Diabetes mellitus is one of the diseases that is dangerous for life by the rapid development of complications. The disease is characterized by a huge list of possible consequences affecting various organs and systems of the body.
After confirming the diagnosis, the patient is obliged to develop new food and behavioral habits - to direct all efforts to prevent complications.
Contents
- 1 Causes of complications of diabetes mellitus
- 2 Complications of type 1 diabetes
- 3 Complications of type 2 diabetes
- 4 Late complications of diabetes
- 5 Prevention of complications of diabetes
Causes of complications of diabetes mellitus
Complications of type 1 diabetes are developing due to lack ofinsulin or a violation of its interaction with the cells of the body. So, with type 1 diabetes, insulin deficiency arises because specialized cells that produce this hormone are recognized by the immune system as foreign - it produces antibodies against them, causing death.
This type of diabetes refers to autoimmune diseases. Type 1 diabetes mellitus has a genetic predisposition. The mechanism can be triggered by infections, stress, etc.
Insulin in the second type of diabetes can be produced in the right amount, but the body cells become insensitive to it. Often this phenomenon is observed with obesity, because the fat tissue does not react to insulin.
The pancreas has to work with the load, producing more and more insulin. At some point, its compensatory mechanisms are depleted, and insulin production is reduced.
The function of insulin is to deliver glucose to the cells of the body for use as an energy material. Unused cells, glucose, circulates in the blood, excreted in the urine. Cells begin to suffer from a lack of energy, metabolic processes are disrupted.
Complications of type 1 diabetes
Complications of type 1 diabetes are acute and develop very rapidly. In most cases, a diabetic needs a doctor's help.
1. Ketoacidosis - when the insulin level falls, ketone bodies in the blood and glucose in excess are detected. If deficiency of insulin in time is not replenished, then within a short time ketoacidotic coma can develop.
2. Hyperosmolar coma. The cause of its development in the increase of sugar in the blood. Cells lose water, dehydration occurs, and in the absence of therapy death may occur.
3. Hypoglycemic coma. Occurs in the case of an erroneous introduction of insulin in doses substantially exceeding those chosen by the physician. The brain is hard to tolerate glucose deficiency, so when the level falls sharply, normal brain function is disrupted.
This causes turbidity or complete loss of consciousness, and in the future to whom.
The complications of diabetes in children are dangerous because of their high lethality and are manifested as ketoacidotic and hypoglycemic coma.
Late forms are similar to those in type 2 disease - they have a slow but progressive course.
Complications of type 2 diabetes
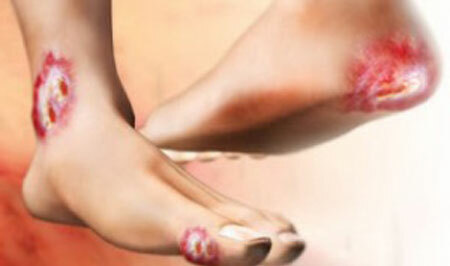
Risk of developing the "diabetic foot" syndrome
In case of type 2 diabetes, the disease can go on for many years without being noticed. Often the disease is revealed quite unexpectedly, during the delivery of tests on another occasion or only at the time of detection of complications.
- Hyperosmolar coma.
- Somewhat less often occurs hypoglycemic coma
- Eye damage. At the same time, the lens and the retina of the eye suffer. It is manifested by the development of cataracts, hemorrhages and detachment of the retina, which leads to a decrease in vision or complete loss of it.
- Renal damage is a gradual loss of its functions. Reabsorption of the protein is disturbed and it appears in the urine. With the years in the kidneys there is a growth of scar tissue, which removes the kidney tissue.
- Vascular complications are pathological changes in the walls of vessels of large and small caliber. It is manifested by increased fragility, hemorrhage, thrombosis and the development of atherosclerosis. Infarctions and strokes in diabetics are the main cause of death.
- Neuropathy - changes in nervous tissue. Is manifested by a violation of sensitivity, pain along the nerve fibers.
- From the side of the brain, diabetic encephalopathy is detected. It manifests itself in the form of depressions, inability to respond adequately to events, etc.
Late complications of diabetes

Detachment of the retina
Late complications are those clinical manifestations that develop after several years from the onset of the disease. Such complications, unfortunately, sooner or later appear in almost all patients, regardless of what type of diabetes it is.
With type 2 diabetes, most people find out about their ailment only after the development of these complications.
1. Angiopathy. Changes in the vessels lead to heart attacks, increased pressure, strokes and thrombosis.
2. Retinopathy. Disturbance of blood circulation in the retina of the eye can lead to its detachment and complete blindness.
3. Nephropathy. Becomes the cause of hypertension and chronic renal failure.
4. Polyneuropathy. Inflammatory and degenerative changes in nerve fibers. It leads to a loss of sensitivity and the appearance of pains of an uncertain nature.
5. The formation of the syndrome of diabetic foot. Due to the fact that with diabetic nerve fibers and small vessels of the extremities suffer, the feet lose sensitivity, blood circulation is disturbed. A diabetic may not feel injuries, temperature changes, wear shoes that press him, etc.
As a result, damage occurs that does not heal for a long time. Because of metabolic disturbances, poor blood circulation, wounds can not regenerate quickly, and increased "sweetness" of blood is the best food for microorganisms.
The infection is further inhibited by healing. Fabrics can die completely. The process goes so far as to amputate the toes or the entire limb.
- More on diabetic foot syndrome
- Recommendations for choosing footwear for diabetics, prevention of
syndrome Prevention of complications of diabetes mellitus
Diabetics should visit the endocrinologist regularly and take tests to monitor the condition of target organs.
- Blood glucose - daily.
- The oculist - every six months.
- Urinalysis - at least 4 times a year.
- ECG - with pain heart in heart.
- Blood pressure - it is desirable to have a tonometer in the home medicine chest and measure the pressure every day. Especially if there were cases of its increase.
- If there is a sensitivity disorder in the lower extremities, then every 3 months it is necessary to be examined for the presence and severity of neuropathy.
Most endocrinologists believe that diabetes is a special way of life. Prevention of complications lies in a special diet, regular intake of insulin or medicines and daily monitoring of glucose.
Only strict adherence to these rules will help to avoid the development of complications. With diabetes, caused by obesity, it is enough to lose weight and the level of sugar comes back to normal.



