The task of the adrenal glands, as a paired organ, consists in the production of vital hormones that ensure the adaptation of the body in conditions of increased stress loads. In representatives of the order of mammals, they are located above the kidneys in the layer of retroperitoneal tissue, but only in humans are endocrine-type glands in the immediate vicinity of the upper poles of each kidneys.
Features of organ diseases are manifested by an increased or decreased level of one or more hormones produced, of which the most important are sex hormones.
Record content:
- 1 What are the adrenal glands, where are they located
-
2 The structure of the adrenal glands
- 2.1 Cortical layer
- 2.2 Medulla
- 3 Functions in the human body
- 4 Common symptoms of adrenal disorders
-
5 Diseases of the adrenal glands
- 5.1 Diseases on the background of hyperfunction
- 5.2 Pathology against the background of hypofunction
- 6 Adrenal video
What are the adrenal glands, where are they located
Among the organs of the retroperitoneal space, which are not so easy to diagnose, an important role is given to the adrenal glands. They are paired glands of light brown shade and small size (maximum 6x3 cm), framing the tops of each kidney.
The work of the adrenal glands is controlled by the endocrine system, therefore their role in the human body is associated with the production of vital hormones (steroid) - adrenaline and norepinephrine, corticosteroids and androgens. Due to the production of these substances and a close relationship with the functioning of the thyroid gland, the adrenal glands are involved in the following processes:
- providing emotional and physical activity;
- the correct functioning of the circulatory system;
- the formation of metabolism, as well as immunity;
- the formation of primary and secondary sexual characteristics.
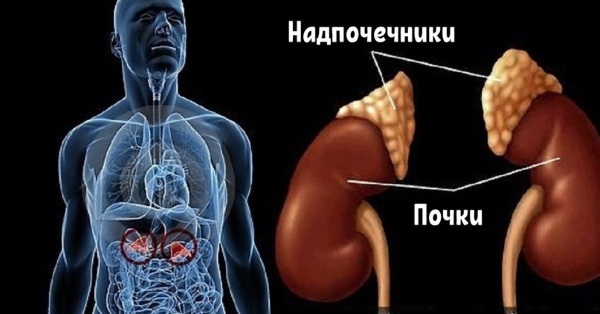 The development of pathological processes in the complex structure of the adrenal glands results in the appearance of unexpected symptoms of various diseases.
The development of pathological processes in the complex structure of the adrenal glands results in the appearance of unexpected symptoms of various diseases.
Failure in the production of hormones in women leads to the appearance of endocrine and cardiovascular pathologies, disturbances in the work of various organs, which is manifested by the strengthening or suppression of their functions. In the case of hyperactivity of the endocrine glands of small weight (no more than 13 g in an adult), the threat of the development of hormone-dependent tumors increases.
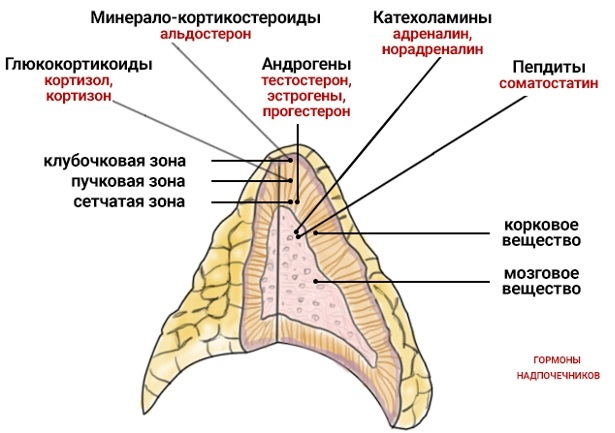
The structure of the adrenal glands
The complexity of the structure of the paired organ lies in the fact that the external (cortical) and internal (cerebral) layers can function as independent glands, despite the anatomical union into one structure. In addition, the nervous system regulates the work of the medulla and cortical substance in the composition of the common fibrous capsule.
Cortical layer
The substance of the adrenal cortex has a yellowish color, consists of nervous tissue that produces 2 groups of hormones to regulate metabolic and energy processes. The task of one group is to turn proteins into carbohydrates, as well as to increase the degree of the body's resistance to the influence of unfavorable factors.
Thanks to hormones of another group, the regulation of salt metabolism is ensured. Steroid (nonsexual) compounds produced by the cortex are classified as corticosteroids. It is represented by glucocorticoids (anti-inflammatory steroids) and mineralocorticoids used to restore mineral metabolism.
The adrenal glands in humans are located at the tops of the kidneys, the pole of the left is crowned with a triangular adrenal structure, and the right is conical. The cortical layer, which produces more than 50 types of hormones, accounts for almost 80% of the entire structure of the paired glands of the endocrine system.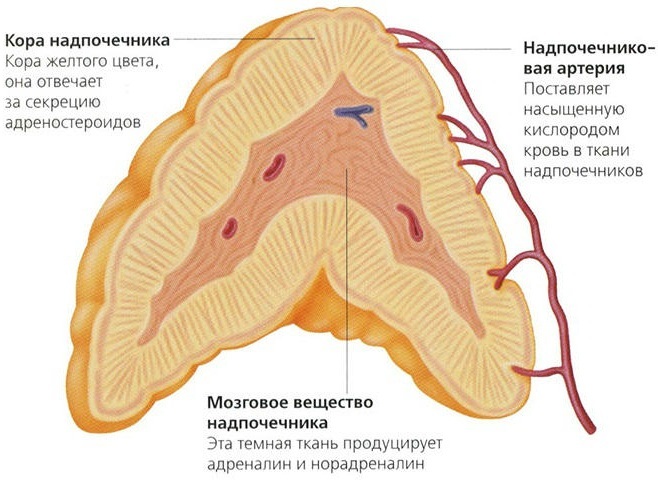
From the point of view of the morphofunctional structure, the adrenal cortex is formed by 3 layers - glomerular, bundle, reticular, each of them synthesizes certain types of hormones.
| Zone name | Summary of Produced Substances | |
| Glomerular | Among the mineralocorticoid group, aldosterone is the most important. A hormone with a strong selective effect on the process of water-salt metabolism contributes to an increase in blood pressure, an increase in the volume of blood circulating in the body. Two other hormonal substances are among the factors that have little effect on life processes. The mineral activity of corticosterone is much weaker than that of aldosterone, and deoxycorticosterone contributes to an increase in skeletal muscle strength and endurance. | |
| Beam | Cortisol | The synthesis of a glucocorticosteroid is necessary to regulate metabolic processes (proteins, fats, carbohydrates). The secretion of the substance depends on the time of day - at least in the evening, maximum in the morning. In women, cortisol levels are influenced by the stage of their period. |
| Cortisone | Secretion into the blood stimulates the synthesis of protein from carbohydrates, increases resistance to the destructive effects of stress. The level of cortisone affects the state of the hematopoietic system, ensuring the growth of red blood cells, a decrease in lymphocytes. | |
| Mesh | Group of gonadosteroids | Unlike the sex hormones secreted by the gonads, the activity of this type of hormones is not affected by the moment of puberty. The most significant are androgens, which contribute to the development of sexual characteristics of the secondary type. |
Less studied is the highly developed reticular zone where androgens are produced - inactive male hormones (sex). These substances, which are the precursors of female steroids (sex), have a strong anabolic (cell renewal) effect, the ability to lower blood glucose levels.
Androgens affect the mass of body fat, the level of psychosexual excitability, the development of secondary sexual characteristics - important for the formation of the body's sex.
Medulla
The adrenal glands, like the organs of internal secretion in humans, are lined from the inside with a softer substance with a dark brownish color due to chromium salts. The layer is formed by an accumulation of large cells, where there are centers for the production of active substances called catecholamines, or "hormones of adaptation".
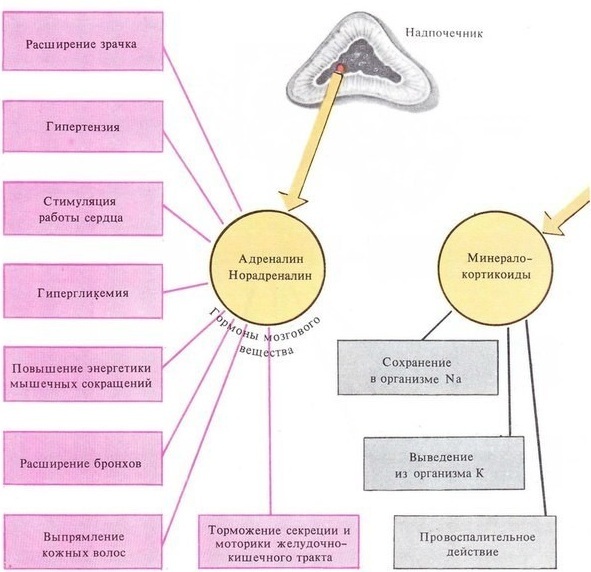
- Adrenaline is the "fear hormone". Its release into the blood is associated with fear, intense excitement or great physical exertion, which causes the heartbeat to become more frequent. Due to the presence of adrenaline, glucose more easily penetrates the cell membranes, and the rate of decay increases. carbohydrate and fat compounds, the work of the heart is activated and the vasoconstriction of the internal organs against the background of expansion muscle vessels.
- Norepinephrine is the "rage hormone". When it enters the bloodstream, an aggressive reaction grows, which is manifested by a significant increase in muscle strength. The acceleration of the secretion of the hormone is facilitated by stressful situations, heavy physical labor, and profuse blood loss. The rapidity of restructuring of the body is due to a strong vasoconstrictor effect, an increase in the volume of circulating blood, as well as an increase in blood flow velocity.
Both hormonal substances have a similar effect, their small amount is present in the blood even in a calm state.
However, in extreme situations, the activity of the medulla increases sharply, and the volume of produced hormones increase sharply, which ensures the rapid mobilization of the body with takeoff performance. The source of their synthesis is tyrosine, produced by the liver, as well as entering the body with food.
Functions in the human body
The main task of the adrenal glands is hormonal regulation through the secretion of hormones necessary to ensure various physiological effects. Steroid compounds are especially important for the formation of the body's defense response to stress syndrome - a variant of excessive external irritation.
At the moment of high stress (danger), there is a significant increase in the body's stability with the mobilization of difficult working defense mechanisms. At the moment of a threat to a person, a special part of the nervous system (hypothalamus) perceives danger signals, correcting the functioning of the internal secretory glands.
As a result, the pituitary gland secretes the release of a special hormone ACTH (adrenocorticotropic) into the blood, due to which the production of adrenal steroids increases. As a result, many organs and systems of a person for a short period of time work at the limit of their capabilities, which prevents the destructive effect of an unfavorable factor.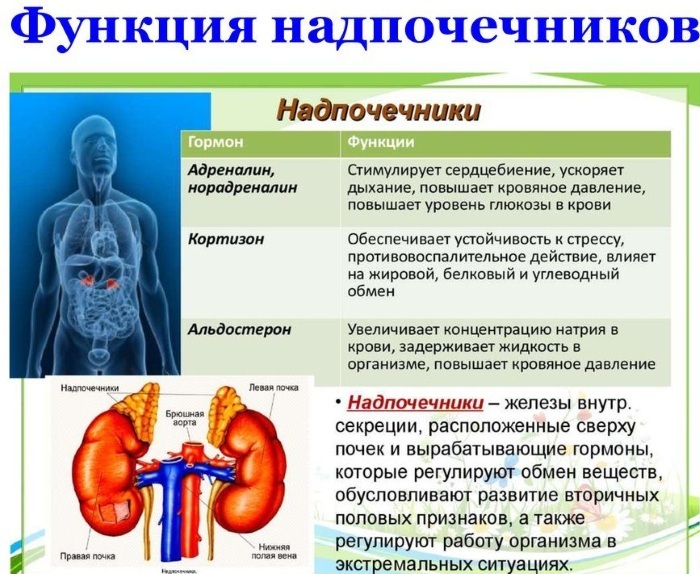
Thus, the paired glands of the endocrine system in the male or female body help to solve the following tasks:
- recover from exposure to stress;
- adapt to environmental conditions;
- control the level of stress resistance;
- participate in metabolic processes.
The human adrenal glands are located in the place where the arteries are concentrated; each gland is supplied with blood by 25-30 venous channels. The branches of the highways pass through the cortical layer, branching in the area of the medulla, due to which the paired organ has a specific ability - it increases in size if it is necessary to increase the production of hormones.
Numerous functions of the adrenal glands rely on the production of hormonal compounds:
- mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone) of the glomerular layer promote the reabsorption of sodium, as well as the excretion of potassium (in the urine);
- glucocorticosteroids of the bundle zone, synthesized from cholesterol, are important for protection against infection, regulation of fat metabolism;
- androgens of the reticular layer synthesize testosterone in the female body, they are needed to maintain vascular tone, call glucose from the depot to break down fats.
In a woman's body, more than 60% of testosterone is produced by the breakdown of androgens secreted by the adrenal cortex. Adrenaline stimulates the nervous system, which ensures an increase in activity and wakefulness, and ensures the stability of the psyche.
Normal production of adrenaline activates the sympathetic nervous system, including the mechanism of adaptive responses. Adequate volume of norepinephrine is important for stimulating heart rate, regulating blood pressure, and peripheral vascular resistance.
The work of the female and male body has certain differences. If the male gonads produce testosterone (male sex hormone), then the female - the necessary amounts of estrogen and progesterone.
The load on the female adrenal glands increases during pregnancy - androgens that have passed through the placenta are transformed into estrogens. The need for hormones rises sharply, so the mass of each gland can increase by almost 2 g. Only from 2-3 semesters can we expect the stabilization of the woman's condition, when the fetus begins to synthesize its own hormonal substances.
During the climacteric period, the endocrine glands work under the influence of an enormous load due to the cessation of the secretion of estrogen by the ovaries. Therefore, the hormones necessary for the female body are produced by the adrenal glands, slightly reduced in size.
Common symptoms of adrenal disorders
For certain reasons, paired glands can suffer from a deficiency or excess of the hormones produced. A lack of steroids provokes the development of adrenal insufficiency (primary, secondary type), which proceeds in an acute form or has become a chronic pathology.
With an excess of adrenal hormones, tumors appear in one of the three described zones, and the diagnosis of hypertrophy of the cortical layer is also possible.
The adrenal glands in humans are located in the zone of production of vital hormones. Therefore, the manifestation of dysfunction in the work of the glands depends on the lack or excess of the secretion of specific hormonal compounds.
In general, special attention should be paid to the following symptoms:
- a state of chronic fatigue accompanied by muscle weakness;
- the appearance of increased irritability, sleep disturbances;
- fluctuations in blood pressure indicators, heart palpitations;
- changes in the skin - darkening, pigmentation, sensitivity, stretch marks;
- frequent dizziness, severe headache;
- changes in body weight - increase to obesity, decrease to anorexia;
- increased sweating, partial or complete hair loss;
- the development of an anxiety syndrome, signs of irritability and fear.
Androgen deficiency in women is manifested by a violation of the menstrual cycle (delay), as well as increased hair growth in the pubic and armpit areas (failure in the production of several hormones at once).
 In addition, the patients suffer from male-type body transformations - facial features become coarse, the labia are transformed by analogy with the male scrotum. The pathologies of the adrenal glands are signaled by intolerance to sunlight, constant depression, a decrease in the size of the mammary glands with an increase in pain in them.
In addition, the patients suffer from male-type body transformations - facial features become coarse, the labia are transformed by analogy with the male scrotum. The pathologies of the adrenal glands are signaled by intolerance to sunlight, constant depression, a decrease in the size of the mammary glands with an increase in pain in them.
If such symptoms appear, you should visit an endocrinologist to clarify the diagnosis based on the results of a medical examination. Normally functioning glands themselves cope with adverse effects by regulating metabolic processes.
Diseases of the adrenal glands
Each type of pathology of the glands has its own specific symptomatology, but the adrenal glands themselves hurt only in case of suppuration or a rapid increase in the tumor formed in their thickness. Disorders in the work of the endocrine organ are not accompanied by specific pains, and its diseases are classified, focusing on the features of functioning.
The adrenal glands in humans are located on both sides of the spinal column and are covered with a layer of skin with subcutaneous fatty tissue, which does not allow palpation of paired organs.
Therefore, to diagnose pathological disorders, the doctor needs to study the results of ultrasound or CT of the retroperitoneal organs. The data of a laboratory blood test for the content of hormones make it possible to clarify in which direction the deviation occurred.
The most common pathologies include the following types of diseases caused by increased (hyperfunction) or decreased (hypofunction) production of adrenal hormones.
Diseases on the background of hyperfunction
The development of hyperaldosteronism, also called Conn's syndrome, is associated with increased production of aldosterone along with the rest of the mineralocorticoids of the cortical layer.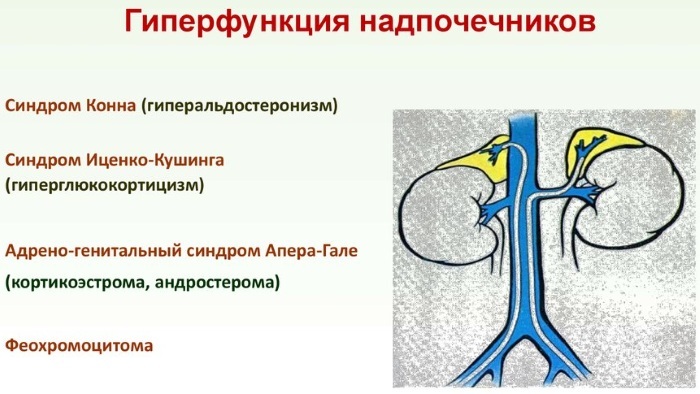
The disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- persistent increase in pressure, which cannot be normalized with standard drugs;
- the appearance of cramps and muscle weakness, as signs of potassium deficiency, swelling of the extremities;
- constant fatigue, the development of tachycardia and cardiac arrhythmias, headache symptoms.
The chronic form of pathology causes a violation of the urination regime - large volumes of daily urine (polyuria) or the predominance of nocturnal urges (nocturia). The primary form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of a tumor in the cortical zone, secreting aldosterone. In a chronic course, the culprit for an increase in the level of adrenal hormone is not a tumor, but a disturbed water-electrolyte metabolism.
Pheochromocytoma is a tumor localized in the medulla and consisting of cells of the chromaffin type. The clinical picture is manifested by catastrophic pressure surges even for a minor reason. Indicators decrease between attacks, during crises, vision problems are often recorded.
In the case of arterial hypertension of the malignant form, the threat of its rapid metastasis is not excluded. The process is accompanied by a clinic typical for diseases of the affected organs.
Pathology against the background of hypofunction
Other diseases usually become the reasons for the development of adrenal insufficiency. In a rare endocrine syndrome called Addison's disease, the patient suffers from a lack of production of mainly cortisol. Hypocorticism grows slowly (months, years), and manifests itself suddenly in a stressful situation, when the need for glucocorticoids increases sharply.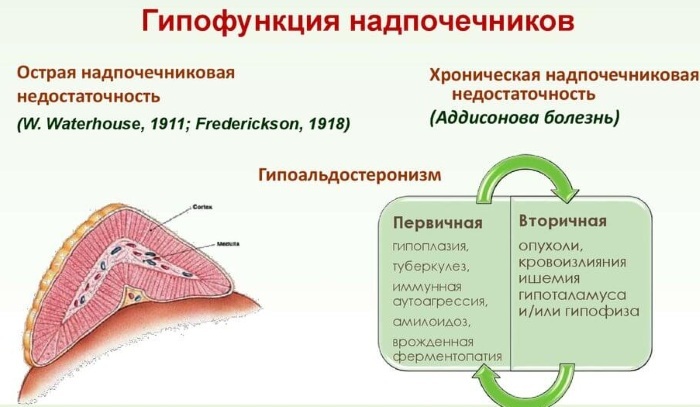
In addition to the characteristic symptoms of problems with the adrenal glands, in women, the disease signals:
- reduced pressure, especially in an upright position:
- irritability and irascibility, attraction to salty;
- irregular flow of menstruation, excessive amount of urine.
Hypocorticism can be primary, when the adrenal cortex is affected, and also secondary - a decrease in corticotropin production due to pituitary pathology.
All metabolic processes suffer from a lack of hormones, which is noticeable by external signs such as hyperpigmentation, which affects not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes. The acute stage of failure threatens to stop the production of adrenal steroids.
Disturbances in the work of the adrenal glands can also develop with their function unchanged, as evidenced by the signs of Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome. Pathology is not considered an independent disease, since it progresses against the background of a tumor that appears in a person on another organ.
The culprit of the pathological condition is not in the adrenal glands, but in the blood saturated with a large amount of ACTH (pituitary hormone). The cause of the condition is associated with a pituitary adenoma or an infectious lesion of the central nervous system.
Adrenal video
Physiology of the adrenal glands:



