Content
- Definition
- Forms
- Casualties
- Systemic
- Feedback type
- Statistical
- Target
- Principle
- Practical implementation in the cultural and historical concept
- Determination Concepts
- Behaviors
- Mental development
- Subjective determinants of psychological development
- Sociocultural
- Social
- Personalities
- Problems and criticism
- Determinism video
The first mention of the term "determinism" recorded back in the Middle Ages. Then this is a logical explanation of the concept and the antonym of the word "generalization". The first theories and ideas of determination in ancient Greece were associated with causality and necessity were described by Leucippus in the 5th century BC, then Democritus was engaged in their study. In the XVI-XVII centuries, this concept in psychology takes on a new meaning - conditioning.
During this period, the foundation was laid for the formation of mechanistic determinism. From this point on, the concept is used to explain the regularity, universality and dynamics of certain objects and categories.
Definition
Determination is the dependence of the phenomena of psychological processes on the specific circumstances that form them. The concept of "determinism" comes from the Latin "determinare", which translates as to define, limit, which reflects the main idea of this direction in psychology - the relationship of the phenomenon and processes.
The theory of determination originates from the teaching of philosophy, which recognizes the lawfulness of the interdependence of the phenomena of the objective world. This approach has become the most important component of scientific methodology, which set itself the goal of research to identify the causes and patterns of occurring phenomena. Determination is used to study nature, society and the human psyche.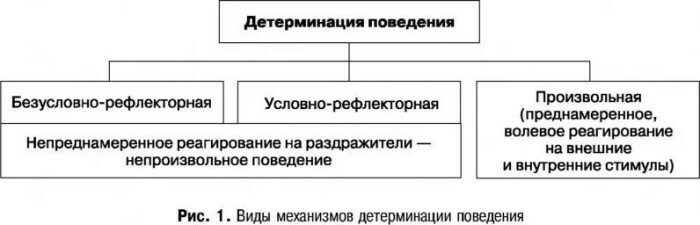
Main directions:
- Mechanistic determination. It arose in the 17th century during the period of active development of science. The principle of determinism was most developed in the studies of R. Descartes: separated body and soul.
- Biological determination. It appeared in the middle of the 19th century. Charles Darwin and Bernard are considered to be the founders of this trend. According to their ideas, life is expedient and each organism strives for self-preservation and survival.
- Psychic determination. The author is considered V. Wundt, who put forward the theory of the closure of the causal series: some phenomena of consciousness cause others.
- Macrosocial determination. Prerequisites in the teachings of J. Locke, who argued that a person is born with a blank sheet on which humanity writes its letters. This direction is focused on the study of psychological causes in the social life of a person.
- Microsocial determination. The psyche is due to the interpersonal interaction of people: social experience, communication and interaction with another person, etc. The prerequisite was the work of Freud, in which he argued that personality traits are formed in the family.
The authors of the determination:
- Outstanding philosopher and psychologist S.L. Rubinstein developed an approach in psychology that is based on a philosophical principle: external causes act through internal conditions. Accounting believed that the development of an individual's brain activity directly depends on external environmental factors. The formation of the nervous system occurs as a result of the interaction of the individual with the outside world.
- According to the teachings of L.S. Vygotsky, the certainty of mental processes is based on causation. Nothing happens by accident, there must always be a reason. Thus, manifestations of human will are based on the principles of necessity and regularity.
- TO. Höfer believed that any phenomenon is formed under the influence of the conditions, phenomena and laws of nature that precede it.

Determination in psychology.
Modern determinism has absorbed all previous theories and approaches, up to the ancient one. For example, the specifics of causation is difficult to comprehend without the interconnection of different processes, phenomena or objects. Movement and matter have the ability to move, transform, information is transferred and reincarnated from one form to another.
Forms
Determination in psychology is the interconnection of processes and phenomena, which is characterized by the following forms:
Casualties
Considers causality as a complex of circumstances, factors that preceded a specific event in time and influenced its formation.
Systemic
A form that defends the perception of the dependence of specific system components on the properties of the system itself.
Feedback type
The consequence affects the cause that caused it.
Statistical
The origin, for identical reasons, of effects differing within certain limits, depending on statistical regularities.
Target
The goal defines the process aimed at achieving it.
Principle
Determination in psychology is scientific knowledge, the development of which for a long period was focused on mechanical determinism, representing the causality of the occurrence of certain mental phenomena, phenomena, processes by material causes by analogy with the work of mechanisms. Despite the primitiveness of this ideology, it gave psychology a number of important doctrines (about affects, associations, reflexes, and others).
Biological determinism developed in the middle of the 19th century. If, in the era of the mechanical, the psyche was considered as a phenomenon, the formation of which depended exclusively on from external factors, then biological, perceives the psyche as an integral part of life person.
The formation of psychological determination is carried out with the understanding that the psyche has an independent causal meaning.
Mechanical and biological determinism is reflected in the need to study mental phenomena, phenomena, processes inevitable dependence on the factors provoking them.
Psychological determinism is based on the understanding of the fact that mental phenomena, processes and phenomena, predetermined by the influence of external factors, arise according to laws that differ from physical and biological.
The development of the psychological direction led to the rejection of the perception of the psyche as an education, closed in himself, which made it possible to reveal the area of mental development for the implementation of objective research.
Practical implementation in the cultural and historical concept
The cultural-historical concept is based on the idea that as a result of the individual development of a person under the influence socio-historical circumstances and the individual's assimilation of human culture during communication with other people, natural mechanisms of mental processes.
The most important stage in the practical application of determination in psychology was the formation of the historical and cultural theory of the Soviet psychologist L.S. Vygotsky, who is the founder of the Marxist experimental tradition of mastering the higher functions of human psychology. This theory was developed in the 20-30s of the XX century and considered the social environment as the main source of personality development.
As they grow older, the formation of a child as a person is carried out under the influence of cultural and natural processes of maturation, as well as developing behavior and thinking.
According to the psychologist, the formation of thinking and other mental functions can occur in combination with external activity using social factors and cultural means. This theory proved that the source of a child's development is cooperation and the creation of a dialogue with an adult.
It follows from this that the principle of determination is one of the fundamental principles of psychology, causing the need for a comprehensive study of psychological phenomena, phenomena and processes.
Determination Concepts
Determination is in psychology three types of factors: social, cultural and hereditary. The latter are also called "physiological determinants." These are unique, individual traits for each individual personality, which mean size anxiety threshold, how much a person is conservative and concentrated or, on the contrary, emotional and absent-minded.
Behaviors
Determination of personality behavior in psychology consists not only of individual qualities, but also of the characteristics of the external environment. This is expressed in the inevitable activity of a person in the social field, which refracts personal intentions and forms specific roles in the behavior of a person.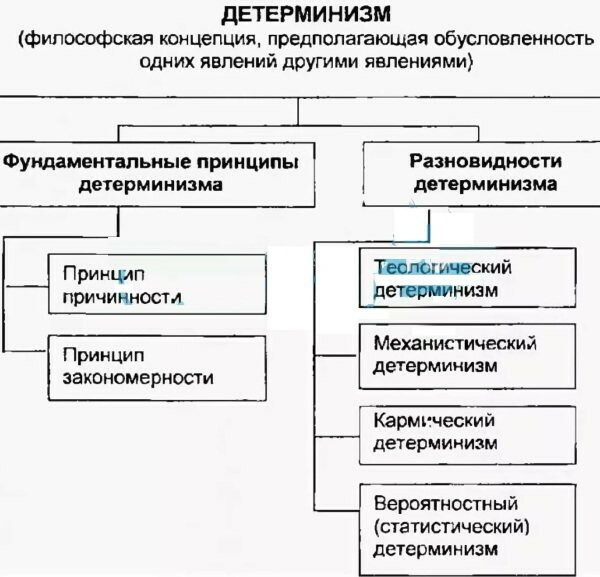
External determination can be expressed in the form of social coercion, manipulation, and violence. It is society as a whole, its social institutions that influence the life and activities of a person, from modeling his feelings to industrial and family relations. Society acts as a framework that influences all human manifestations.
Through the main goal, internal psychic determination affects the public domain. Interacting with society, a person consciously determines the goals of his activity and life, however, they, like the method of achieving them, are closely related to the intrapsychic determination of the personality. It has, albeit indirectly, a serious impact on social behavior and determination.
Mental development
Determination in psychology is a technique that determines the factors that shape the behavior of an individual and her mental internal processes. The development of the psyche depends on many factors that can be conditionally divided into objective and subjective.
Objective determinants include factors that consist of macrosocial elements:
- the degree of development of society in terms of culture and economy;
- the specifics of raising a child;
- an indicator of care for a person and the level of satisfaction of his need for intimacy;
- ethnocultural specificity.
Also, the objective factors of formation include microsocial, physiological and mental determinants. The first include educational processes in the family, kindergarten, school.
Physiological and mental reasons include:
- features of genetics;
- diseases;
- character.

Distinctive features of objective determinants are that the child is not a participant and active subject in the sense that a certain activity does not depend on the specifics of a particular person, but satisfies the interests of certain groups of people, or is an external circumstance (features of genetics, diseases).
Subjective determinants of psychological development
Despite the fact that subjective reasons are directly conditioned by objective ones, they constitute an important part of the internal logic of personality formation, especially self-development. These determinants cover the process of development of the motivational-need area, the development of consciousness and self-awareness, as well as the style of human behavior.
Sociocultural
Sociocultural determination includes the impact of society on something (practical and social needs, ethnic and cultural traditions, moral and ethical rules, political and ideological installations, etc.).
The social environment in which a person acts and exists is a collection of different meanings: images, physical objects, emotions, colors, people.
People give meanings to objects in the form of definitions, depending on their properties. But any item has several properties. The creation of meanings consists in the process of highlighting some of the properties, due to generally accepted, culturally fixed methods of their use.
Social
Social determination is one of the basic laws of sociology, which lies in the universal relationship and cause-and-effect relationships of various social phenomena.
This direction was first studied by the French philosopher, Emile Durkheim.
The social processes of the individual can be influenced by the forces that regulate the flow of ideas. Forming beliefs in the society of an individual, his reactions and actions to impulses are predetermined in order to comply with social norms imposed on the individual. A worldview can be created through social institutions: schooling, which is a territory where opposing forces reflect their political and social interests.
Personalities
The ability to carry out purposeful activities, which is expressed in building communications with others members of society, getting an education, mastering a profession, etc., a consequence of the full development of the psyche is formed personality.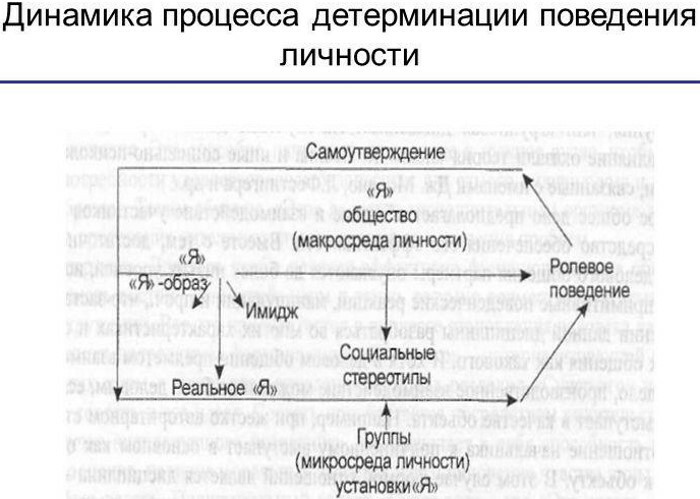
As they grow older, the mental development of a person constantly goes to new stages. With the deepening of consciousness, actions are enriched. Thanks to positive activity, socialization takes place in society: the construction of personal relationships, implementation in the profession, take a certain position, form a circle of friends, and more.
Problems and criticism
The problem of determination in psychology directly affects the themes of freedom of choice, expression of will and responsibility for one's own destiny.
The ability of a person to have his own opinion and to choose is called self-determination. It is she who distinguishes people from other living beings.
The paradox and complexity of the concept often leads most scientists to side with indeterminism - a philosophical doctrine that denies the objectivity of causality, or its value in studying with a scientific points of view.
Representatives of the idea are critics of determinism and believe that the will of a person is autonomous and does not obey any reasons and laws. Despite this, among Russian and foreign scientists, there are representatives who adhere to a strictly deterministic approach and argue the modernity and relevance of this doctrine.
One of the fundamental principles in psychology is determination. This teaching is the dependence of mental processes on certain objective or subjective factors. This approach is used for comprehensive scientific activities, focusing on the need for a comprehensive study of psychological phenomena.
Determinism video
Determinism: