Content
- Heart rate
- Why is a high pulse dangerous?
- Increased pulse at normal pressure
- At low pressure
- Causes of increased heart rate at rest
- Above 110 bpm.
- Pulse above 120 beats / min.
- Pulse above 130 beats / min.
- Pulse 140 beats / min.
- High heart rate in the morning
- High heart rate at night
- After meal
- Which doctor should I go to?
- What to do with a high heart rate?
- First aid with high heart rate
- Video about tachycardia
An increased heart rate is called an increase the normative number of heart contractions for the control period of time, which is considered to be 1 min. In a calm state, the disorder occurs for physiological or pathological reasons.
Heart rate
The rate of blood output is measured by the number of jerky vibrations of the walls of the arteries. The rhythm of the hemodynamic process is due to the frequency of cardiac activity and is directly proportional to the number of myocardial contractions.
The exact heart rate has not been established. The physiological indicator is purely individual.

The frequency of sensible vibrations of the walls of the arterial channels depends on:
- age;
- gender;
- degree of physical activity;
- body and environmental temperature;
- the general somatic state of the body;
- psychoemotional status at the time of measurement.
The resting heart rate is typically 60-80 beats / min. The greatest influence on the change in the physiological parameter is exerted by physical stress or sports load.
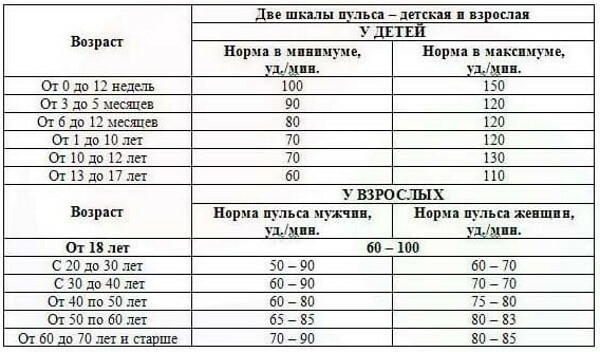
Conditional reference values of pulse activity for different ages are shown in the table.
| Age, years | Minimum rate | Limit value | Conditional norm |
| 0-1 | 105 | 165 | 133 |
| 1-2 | 95 | 155 | 125 |
| 2-5 | 85 | 125 | 105 |
| 6-8 | 80 | 120 | 100 |
| 8-10 | 70 | 110 | 90 |
| 11-12 | 65 | 105 | 85 |
| 13-15 | 60 | 90 | 80 |
| 16-50 | 62 | 85 | 72 |
| 51-59 | 65 | 86 | 75 |
| 60-80 | 70 | 90 | 80 |
The rhythmic heartbeat generates a shock-oscillatory wave that is reflected from the arterial walls and is called the pulse. Throughout life, the individual physiological indicator changes insignificantly and averages 70 beats / min.
Why is a high pulse dangerous?
Acceleration of the jerky-vibrational activity of the blood is associated with the concept of tachycardia or tachyarrhythmia. Such a diagnosis is not made, since the violation is considered not a separate nosological unit, but a symptomatic manifestation of numerous cardiovascular pathologies.
A steadily accelerated pulse provokes a stroke. In the left atrium, there is an area with physiologically slow blood flow. The increased frequency of myocardial contractions, recorded by the accelerated oscillation of the arterial walls, contributes to the excessive injection of shaped hematological elements into this zone.
As a result, the risk of blood clots increases. A blood clot can block the heart or cerebral vessels. The normal rhythm of the cardiological organ ensures the transport of oxygenated (oxygenated) hematological fluid to the internal organs and the brain.
With an excessive concentration of respiratory atoms, dizziness, fainting, vestibular disorders occur. Cardiological pathologies, acute functional organ failure develop.
Symptomatically, this condition is felt:
- interruptions in heart rhythms;
- an increase in the QT interval;
- paresthesia in the upper or lower extremities;
- sudden weakness;
- respiratory disorders;
- vertigo syndrome.
An increased pulse causes a violation of hemodynamics, creates an excessive load on the arterial walls. Tachycardia leads to a decrease in pressure in the vascular beds. The blood does not have enough time to be saturated with oxygen.
This causes hypoxia of the internal organs. The pathological effect is compensated by the continuous work of the myocardium in an enhanced mode, which leads to premature wear of the heart muscle.
Increased pulse at normal pressure
A specific symptom is characteristic of pregnancy. In women in such a physiological state, the pulse oscillations of the arterial walls are often accelerated against the background of normal blood pressure.
The danger of violation lies in the risk of:
- cardiogenic shock caused by dysfunction of the cardiac conduction system;
- pulmonary edema associated with massive effusion of transudate from the capillaries into the surrounding organic tissues;
- increased frequency of short-term fainting triggered by impaired oxygenation;
- asthmatic attacks;
- the occurrence of stabbing pains in the chest or under the scapula;
- darkening in the eyes;
- dizziness and muscle weakness, which develop against the background of hemodynamic disturbances.
The pulse in a calm state with normal systolic and diastolic pressure periodically accelerates in patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia, anemic conditions, endocrine pathologies.
This effect is often due to the situational increased demand of cells for oxygen, which is typical for physical exertion, neurotic disorders, and strong emotional experiences.
At low pressure
The combination of an accelerated pulse with hypotension occurs after drinking a large dose of alcohol, taking diuretics or beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors. This effect is caused by energy drinks, strong coffee, insufficient physical activity.
An increase in pulse activity against a background of a decrease in blood pressure is determined by physiological or pathological factors. In the first case, unpleasant manifestations do not pose a great danger and are of a short-term nature.
The symptom occurs against the background of chronic lack of sleep, overeating, nervous overstrain. After the end of the provoking effect, the pulse returns to the standard value.
Pathological tachyarrhythmia is much more dangerous. Increased pulse activity is associated with hyperthyroidism, respiratory disorders, hormonal imbalance.
The last variant of tachycardic disorder is characteristic for women during pregnancy or menopause. The danger of a pathological increase in pulse activity is an increased risk of myocardial infarction or thromboembolism of an artery of the pulmonary organ.
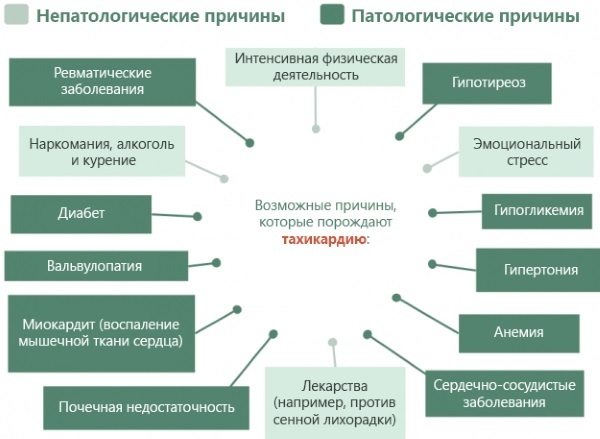
Causes of increased heart rate at rest
The symptom is accompanied by cardiac pathologies, hemodynamic dysfunctions, infectious and inflammatory processes. Acceleration of blood pulsation is characteristic of a vegetative crisis. The clinical picture is complemented by profuse sweating, chills, dry mouth.
This effect is caused by:
- deterioration in the elasticity of the arterial walls;
- damage to the valve elements of the ventricles or atria;
- functional disorders in the work of the thyroid gland, which is responsible for metabolic regulation;
- emphysema - an obstructive process in the structure of the lungs;
- violation of neurohumoral regulation;
- purulent-septic processes causing hyperthermia;
- iron deficiency in the blood;
- pneumonia;
- tuberculosis;
- chronic bronchial asthma;
- diabetes;
- impaired secretion of pituitary hormones;
- dysfunction of the adrenal glands;
- rheumatism;
- pericarditis.
Increased heart rate is a common side effect of many drugs. The symptom develops against the background of the use of hallucinogenic substances, sexual stimulants, energy drugs.
Medical reasons for a temporary increase in heart rate include taking:
- doping compounds;
- antidepressants based on amitriptyline;
- antiarrhythmic drugs - Dinexan, Cardiodarone, others;
- diuretic drugs - Cyclomethiazide, Diacarba;
- cardiac glycosides - Digoxin, Strofantin;
- vasodilating nasal drops - Naphtizin, Sanorin.
With drug-induced pulse acceleration, other physiological parameters, including blood pressure, may remain within normal limits.
Above 110 bpm.
Such an indicator is caused by pathological reasons or the result of external influences. The latter include intense physical work, sports activities, the use of stimulating substances or spicy foods. The effect disappears spontaneously after stabilization of the state of the body.
An increase in heart rate is accompanied by:
- activation of the sweat glands;
- intermittent breathing;
- muscle tension;
- trembling of fingers.
Pulse above 110 beats / min. often observed in cardiovascular diseases. The regular occurrence of a symptom in a calm state signals hypertension or chronic tachycardia. In the early stages of such diseases, accelerated blood pulsation is the only sign of a progressive pathological process.
As it aggravates and in the absence of adequate therapy, appear:
- sharp chest pain;
- dyspnea;
- feeling of constant fatigue;
- cephalalgia.
Periodic increase in heart rate up to 110 beats / min. provoke iron deficiency anemia, infectious diseases. The latter are obliged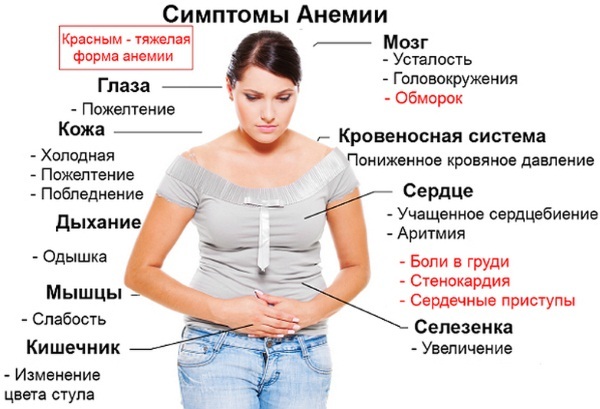 flax is accompanied by hyperthermia, which leads to such a physiological effect.
flax is accompanied by hyperthermia, which leads to such a physiological effect.
For non-pathological reasons, an increased secretion of adrenaline, provoked by a stressful situation, is noted. The hormone synthesized by the adrenal medulla has a direct effect on the rate of myocardial contractions.
Pulse above 120 beats / min.
This condition is caused by severe physical overstrain or the intake of stimulating substances. From the pathological reasons for the increase in the oscillation of the arterial walls to the level of 120 beats / min. secrete hyperactivity of the endocrine glands.
The symptom is typical for anemias of various etiologies - clinical and hematological syndromes caused by insufficient concentration in the blood of erythrocyte bodies responsible for the transport of iron-containing protein and oxygen.
The indicator of pulse activity is over 120 beats / min. often accompanied by hypoxia of tissues of internal organs. The condition is life-threatening. It is recommended to make an electrocardiogram and go through a full cycle of diagnostic examination.
Another common reason for the acceleration of the heart rate to 120 beats / min. - pumping by the cardiac apparatus of insufficient blood volume to meet the oxygen demand of cells.
This condition signals the development of dangerous pathological processes. The cellular demand for oxygen and nutrients increases with acute inflammation, causing the body temperature to rise to febrile values.
Pulse above 130 beats / min.
Such a heart rate against the background of fluctuations in blood pressure is characteristic of stressful physical exertion or vegetative vascular dystonia, which occurs with excessive sympathetic tone nerve circuit.
Pulse activity rises to 130 beats / min. with thyrotoxicosis or progressive pheochromocytoma - tumor neoplasia in the adrenal medulla. An increase in arterial wall vibrations to such a frequency at normal pressure is characteristic of tachycardia.
Other common causes of the pathological condition:
- acute infectious and inflammatory processes of any localization;
- heart failure with chaotic ventricular fibrillation;
- drug intoxication;
- food poisoning;
- a decrease in the flow of oxygen and glucose to the myocardium or cerebral areas.
Increased heart rate up to 130 beats / min. can signal vascular insufficiency, arterial collapse, exacerbation of chronic respiratory diseases.
Of the non-pathological reasons for the acceleration of vibrations of the walls of the bloodstream, there is a sharp cancellation of antiarrhythmic drugs, the intake of an excessive dose of hormonal drugs.
This condition is characteristic of unmotivated anxiety in mental disorders and panic attacks. Such symptomatic manifestations require medical intervention.
Pulse 140 beats / min.
For such an acceleration of the vibrational activity of the arterial walls, there are physiological or pathological prerequisites. This frequency is considered high. Among non-pathological reasons, strong excitement or a feeling of fear is distinguished.
The pulse in a calm state for a short time reaches 140 beats / min. with the activation of metabolic reactions.
Pathological factors of increasing the frequency of vibrations of the arterial walls:
- Cardiological pathology. The defeat of the aortic, mitral or tricuspid valve of the heart leads to an episodic increase in pulse activity up to 140 beats / min. The symptom is provoked by congenital organ defects or acquired stenosis, anatomical destruction of the interventricular septum or the membrane dividing the atria.
- Vascular disorders. Increase in pulse activity up to 140 beats / min. causes coarctation of the aorta - congenital narrowing of the blood lumen. The symptom periodically occurs in the absence of obliteration of the canal communicating the pulmonary artery with the aorta.
- Postinfarction syndrome. With myocardial damage, a partial ischemic state develops in combination with tissue necrosis. Such a pathological process leads to the formation of an aneurysm - a sac-like protrusion of the atrial walls, which causes an increase in the pulse rate.
-
Vascular atherosclerosis. The disease is characterized by the deposition of plaques on the endothelial walls, which narrow the blood lumen.
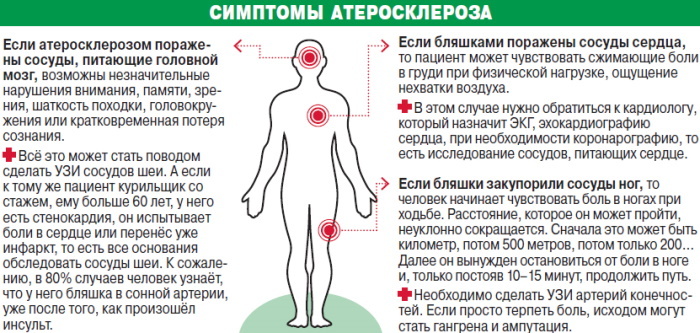
- Dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary mechanism. In these cerebral divisions there are centers responsible for respiration, heart contractions, thermoregulation. If their work is disrupted, tachycardic syndrome develops.
Increased heart rate up to 140 beats / min. cause pathologies of glands secreting sex hormones. Increased synthesis of estrogen in women and testosterone in men leads to an increase in the contractile activity of the heart muscle.
High heart rate in the morning
In the phase of night sleep, metabolic reactions, respiratory activity slow down, and blood pressure decreases. Upon awakening, the neurohumoral mechanism reduces the activity of the vagus nerves - the vagus.
There is an increase in the secretion of stress hormones cortisol and norepinephrine, which increase the heart rate. Activation of the functions of the parasympathetic part of the nervous system for the entry into the blood of a large dose of such biochemical compounds increases the blood output.
A sharp adoption of an upright position of the body after sleep can provoke a tachycardic effect. This condition is caused by the adaptation of baroreceptors, which is expressed in a decrease in arterial resistance and intravascular pressure.
High heart rate at night
In a healthy state, pulse activity decreases during sleep. Natural physiological processes change psychostimulating substances, caffeine-containing drinks, neurotic states.
Factors that increase the heart rate at night include stress, insomnia, and smoking. Tachycardic symptoms are caused by negative emotions, apnea syndrome.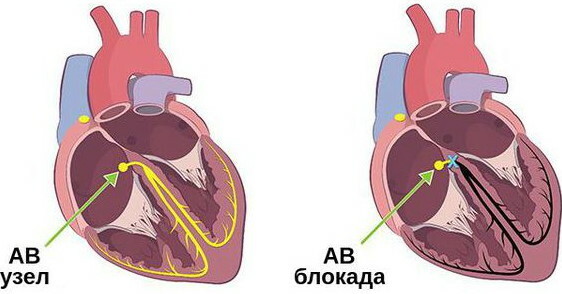
An increase in pulse activity during sleep is observed with abdominal obesity, hypertension, and impaired respiratory function during sleep. Such disorders are provoked by atrial fibrillation, blockade of the His bundle.
After meal
Symptoms after meals are rare. This condition provokes an enhanced mode of operation of the gastrointestinal tract, caused by the use of heavily digestible food. Tachycardic signs provoke bowel or stomach diseases.
Resting heart rate after eating rises due to hepatobiliary dysfunctions. This effect is caused by disorders in the work of the pancreas when eating fatty or spicy foods.
Heart rate is affected by some bioactive food additives, reactions of individual intolerance to a particular chemical compound or nutrient. This is due to an inadequate immune response to the entry of foreign substances into the bloodstream.
Dense food causes a short-term tachycardic effect in vegetative-vascular dystonia, chronic gastritis, pancreatitis. An increase in heart rate provokes dyskinesia of the biliary tract after eating foods or foods with high fat content.
Which doctor should I go to?
A cardiologist deals with the treatment of diseases with tachycardic symptoms. After the initial examination, depending on the established etiological factor of increase pulse activity may require consultation:
- angiologist;
- allergist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- oncologist;
- immunologist or other narrow specialist.
It is necessary to consult a doctor in case of frequently recurring attacks of tachycardia, pulse rate over 140 beats / min., Periodic loss of consciousness.
What to do with a high heart rate?
The tactics of therapy is determined by the cause of the symptom. Anemic conditions are eliminated with a course of iron-containing drugs.
For colds, inflammatory or infectious causes of acceleration of vibrational contractions of the arterial walls are prescribed:
- antipyretic drugs;
- antibiotics in accordance with the sensitivity of the pathogen;
- antibacterial agents of a wide range of effects;
- antiviral medicines.



For the relief of cardiac arrhythmias, glycosides are used, cardiological drugs of various pharmaceutical categories, depending on the revealed dysfunction. Complex therapy includes selective beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors - Atenolol or Propranolol.
With increased production of adrenaline, which causes tachycardic symptoms, Phentolamine is prescribed. To eliminate signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia, nervous disorders, plant-based preparations are used - Persen, Novopassit or analogues.
In severe cases, Diazepam or Phenobarbital is used. Effectively suppress tachycardic symptoms of Valocardin, Tenoten, Afobazol. Drug therapy is combined with the elimination of factors provoking an increase in the frequency of oscillations of the arterial walls.
First aid with high heart rate
Intravascular pressure and heart rate normalize green tea. Such a drink can be used as part of pre-medical non-drug care. With increased pressure, take Furosemide or Metoprolol.
Of the first-aid techniques, the Valsalva test is used to reduce the heart rate, which consists in performing deep breathing movements and trying to release air with the palm of the nose and mouth clamped, tension of the anterior peritoneal walls.
The activation of the cough or gag reflex helps to reduce tachycardic symptoms. The techniques are used with an extreme increase in pulse activity. The meaning of such manipulations is to stimulate the vagal mechanism.
Carotid sinus massage is performed by pressing several times on a rapidly pulsating point of the cervical surface in the area of the carotid artery. It is forbidden to carry out a stimulating procedure in case of atherosclerotic lesion of the target blood channel.
This method of decreasing the pulse rate is contraindicated in patients with myocardial infarction, ischemic disease, and stroke. It is advisable to eliminate an increased heartbeat in a calm state before medical intervention with safe and light herbal preparations - Corvalol, motherwort tincture.
Video about tachycardia
Rapid pulse. How to cure without pills: