Content
- What is this tooth?
- When do they appear?
- Teething features
- Growth symptoms
- Relief of symptoms
- How do children develop
- Complications of teething
- Removal in adults, risks
- Interesting facts about "eye" teeth
- Ophthalmic tooth video
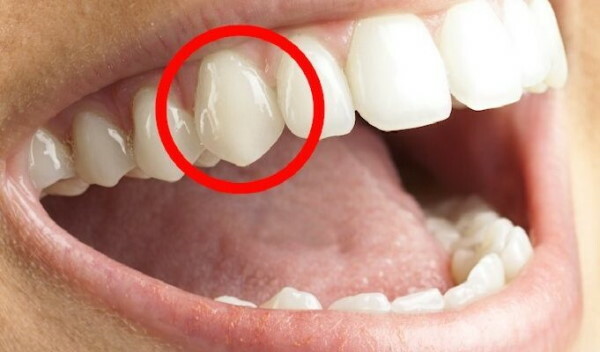
Upper canines are unofficially named "Eye" teeth, which is not related to the accepted dental terminology. These are the most mythologized and prejudiced units of the jaw apparatus. They are located next to the facial nerves connected to the optic analyzer.
What is this tooth?
According to the dental classification, the most powerful single-rooted elements of the upper jaw have atomic number 3. The common name was introduced by the dentists themselves for ease of communication with patients.
The "ocular" tooth is located between the anterior incisor and premolar units. The branches of the facial nerve bundle located nearby are characterized by pain radiating with irritation to the upper part of the skull, where the optical organ is located.
This explains the unofficial name of the upper canines. Despite their own name, they do not affect vision. Symmetrically located "eye" teeth have a powerful and strong root.

This anatomical design, when removed in adults, requires an increased dose of anesthetic medication. A thick layer of enamel coating provides reliable protection of the dentin tissue.
The "eye" teeth are rarely exposed to carious lesions and the development of other dental diseases. Visually, these units of the jaw structure look like a thickened cone. They have individual characteristics of eruption and growth.
When do they appear?
The normal period for the formation of the upper canines in the milk bite is considered to be the age of 16-22 months. The time of the appearance of "eye" teeth in children is individual. Therefore, small deviations in the timing of formation are permissible.
Permanent units of the jaw structure appear at 10-12 years of age. In case of malocclusion, orthodontists wait for the formation of "eye" teeth for the installation of a correction plate or bracket system. The exact timing of eruption or late appearance is influenced by numerous factors.
The delay in the appearance of "eye" teeth is due to:
- genetic characteristics;
- childhood diseases, the severity of their course and complications;
- pathologies of the mother during pregnancy, affecting the mineralization of the skeletal structures of the embryo;
- jaw osteomyelitis of infancy;
- nutrition of the child;
- maxillofacial injuries.
Milk teeth usually appear quickly - in 2-3 weeks. Permanent "eye" teeth can take 4-6 months or more to form. It depends on the individual characteristics of the organism, the assimilation of calcium-phosphorus compounds and the presence of such trace elements in the child's diet.
Such elements of the chewing apparatus are formed longer than other teeth, which is associated with the functional purpose of the canines. These elements of the maxillary structure are involved in creating the oval of the face and tearing up dense or hard foods.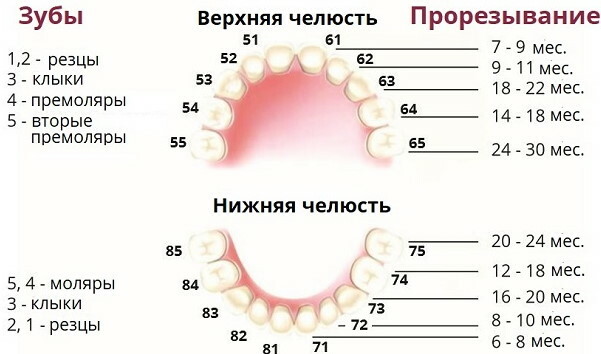
They are hardy, not prone to chips, cracks, loosening. The powerful anatomical structure determines the relative duration of the formation of "eye" teeth.
Teething features
The appearance of the upper canines, which some scientists tend to consider rudimentary and unnecessary for humans, is due to natural physiological changes in the child's body.
The growth of "eye" teeth often coincides with the transition from breastfeeding and nutritional formula for newborns to heavier and denser foods. Its use is necessary for the further development of the body.
The "eye" tooth is located near the facial optic nerves, which are irritated by inflammation, which causes severe pain. The upper canines play a key role in chopping food.
They are evolutionarily adapted to bite off. Such teeth have a reinforced anatomical design with a pair of cutting edges converging at right angles. They are covered with a thick layer of calcium-phosphorus enamel.
The "eye" teeth are subjected to significant stress, which is 25% higher than the pressure exerted on the counterparts of the lower jaw in the process of tearing and chewing food. This feature requires a long formation time.
Growth symptoms
The signs of the formation of the upper canines resemble the eruption of other chewing elements, but to an excellent degree. An aggravated reaction of the body is considered a physiological norm. The main symptoms of the growth of the upper canines are presented in the table.
| Sign | Clinical features |
| Gingivitis | Inflammation of the epithelial covering of gingival tissue, accompanying the growth of "eye" teeth, is infectious or aseptic in nature. |
| Hyperthermia | The child's body temperature, depending on the severity of the eruption process and the immune status, rises to subfebrile values or exceeds 38 °. |
| Swollen gums | The symptom is associated with the development of gingivitis, characteristic of the eruption of "eye teeth." |
| Swelling of the tissues surrounding the dental bed | The rupture of the fibers by the erupting jaw unit leads to such a pathological effect. Puffiness is of varying severity and is accompanied by hyperemia of the mucous membrane. |
| Non-infectious rhinitis | Vasomotor symptom caused by the proximity of the root system of the "ocular" tooth to the upper respiratory tract. The eruption process disrupts the tone of the blood capillaries of the nasal cavity. |
| Hypersalivation | Intense salivation is not associated with a disorder of the functions of the central nervous system. This symptom is due to the increased activity of the corresponding glands and their inflamed condition. |
| Conjunctivitis | The proximity of the dental root to the nerves of the optic organ causes vasomotor irritation the mucous membrane of the eyes, which is expressed by redness, tearing, slight inflammation conjunctival sac. |
 Children during the period of teething are characterized by tearfulness, capriciousness, excessive psychomotor agitation, or vice versa lethargy, which is characteristic of the inflammatory process.
Children during the period of teething are characterized by tearfulness, capriciousness, excessive psychomotor agitation, or vice versa lethargy, which is characteristic of the inflammatory process.
The risk of infection with bacterial agents, viral pathogens, pathogenic fungal microflora increases due to excessive load on the immune system.
In severe cases, the eruption of "eye" teeth is accompanied by:
- cough;
- vomit;
- insomnia;
- unmotivated concern;
- increased anxiety;
Children refuse food due to severe pain and an inflamed condition of the oral cavity. Diarrhea is considered a pathological symptom of the growth of the upper canines, conventionally called "eye" teeth.
Defecation disorders and digestive upset signal the introduction of gastrointestinal infections against the background of a weakened immune system. Such effects can be accompanied by cutting pain in the abdominal cavity.
Relief of symptoms
There is an extensive group of anesthetic drugs for the relief of teething syndrome in a child. Their use is the fastest and easiest, but not the only way to suppress unpleasant physiological symptoms.
To alleviate the condition of the child during the eruption of "eye" teeth use:
- Light massaging of the gum tissue. The procedure increases blood circulation and has a distracting effect. Index finger for 1-2 minutes. massage the gums around the erupting upper canines. The manipulation is repeated no more than 2-3 times a day.
-
Special teethers. The products have a cooling effect. They are given to the child to nibble. This is a kind of massage of the root system of the tooth and a way to quickly reduce the local tissue temperature accompanying the eruption process.
- Anesthetic gels. Dentinox, Kamistad and many other drugs that are freely sold in any pharmacy are classified as such external use agents. Anesthetic gels are lidocaine based. They contain natural herbal ingredients with anti-inflammatory properties and mild sedative effects. Medicines in this category are distinguished by a quick analgesic effect.
- Vasodilator nasal drops. Such means can eliminate the congestion that accompanies the eruption of "eye" teeth. Use Otrivin or Quicks.
- Antipyretic drugs. Apply when the temperature rises to 38 ° and above. For children, Paracetamol or Ibuprofen in the form of a sweet syrup is suitable.
From folk recipes, cotton swabs soaked in a decoction of oak bark and an extract of chamomile are used, which are applied to the inflamed gums. As a symptomatic treatment, clove oil, homeopathic suppositories Viburcol are used.
How do children develop
The laying of the rudiments of the most powerful units of the jaw apparatus occurs during embryonic development, which creates the preconditions for further eruption.
During the period of intrauterine formation, the "eye" tooth is located immediately near the optic nerve bundle. The source of the root system is a special epithelial-cartilaginous plate embedded in the periosteum.
The eruption of such units of the jaw row is a difficult and painful process for a child. The upper canines appear first, then the lower ones. Exceptions to this rule are rare.
Such teeth have an elongated root deeply embedded in the jaw structure. The facial sensory fibers passing nearby innervate the facial muscles and lacrimal glands.
Therefore, the process of eruption of "eye" teeth is accompanied by intense pain syndrome, lacrimation, and other symptoms. In about 20% of cases, the lower canines appear earlier.
Complications of teething
The growth process of deciduous or permanent teeth is physiological. Therefore, complications do not arise in most children.
In rare and exceptional cases, the following are observed:
- gingival cyst, which is a pathological rounded structure of a compacted consistency and accompanied by the destruction of the jaw bone tissue;
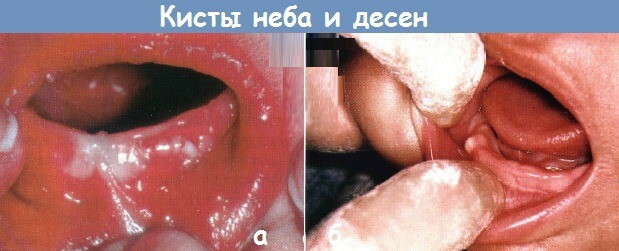
- abnormal appearance of the 2nd row of teeth, which occurs when the milk bite is changed to a permanent one, - pathology is considered an extremely rare phenomenon;
- hyperdondia, called overweight;
- retention - orthodontic deviation, leading to a distortion of the anatomical bite;
- dystopia - a dentoalveolar anomaly, characterized by an incorrect location or curvature of the erupted unit;
- crowding - a decrease in interdental spaces, contributing to the development of caries.
Any complication leads to difficulties with chewing food, aesthetic defects, distortion of the facial oval. The formation of a gingival cyst causes atrophy of the inert cells of the jaw, necrotic processes in the soft tissues of the dental bed.
Purulent exudate with blood inclusions is released. Development of chronic sinusitis is possible due to the close location of the root system to the corresponding sinuses.
A complication of the eruption of "eye" teeth is the growth in 2 rows. A rare anomaly begins to appear at the age of 5-14 years. It is caused by improper formation of the jaw apparatus due to complications caused by the eruption of "eye" teeth.
Removal in adults, risks
Loss of vision due to unsuccessful amputation of the upper canines is fiction. However, dentists take some caution when removing them. This procedure is performed only when absolutely necessary.
The "eye" tooth is located near the nerve plexuses. The risk of damaging them during removal is minimal, but it does exist. The absence of upper canines has an extremely negative effect on the chewing function and aesthetics of the face.
After removal of such an element of the upper jaw in adults, prosthetics are immediately performed. Partial one-sided blindness and numbness of a part of the face are theoretically possible only with anomalies in the development of the upper canines.
It is characterized by the contact of the optic or facial nerves with the root system of the jaw unit. An x-ray is taken before the extraction procedure. The resolution of modern diagnostic equipment allows for detailed visualization of the dentoalveolar structure.
Timely detection of abnormal deviations of the anatomical structure ensures safe removal of the "eye" tooth without complications or undesirable consequences. It is recommended that you consult with an orthodontist and an orthopedic dentist beforehand to find out the possibility of preserving the upper canine.
An important function of such teeth is the transmission of individual sounds. After removal, diction may deteriorate. In the absence of an upper canine, its chewing function is assumed by incisors with premolars, which are evolutionarily worse adapted for such work. This leads to their rapid destruction.
Interesting facts about "eye" teeth
Mythologized and obsessed with many prejudices, the most powerful external elements of the jaw structure do have several unique characteristics.
Interesting and little-known facts about "eye" teeth:
- Durable material. The enamel coating of the upper canines is the most resistant tissue of the human body to stress. It is able to withstand extremely intense mechanical pressure. Therefore, dental drills with high-strength diamond dusting are used to process such teeth.
- The amount of calcium. 80% of the building material of bone structures in the body is contained in the teeth. The upper canines have the largest specific gravity of calcium in relation to weight and size.
- Tooth enamel. Unlike other body tissues, it is unable to regenerate. The destroyed enamel coating of "eye" and other teeth can be restored only with a filling mixture.
- Powerful muscles. Of all the muscle fibers in the human body, chewing is considered the strongest. They provide the force necessary for tearing dense or solid food "eye" teeth. A maximum pressure of 15-20 kg is used to chew food. The maximum capacity of the chewing muscles is estimated at 100-120 kg.
With inflammation of the "eye" tooth, pain can be reflected in the visual analyzer due to the fact that the most powerful element of the jaw structure is located near the optic nerves. This is another reason for the informal name of the upper canines.
Ophthalmic tooth video
Where is the eye tooth in adults, in a child: