Content
- How the throat is connected to the ears and why congestion occurs
- What diseases cause sore throat and congestion in the ears, which ones cause fever
- ARVI
- Tonsillitis
- Exudative otitis media
- Acute pharyngitis
- Wisdom teeth
- Swelling in the throat
- Damage to the salivary glands
- Bacterial infection, streptococcus
- Viral infection, mononucleosis
- Allergy
- Pathology of the maxillofacial joints
- Sinusitis
- How to diagnose the cause
- Laboratory research
- Physical and instrumental examination
- Methods and treatment regimens, depending on the cause of the disease
- Drugs
- Folk remedies
- Physiotherapy
- Videos about ear congestion and sore throat
Infectious processes in the upper respiratory tract cause swelling of the mucous membrane, pain, irritation. Similar symptoms are observed with angina, pharyngitis, colds. In such cases, not only sore throat, but also clogs ears.
How the throat is connected to the ears and why congestion occurs
Since the ear, nose, and throat are connected, they function as a single unit. The downside is that a breach in one area can cause problems in another. The ear, nose and throat are part of the upper respiratory tract and share the same mucous membranes. ENT organs always share infections with each other because the ducts and pathways that connect the ear, nose, and throat allow viruses and bacteria to move between them.
- The ear has 3 parts: outer, middle and inner. The middle ear is connected to the upper part of the posterior wall of the pharynx by the Eustachian tube, which is lined with mucous membranes, like the inside of the nose and throat. The eustachian tube contains tiny bones through which sound travels to the ear.
- The nose is divided into 2 parts: the visible part is called the front, and the inside is called the back. Both bows lead directly to the throat.
- The throat consists of 3 parts; the nasopharynx, located behind the nose, the oropharynx behind the mouth, and the larynx, where the voice box is located.
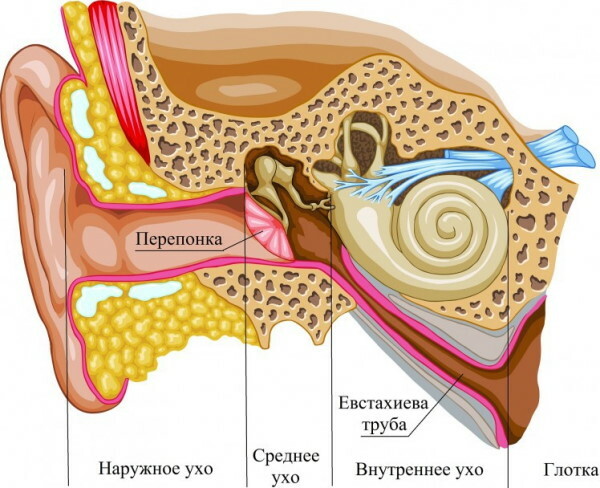
The entire system is surrounded by a system of cranial sinuses with a diameter of no more than 2, see. They are located on the cheekbones, in the center of the forehead, between the eyes and in the nose. This interconnected ENT system helps breathe, smell and taste.
A sore throat and obstructed ears are common when an illness or infection affects the area around the head. Each ear has a narrow passageway that connects the middle ear (the part containing the eardrum with tiny bones that help transmit sound) with the back of the nasal passages and the top throat.
These tubes (Eustachian tubes) open and close regularly to regulate the air pressure in the middle ear, remove natural fluids from it and circulate new air inside ear.
When a person is struggling with an upper respiratory infection or allergies, the openings of the Eustachian tube may be partially blocked due to tissue inflammation and mucus secretion. The inflammatory process interferes with the normal functioning of the tubes, which leads to pressure imbalances. This produces a blockage-like sensation that occurs due to a sudden change in air pressure, such as when a person is on an airplane.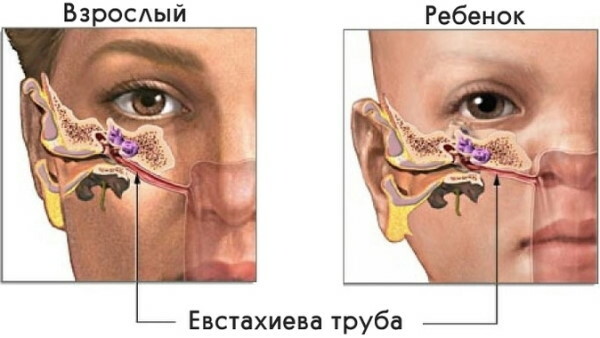
The inflammation in the throat leads to a buildup of fluid, which creates additional pressure in the ears. When the Eustachian tubes are partially blocked, it is more difficult for secretions from the middle ear to drain down the back of the pharynx, which can lead to an uncomfortable feeling of fullness in the pinna.
What diseases cause sore throat and congestion in the ears, which ones cause fever
Sore throat and clogs ears in case of infectious diseases: otitis media, measles, fever, chickenpox, tubotitis, diphtheria, tonsillitis. There are many reasons for ear plugging: from the formation of a sulfur plug to the pathological condition of the maxillofacial joints.
ARVI
Placing the ears during the period of ARVI disease is associated with the structure of the ENT organs. The painful process makes it difficult for air to pass during a cold. This leads to short-term obstruction of the ears. As the condition improves, hearing is restored, and the feeling of congestion disappears.
Tonsillitis
With inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils, swelling of the soft tissues increases.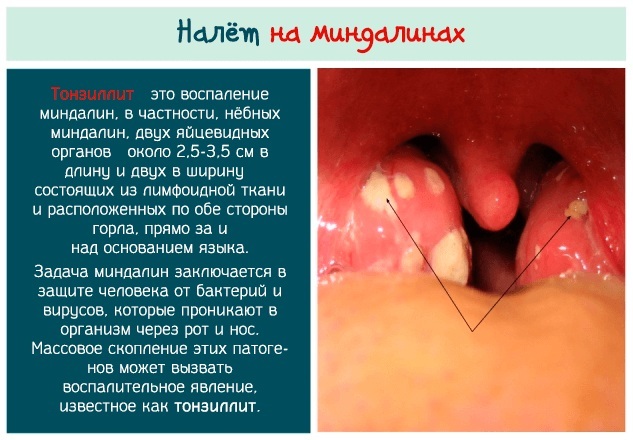 The painful process disrupts normal air circulation and leads to ear congestion.
The painful process disrupts normal air circulation and leads to ear congestion.
Exudative otitis media
The disease affects the middle ear. Serous-mucous fluid begins to accumulate in the cavity behind the tympanic membrane. Pathology leads to the development of ear congestion, turning into hearing loss.
Acute pharyngitis
The appearance of ear congestion indicates the spread of the edematous process from the oropharynx to the nasopharynx. The defeat of the mouth of the Eustachian tubes leads to a drop in pressure in the middle ear, which contributes to the obstruction of the ears.
Wisdom teeth
A wisdom tooth erupting can cause differential pressure in the ear. The trigeminal nerve is to blame for this. It connects part of the face, organs of sight and hearing. In addition, the close location of the root system of the upper jaw to the ear canal enhances the influence of the wisdom tooth on the auditory organs.
Swelling in the throat
A swelling in the throat leads to the unpleasant sensation of a clogged ear on one side. An overgrowth of cancer cells blocks airflow, preventing the pressure in the middle ear from returning to normal. Abnormal pressure affects the condition of the eardrum and causes ear congestion.
Damage to the salivary glands
Damage to the facial nerve and directly tumors of the salivary glands disrupt the process of equalizing pressure in the middle ear system. 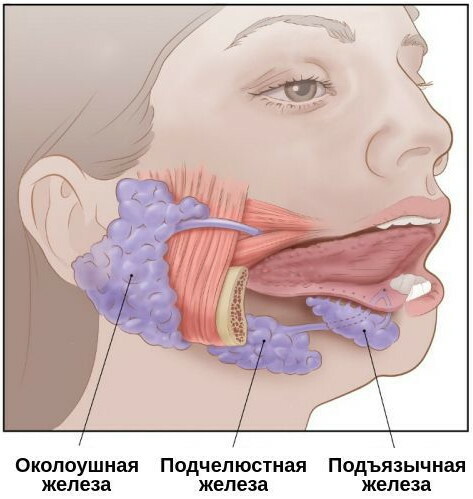 Inflammation of the parotid salivary glands leads to swelling of the surrounding tissues, they press on the eardrum, leading to congestion.
Inflammation of the parotid salivary glands leads to swelling of the surrounding tissues, they press on the eardrum, leading to congestion.
Bacterial infection, streptococcus
The spread of a bacterial infection, in particular streptococcus, leads to the development of eustachitis. Inflammation in the Eustachian tube is the cause of increased pressure in the auricle.
Viral infection, mononucleosis
Pawns ears also in case of viral infections, for example, with mononucleosis. The condition is characterized by a congestion in the nose, throat, or ears. The defeat of the throat and lymph nodes is responsible for the development of swelling in the middle ear and the appearance of congestion. Sometimes there is a sore throat.
Allergy
Contact with an allergen leads to swelling and difficulty in the passage of air into the tympanic cavity. Antihistamines are used to relieve puffiness.
Pathology of the maxillofacial joints
Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint is characterized by general malaise, pain, ringing in the ears, and their congestion. Painful conditions include joint dislocation, internal disorders, arthritis, arthrosis, and musculo-articular dysfunction. The main causes of illness are injuries, eating rough food, systemic disorders, infectious processes, bad habits and improper dental treatment.
Sinusitis
Inflammation of the lining of the paranasal sinuses or sinusitis develops due to infection with a virus, bacteria, fungi, or due to an allergic reaction. 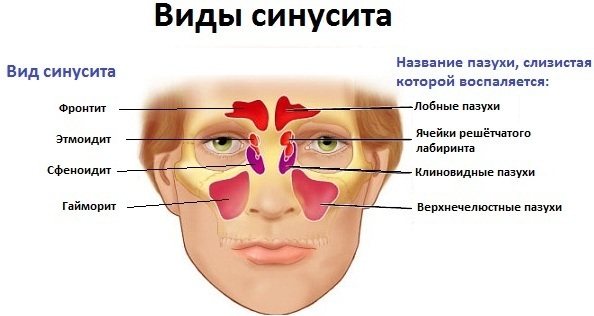 Nasal congestion with purulent fluid provokes swelling, the entry of the pathogen into the Eustachian tubes, which leads to a feeling of ear congestion.
Nasal congestion with purulent fluid provokes swelling, the entry of the pathogen into the Eustachian tubes, which leads to a feeling of ear congestion.
How to diagnose the cause
The doctor will investigate the structural causes of hearing impairment, such as genetic diseases, sulfur buildup, or inflammation-based fluid buildup.
A sore throat and obstructed ears with colds that do not require surgery. If fluid from the inner or middle ear is clear (uninfected), then a wait-and-see approach is likely to be suggested.
Laboratory research
Laboratory research is necessary to clarify the etiology of the inflammatory process, accumulation of exudate or pus.
- A complete blood count is a basic test to determine if there is a bacterial or viral infection. With a viral lesion, the number of leukocytes remains normal or underestimated, lymphocytes and monocytes are increased, ESR is normal. With a bacterial infection, leukocytes are increased, lymphocytes are below normal and ESR is increased.
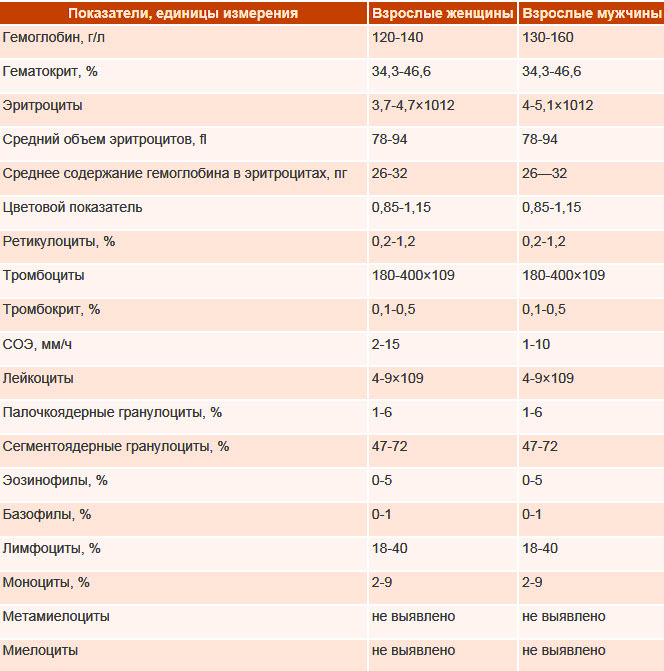
- The analysis of the separated fluid from the ear is examined in the presence of a purulent or serous lesion of the mucous membrane of the auditory tube. The results of the analysis show the presence of an infectious process caused by streptococci, staphylococci, enterobacteria, corynebacteria or yeast-like fungi.
In addition to determining the flora, it will be necessary to sow the discharge for sensitivity to antibiotics.
Physical and instrumental examination
Physical and instrumental examination methods include video endoscopy, audiometry and tympanometry.
- Endovideoscopy allows you to examine the condition of the ear cavity. To do this, use an endoscope - a thin tube equipped with a video camera. The process is painless and takes no more than 10 minutes. Before the examination, the doctor instills a vasoconstrictor to facilitate the passage of the endoscope. The high-sensitivity camera allows visualization and instant display of the image on the monitor for assessment of the condition. The advantages of the method are high quality of examination, early detection of pathology, examination of hard-to-reach areas of the tympanic cavity.
- Audiometry is performed in a special muffled room. Sounds of various frequencies and intensities are transmitted to the patient in headphones. The patient's task is to press the button while playing. The results are presented in the form of an audiogram - a graph of the ability to hear sounds of different frequencies.
- Tympanometry - a method for examining the ossicles, auditory tube and tympanic membrane. Using a tympanometer inserted into the external auditory canal, the presence of foreign bodies or damage to the tympanic membrane is determined. The procedure is painless and takes no more than 20 minutes.
Methods and treatment regimens, depending on the cause of the disease
With a slight inflammation, the use of folk remedies is allowed. However, in the case of the development of an infectious process or other pathologies, specialized drug treatment is required. To enhance the effect of pharmaceuticals, physiotherapy treatments are used.
Drugs
The pressure in the ears is restored when the underlying infection or illness has passed. This can happen either naturally, as with the common cold, or with prescribed medications, such as a bacterial sinus infection.
| Type of disease | Drugs |
| Otitis |
 For otitis media, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drops are required. Salicylate choline is used to reduce discomfort. Such an active substance is part of Otinum, Otovedin. For an additional antiseptic effect, Albucid or another drug based on sodium sulfacyl is prescribed. For otitis media, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drops are required. Salicylate choline is used to reduce discomfort. Such an active substance is part of Otinum, Otovedin. For an additional antiseptic effect, Albucid or another drug based on sodium sulfacyl is prescribed. |
| ARVI | With ARVI, drops based on naphazoline nitrate, oxymetazoline hydrochloride, xylometazoline are used. Nasal drops reduce mucus production and stabilize the pressure in the middle ear. |
| Fungal infection | For infections, antibiotics are used in combination with rifampicin, neomycin sulfate, chloramphenicol, lidocaine, and norfloxacin. The most popular trade names: Otipax, Garazon, Otinum, Otofa, Normax, Candibiotic, Ototon. |
Treatment regimens with the above drugs:
- Otipax - 4 drops 3 times a day for 10 days.
- Garazon - placing a moistened tampon in the ear canal, re-wetting every 4 hours. A new tampon is placed in 24 hours.
- Otinum - 4 drops 2-4 times a day for up to 10 days.
- Otofa - up to 5 drops 3 times a day for no more than 3 days.
- Normax - 1-2 drops 3-4 times a day for no more than 2 days.
- Candibiotic - up to 5 drops 3-4 times a day for no more than 1.5 weeks.
- Ototon - up to 4 drops, 3 times a day.
Folk remedies
Sore throats and blocked ears are unpleasant symptoms, but sometimes local therapy at home provides relief. Folk remedies are used in mild, unperturbed cases, and after consulting a doctor.
- A wet compress helps with sinusitis. The towel is soaked in warm water, wrung out thoroughly and applied to the ear.
- For colds, inhalation over a container of hot water or with an inhaler helps to get rid of mucus. To increase efficiency, add 2-3 drops of eucalyptus oil to the water.
- Congestion relieves gargling with warm salt water. Warm drinks and broths, which should be taken every 3 hours, also help.
- Tea or coconut oil can help with otitis media. Oil in the amount of 2 tsp. l. heated and instilled with a pipette into the ear. After a few minutes, the ears should be cleaned with a cotton swab.
- Purulent discharge helps to remove a tampon soaked in propolis tincture. 1/3 cup of alcohol will require 30 g of propolis. After insisting for a week, the product is ready to use. Tampons are placed superficially in the area of the auricle 2 times a day for 2 weeks.
Physiotherapy
Regardless of the cause of the disease, physiotherapy treatments have a stimulating effect. The use of physical forces allows the drug to be delivered to the target faster and to keep it in the tissues for a long time.
- Electrophoresis. With this method, ionized drug particles are faster delivered to the circulatory and lymphatic systems. Electrophoresis helps relieve swelling, inflammation, relieve pain.
- Aerosol therapy is a method of administering pharmaceuticals. For the treatment of ENT organs, aerosols of medium and low dispersion are used. Steam, wet, oil or dry inhalation helps intensive absorption and accumulation of the drug in the submucosa.
- Ultrasound therapy has a complex effect on the body, helps the intensive accumulation of the drug and its long-term preservation in the body.
- Ultraviolet irradiation causes the formation of biologically active molecules. They increase blood flow, permeability of cell membranes, activate enzymes to stabilize metabolic processes.
- Ultra-high-frequency therapy works with a continuous or pulsed ultra-high power electric field. The technique is used to relieve puffiness, increase vascular permeability and improve microcirculation in the focus of inflammation.
The ENT system is important for health and well-being. If there are chronic diseases in which the ears are blocked, nasal congestion constantly occurs, it often hurts throat, trouble breathing or sleeping, chronic cough, you should immediately make an appointment with ENT doctor. Sometimes, simple ear congestion can be a symptom of a variety of conditions, from a harmless cold to developing throat cancer.
Videos about ear congestion and sore throat
Ears from a cold: