletal muscle. They are composed of thousands of small muscle fibers and attach to bones. Only skeletal muscle lends itself to voluntary control.
- Smooth muscles. They regulate processes unconscious of a person: peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract, inhalation-exhalation, the functioning of internal organs. Their contractions are involuntary.
- Heart muscle. Involuntary, like smooth muscle. Reacts to electrical impulses, provides heartbeat.
The amount of muscle mass determines the shape of the body. Normally, in a healthy person, muscle weight is up to 45% of body weight. In men, muscle tissue is better developed, forms faster and, accordingly, the percentage of muscles is greater than in women. The toughest people, weightlifters, have more than 60% of the muscles of the total body weight. This is approximately 40-60 kg of muscle.
The most powerful
By right, the gluteus maximus muscle (or BLM) is the largest in the human body.
In the lower segment of the body there are 3 gluteal muscles: small, medium and large. The latter is shaped like a rhombus, attached to the ilium and sacrum, coccyx. It stretches from the side of the spine along the pelvis and attaches to the femur on the other side.
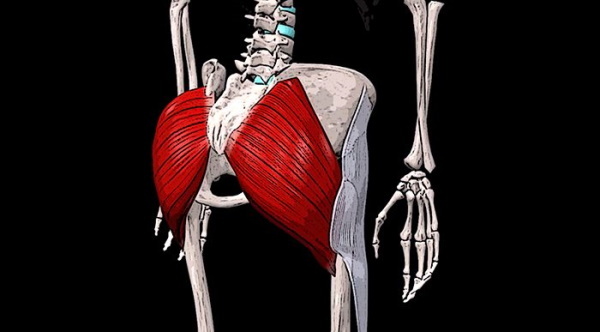
The main function is hip extension during high loads. The BNM is responsible for the relative mobility of the fascia of the thigh to which it is attached. The fascia is a movable process of connective tissue from the femur.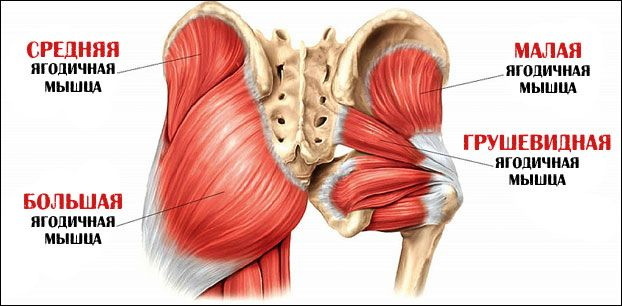
The largest muscle in the human body provides squatting, posture maintenance, walking, stair-stepping, side bends, and running.
The gluteus maximus is a fleshy dense mass of skeletal muscle. In athletes, the muscle reaches 2-3 cm in thickness. Consists of bundles of parallel coarse muscle fibers.
Interesting Facts:
- The gluteus maximus muscle is the most massive and largest muscle in the human body.
- The size of the muscle is typical for bipedal people in general, as it supports the trunk in an upright position.
- Possesses great aesthetic value, as it lies over the smaller gluteal muscles and provides the shape of the buttocks.
Femoral area
The tailor muscle is attached at one end to the ilium, bending around the surface of the thigh, and ends at the anteromedial region of the lower leg. Forms a dense tendon. The upper head of the tailor muscle is the border of the femoral triangle.
This muscle provides inward and outward mobility of the lower leg and thigh joints. It actively participates in raising the leg, straightening the hip, and helps maintain body posture. Helps maintain balance when doing squats.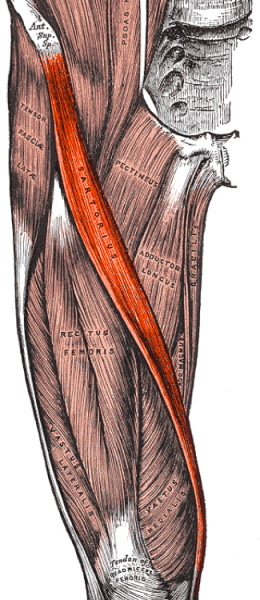
Refers to the muscles of the anterior thigh group along with the quadriceps muscle of the thigh and the articular muscle of the knee. It is innervated by the femoral nerve. The blood supply is carried out by the muscular branches of the femoral artery.
The largest muscle in the human body is well palpated and even visually observed during abduction to the legs to the side or extension of the limb.
Interesting Facts:
- The longest muscle in the human body. The average adult reaches 43-44 cm.
- The function of the sartorian muscle allows a person to sit cross-legged on a firm surface.
- The tailor muscle of the left leg is more active if, simultaneously with the movements, manipulations are carried out with the opposite upper limb and vice versa.
- Called "tailor" because it flexes the hip in a manner similar to how tailors do during the work process.
Calf area
Belonging to the muscles of the posterior surface of the lower leg, the calf muscle is attached with the upper head to the heel plate using the Achilles tendon. Medially, the muscle is attached to the corresponding (medial) femoral condyle, and laterally, respectively, to the lateral.
The function of the muscles is to ensure flexion of the lower leg and foot. In addition, the activity of the muscles is involved in the rotational and translational movements of the ankle joint. It is especially active while walking, driving and running. Provides a stable foot position.
The gastrocnemius muscle is formed by the medial and lateral heads. Their direction is symmetrical. However, the medial head is stronger, originating in the popliteal region of the thigh. The first sections of the heads form the lower border of the fossa under the knee joint. They end by coming together in the middle of the lower leg, after which they form the Achilles tendon, which attaches to the posterior tubercle of the heel.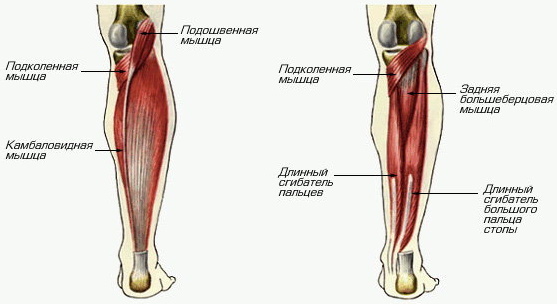
Interesting Facts:
- It is considered the strongest muscle in terms of its ability to stretch. During stress, it is capable of withstanding loads of up to 140 kg, depending on the training of a person.
- Shortened in 90% of people. Causes are underdevelopment of the gluteus muscle and insufficient extension of the foot when walking or running. The danger is the forward movement of the center of gravity. One of the causes of severe cramps is overstrain of the calf muscles. Injuries often occur due to light but long loads.
- Little known anomaly - development of the 3rd head of the gastrocnemius muscle. Usually it does not bring discomfort to a person, but it is rare: in about 3% of people. More often diagnosed in Japanese - 5% of the occurrence. The third head is attached at the top between the rest of the heads and attached to one of them from below.
Head area
The chewing muscles are the muscles of the head. Together with the mimic, they form a complex of the most mobile and sensitive muscles. The structure and tone of the facial muscles affects the shape of the face, predetermines a person's tendency to express certain emotions. The activity of facial muscles changes the perception of a person by others.
Anatomically, all chewing muscles are usually divided into 4 muscles, each of which performs a specific function and participates in the organization of facial expressions and the primary processing of the food bolus. All 4 muscles are attached to the lower jaw.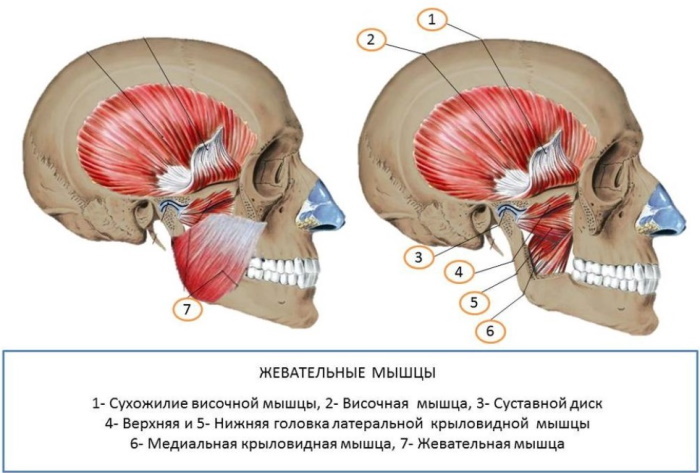
In turn, chewable ones include:
| Name | Location | Function |
| Temporal | It is divided into 2 heads and forms a complex dense tendon resembling a fan. Bends around the zygomatic bone and provides translational movements of the lower jaw | Active during chewing, grinding food. |
| Chewing | Consists of 3 processes: intermediate, upper and lower. The superficial and lower part of the masseter muscle itself starts from the upper and inner surfaces of the cheekbone, respectively. Both are attached to the lower jaw. The intermediate process originates from the inner surface of the cheekbone and attaches to the outer part of the jaw. | The joint activity of all three processes allows the jaw to move forward. Separately, the superficial process provides for the forward movement of the jaw, and the rest for its lifting. Participates in the formation of emotions of discontent, anger and disgust. |
| Pterygoid lateral | It is formed by two processes and resembles a triangle in shape. Located in the infratemporal region. | The activity of the two parts of the muscle allows the lower jaw to be extended. In turn, with the activity of one of the parts, for example, the left one, it shifts the lower jaw to the opposite side of the muscle - to the right. |
| Pterygoid medial | The shape resembles a quadrangle. Located in the lower part of the jaw, under the tongue. Attaches to the pterygoid fossa and tuberosity located on the lower jaw. | Joint contraction ensures the raising of the jaw, relaxation - lowering. Thus, it is active during the grinding of food. Shrinking the right side allows the jaw to move in the opposite direction. Likewise with the left side. |
Thus, the chewing muscles are involved in the processes of crushing, grinding and grinding food. It forms the familiar features and proportions of the face, and also helps to express emotions such as anger, fear and intense excitement. Provides both verbal (verbal) and non-verbal (facial) communication.
The largest muscle in the human body is the gluteus maximus, but the chewing muscles are much stronger and with mimic muscles provide an incredible variety of possibilities.
Interesting Facts:
- The chewing system is capable of creating a pressure of up to 100 kg during extreme loads.
- When grinding, grinding ordinary (that is, not liquid, not solid) food, the chewing muscles create a pressure of 10-15 kg.
- Without exception, all the chewing muscles are involved in the act of raising, lowering or displacing the lower jaw, while the upper remains part of the skull and is motionless.
- A feature of the facial muscles is that they are not attached by two heads to the skeleton, but the chewing muscles are an exception to the rule.
Language
The tongue is in the mouth. The muscles make up the main part of the tongue and are divided into 2 groups: skeletal and proper. Both groups include 4 muscles. The muscles of the tongue are symmetrically divided by a longitudinal fibrous septum. All muscles of the tongue attach to either the hyoid or the mandibular bone.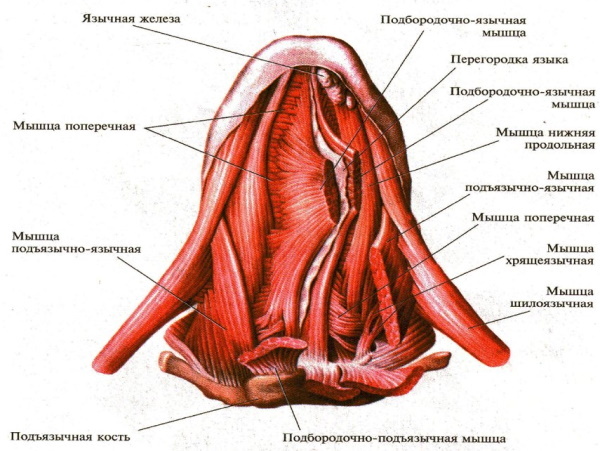
Among the functions of the tongue, the functions of the papillae, located on the mucous membrane of the organ, and the muscles themselves, which make up the bulk of the organ, are divided. There are a total of 8 of them, each of which performs a specific function.
The skeletal muscles of the tongue include:
- Chin-lingual. Provides downward and forward movement of the top of the organ.
- Sublingual-lingual. Participates in swallowing a lump of food: closes the larynx with the epiglottis. Responsible for backward and downward movements.
- Palatine. Provides an elevation of the root of the tongue.
- Awl-lingual. Movement of the tip of the tongue up and back.
All muscles of the second group change the shape of the tongue.
The lingual muscles include:
- Upper longitudinal.
- Lower longitudinal.
- Transverse muscle.
- Vertical muscle.
The tongue is a muscular organ consisting predominantly of striated musculature. The body has the ability to change its shape and position. The entire musculature of the tongue begins with the occipital myotome. Therefore, they are innervated only by the 7th pair of cranial nerves.
Interesting Facts:
- The structure of the tongue, called a muscular hydrostat, has been compared to the trunk of an elephant.
- Most are convinced that the tongue is considered the strongest muscle in the human body, but this is a misconception. The strongest muscle is the chewing muscle.
- The longest tongue was possessed by Nick Stoberl. Its length was 10 cm.
A heart
A hollow muscular organ that ensures the movement of blood through the vessels. The organ is located in the chest, in the center, and shifts slightly to the left. The shape and position of the heart are not the same, and these signs are inherited.
The myocardium is a musculature of the cardiac type. Forms the middle layer of the heart, ventricles and atria. The myocardium includes atrial and ventricular fibers, as well as loose fibrous connective tissue and coronary vessels. Consists of myocytes, which, in turn, are of three types: conductive, contractile and secretory.
The heart muscle is aimed at maintaining homeostasis - the internal environment of the body. The pumping function of the heart is only a part of the hydrodynamics (movement of fluid) of the blood circulation. It is carried out through cyclic contractions and relaxation.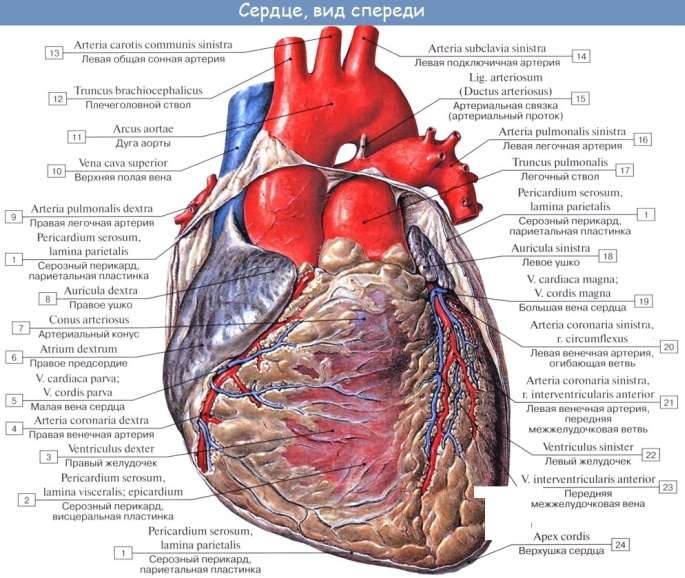
Interesting Facts:
- The most resilient muscle. The myocardium begins to function from birth to death of a person without stopping.
- Factors that lead to a decrease in the tone of the heart muscle are an excess of calcium and a lack of glycogen.
- The myocardium circulates more than 2,500 gallons of blood per day.
- The heart muscle does not have the same ability to regenerate as other muscles.
- Over the course of a lifetime, the heart makes approximately 2.5 billion. reductions.
- In men, the heart weighs more than in women. 300-360 and 250-320 respectively.
Reproductive system
The uterus is located in the pelvic cavity in women near the bladder and rectum. It is divided into the body and the cervix. The norm of length in a healthy woman is about 4-6 cm, and the thickness and width are 4-5 cm. It also depends on the woman's age and the number of births. The uterus is able to occupy different positions and is relatively mobile. The musculature is located in the middle layer of the walls of the organ.
The main function of the uterus is reproductive. This is the ability to fertilize, develop and carry an embryo. The muscles of the uterus stretch the walls and push the baby out during labor.
The uterus is made up of spiral-shaped muscle fibers that point in different directions. The fundus is the upper part of the organ that protrudes above the opening of the fallopian tubes. The body is a triangle-like area that tapers towards the cervix.
The peculiarity of the smooth muscles of the uterus is the presence of nexuses - specific gaps between the fibers, which allow the organ to stretch and even contract in this state. Moreover, the contractile function of the uterus largely depends on the concentration of female hormones.
Interesting Facts:
- The muscle of the uterus is the second most powerful muscle after the masseter muscle.
- In addition to stretching the uterus a lot during pregnancy, the muscle can contract. During childbirth, the muscle pushes the child, which is several times larger than it.
The uterus is considered to be the strongest in the human body if we take into account the weight of the muscle, despite the fact that the gluteus is the largest.
Author: Svitkevich Julia
Human Muscle Videos
TOP 5 muscle facts:


