Content
- Essence and basic principles
- Indications
- Helpful hints
- Approved and Recommended Products
- Phytonutrients
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Whole Grain Products
- Vitamin B12
- Lipoic acid
- Lean sources of protein
- Fruits and vegetables
- Ginger
- Water
- Prohibited foods
- Gluten
- Alcohol
- Added sugar
- Refined grains and cereals
- Trans and saturated fats
- Salty snacks
- Heavy metals
- Spicy and pungent food
- Foods that increase inflammation
- What can replace prohibited
- Main menu
- Menu for a week without restriction of animal products
- Vegan menu for the week
- Efficiency
- Video about a diet for polyneuropathy of the extremities
Polyneuropathy or peripheral neuropathy Is damage to several peripheral nerves in the lower or upper extremities. These nerves are located outside the brain and spinal cord in the body and carry information between the central nervous system and other parts of the body.
Polyneuropathy can affect the nerves responsible for sensitivity (sensory neuropathy), movement (motor), or both (sensorimotor). It can also affect the autonomic nerves that control the digestive system, the bladder, and even regulate blood circulation and heart rate. To avoid the development of this dangerous condition, they take medications and adhere to a certain diet.
Peripheral neuropathy is most often a serious complication of diabetes. In only a few cases, this condition manifests itself as a result of other diseases (such as cancer), alcohol abuse or injury. When feet are affected, people describe their condition as a sensation, as if the feet are ankle-deep in broken glass or hot coals.
The hands, as well as any parts of the limbs, can be affected in the same way. Other possible symptoms of the disease are numbness, itching, weakness, and loss of balance. Medicines do not always help, however, a special diet prescribed for polyneuropathy is known for its high effectiveness.
Essence and basic principles
More than half of people with diabetes experience symptoms of peripheral neuropathy from time to time. This is thought to be due to damage to fragile nerve fibers by high levels of glucose in the bloodstream. In addition, its increased amount can interfere with the transmission of nerve signals and weaken the vessels that supply the nerve endings with oxygen and essential minerals.
In addition to high glucose levels, the symptoms of polyneuropathy are exacerbated by inflammation, which causes heat and tissue swelling. The body uses the inflammatory response to heal damage or fight infection, but too much inflammation causes pain and damage to tissues and nerves.
A diet for polyneuropathy of the lower extremities affects the body in two ways: by reducing blood sugar levels in the bloodstream and reducing inflammation. To date, it has been proven that some foods increase inflammation, while others reduce them.
High glucose levels significantly affect the manifestations of peripheral neuropathy. Most people have the highest blood sugar levels after a meal, so reducing the spike in food intake is the first step in fighting the disease. This is achieved by consuming foods that are high in fiber and / or that are slowly absorbed into the bloodstream (low GI).
On the other hand, refined starches and sugars quickly raise glucose levels, causing further nerve damage and should be avoided. For the same purpose, you should eat in small portions and significantly reduce your carbohydrate intake.
Indications
The manifestations of polyneuropathy may increase or decrease, depending on the daily diet. Certain foods can further damage the nerves by continuing to weaken them. Therefore, it is important to know the list of not only recommended, but also prohibited products in order to prevent the aggravation of tingling, numbness and / or pain.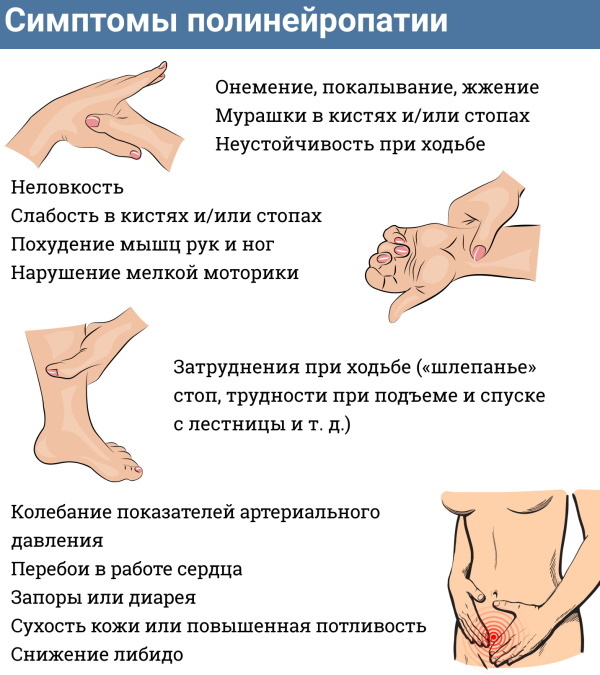
At the same time, it is important to add products to the menu that both help reduce blood sugar levels and are able to strengthen nerve fibers. Such nutrition will improve well-being and general health, as well as prevent new relapses. It is assumed that a vegetarian or vegan diet menu offering moderate amounts of fat and very little - carbohydrates, leads to a decrease in painful sensations in the damaged nerve fibers or even their complete cessation.
It should be borne in mind that some products can help the body even in the restoration of damaged nerves. This means that properly organized nutrition can completely eliminate all symptoms of polyneuropathy.
There are several diets, the principles of which coincide with the requirements for a therapeutic diet. However, in fact, they almost do not differ from each other, and are varieties of the paleo- and keto diet.
The ketogenic nutritional system is considered to be the most suitable for the treatment of neuropathy caused by diabetes mellitus. This is a very low carbohydrate diet (less than 50 grams per day) to help the body produce ketones. It is assumed that an increase in their concentration improves myelination and increases the production of myelin, a compound responsible for the regeneration of nerve fibers.
In addition, by limiting the consumption of foods rich in carbohydrates (cereals, cereals, sugar, as well as potatoes, legumes and fruits), the body enters ketosis. It is a metabolic condition in which the brain and other organs and systems run on fatty acids and "ketones" instead of glucose. As a result, sugar levels do not rise, which is especially important in type 2 diabetes. In addition, a low-carb diet can help you lose weight quickly and maintain your healthy weight.
Helpful hints
The diet for polyneuropathy, which most often affects the lower extremities, in all variants is based on an increased intake of proteins and a reduction in carbohydrates in the menu. Most often, sources of gluten are excluded from the diet, less often dairy products. There are also vegetarian and vegan versions of the diet, the effectiveness of which remains as high as when using animal food.
For each of the diet options, the following recommendations are relevant:
- Limit your sodium intake to less than 2,300 mg per day (with either version of the diet).

- We recommend filling half your plate with vegetables and fruits, a quarter with whole grains, and a quarter with a low-fat protein source.
- Some versions of the diet offer calorie counting, but the daily calorie intake has no effect on the health benefits of the diet.
It is believed that peripheral neuropathy can be completely cured. That said, controlling glucose levels and keeping them healthy in the body are usually more important than fighting inflammation. First of all, reducing the amount of sugar
leads to the resumption of nerve growth and a significant reduction in pain.
Approved and Recommended Products
A diet for polyneuropathy of the lower extremities eliminates the symptoms of this painful condition, and in some cases completely restores the damaged nerve fibers. Currently, there are more and more scientifically proven facts that there is a direct connection between food intake and the state of the nervous system (and it can be both positive and negative).
Neuropathy is usually a consequence of other diseases, and above all diabetes, therefore it is very important to control the sugar level in the body. This will avoid the appearance of new unpleasant symptoms.
Regardless of what causes your polyneuropathy, it's important to eat a diet rich in lean protein, whole grains and cereals, vegetables and fruits.
Making a daily menu of foods rich in phytonutrients, omega-3 fats, vitamin B-12 and lipoic acid, and whole grains will help your nerves function properly. It is desirable that these categories make up a significant part of the diet.
Phytonutrients
Phytonutrients, or phytochemicals, are natural compounds found in plants that keep them healthy by protecting against bacteria and other external threats. The beneficial effect of these pigments extends to the human body when consuming plant crops. All of these foods are bright or dark in color and have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that protect the cardiovascular and nervous system. They also strengthen the immune system and maintain hormone balance.
Phytonutrient-rich foods include:
- carrot;
- Bell pepper;
- tomatoes;
- cabbage;
- spinach;
- Bok Choi.
Asian meals are a great way to include phytonutrients in your diet. All of the above vegetables can be used to make stir-fry or stews paired with brown rice or noodles, and even tofu.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3s are a “good” type of fat that the body does not naturally produce, so you need to consume natural sources on a regular basis. This group includes eicosapentaenoic (EPA) and docosahexaenoic (DHA) fatty acids, which are essential for the proper functioning of the eyes, brain and nervous system. These fats help the body lower blood pressure and homocysteine levels, thereby protecting blood vessels and the heart.
The foods richest in omega-3 are fish of some varieties:
- mackerel;
- salmon;
- sardines;
- herring;
- tuna.

Mackerel is not as widely used as other types of fish, yet tastes great and is inexpensive. A good way to prepare a dish from it is to fry the carcass pieces or fillets with olive oil, garlic, salt and coarsely ground pepper. Walnuts are a good plant source of these essential fats.
Whole Grain Products
Whole grains are a rich source of essential nutrients - like macronutrients (primarily protein and fiber) and minerals (iron, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc and copper) and vitamins. They are usually low in fat and keep you feeling full for longer. The complex sugars in whole grains stabilize blood glucose levels and promote better brain nutrition. This means that they can be effective in the fight against diabetic polyneuropathy.
The most recommended among them are:
- whole oatmeal;
- brown rice;
- corn;
- quinoa;
- whole wheat couscous.
A lot can be made from whole grains, from light snacks to wholesome, hearty meals. Quinoa, brown rice, or couscous are easiest to use as a side dish - just boil them in water and serve with other lunch or dinner items.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is an essential part of nerve and red blood cell development. Although the entire family of B vitamins is an important component in maintaining a healthy nervous system, B12 is the only micronutrient that is constantly used by the body. It is an integral part of the myelin sheath, which contains nerve fibers. Vitamin B12 can only be obtained from animal products, so vegetarians and vegans should keep this in mind and take appropriate supplements.
Foods rich in vitamin B12 include:
- lamb or beef offal (liver and kidney);
- cooked shellfish (mussels, scallops, etc.);
- minced beef;
- plain yogurt;
- homogenized milk.
By-products are not eaten by everyone, but other elements of the above list are popular. In addition to common dishes, you can always cook something interesting and original from them. For example, whole grain pasta (linguini) with mussels and aromatic herbs.
Lipoic acid
This powerful antioxidant has unique properties that help maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Lipoic acid also neutralizes free radicals that damage healthy tissue, which reduces oxidative stress and inflammation.
It is found in several foods (but in very modest amounts, so it is recommended to additionally take it in the form of a dietary supplement):
- spinach;
- broccoli;
- yam;
- potato;
- Brussels sprouts.

All of these vegetables are great side dishes boiled, baked or fried.
Lean sources of protein
Protein is needed by the body to build and repair new tissues. However, it's important to stick to low-fat sources to avoid consuming too much saturated fat. Low-fat dairy and poultry are good options. People with peripheral or diabetic neuropathy should increase their intake.
Fruits and vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are loaded with a variety of minerals, vitamins, antioxidants, and dietary fiber. When taken together, they help build a strong immune system that prevents and fights disease and ailments at the same time.
It is recommended that you eat at least 5 servings of different fruits and vegetables every day to see real results. At the same time, it is advisable to choose crops that have a very high level of antioxidants - berries, cherries, grapefruit, oranges, Brussels sprouts, onions and bell peppers.
In addition, many people with polyneuropathy have diabetes, and eating more fruits and vegetables will help them better control their glucose levels. Another great advantage of these products is that they can be purchased ready-to-use. As a result, there is no need to spend time preparing and preparing them, which for some means additional free time.
Ginger
Ginger is a powerful, natural pain reliever. This means that its consumption in polyneuropathy can improve well-being. In addition, ginger contains gingerols,  which have anti-inflammatory properties, thereby increasing the mobility of people with severe and chronic pain, and helping them become more mobile.
which have anti-inflammatory properties, thereby increasing the mobility of people with severe and chronic pain, and helping them become more mobile.
Water
Pure water should be a standard ingredient in any healthy diet. It does not have pronounced medicinal properties, but it can relieve inflammation. This means that the pain experienced by the manifestation of polyneuropathy will not worsen. Conversely, when the body begins to dehydrate, the blood thickens, and the muscles involuntarily contract. As a result, inflammation occurs, affecting the areas where pain receptors and nerve endings are located, and unpleasant symptoms will worsen.
If you maintain healthy fluid levels at all times by drinking plenty of water, all bodily functions will function better, thereby improving overall well-being.
Prohibited foods
A diet for polyneuropathy of the lower extremities allows you to control the manifestations of this condition, using proper nutrition as the main tool. One of the best ways to manage the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy is by targeting the underlying cause. For example, in diabetes, this means constant monitoring of the body's sugar level.
In addition, effective treatment for neuropathy is combined with dietary recommendations that improve well-being and overall health. Along with recommended and healthy foods, the rules of a therapeutic diet prohibit the use of certain types of food. It is believed that these products can exacerbate the manifestations of polyneuropathy and provoke new symptoms.
Gluten
To date, it has been proven that gluten can cause a deterioration in well-being, not only with celiac disease. and allergies to it, but also in the case of increased sensitivity of the body to potential irritants. Quite often, this applies to people with peripheral neuropathy.

Common sources of gluten include any food that contains bleached, all-purpose, whole grain, or baked wheat and rye flours. It is also found in several other foods (such as traditional soy sauce), so it's important to read the ingredients on the labels and look for options labeled "gluten-free." Eating gluten when the body cannot properly digest it can lead to the development of inflammatory processes that aggravate the inflammation of the nerves with peripheral neuropathy.
Alcohol
As a neurotoxin, alcohol can damage nerves. Even a healthy person who drinks too much alcohol may begin to experience symptoms such as numbness, pain, and tingling in the hands or feet. This condition is known as alcoholic neuropathy, and is due to the fact that a person's peripheral nerves are damaged due to exposure to alcohol and become unable to transmit signals between the body and the spinal cord and brain properly way. This can aggravate pre-existing problems with the nervous system.
Added sugar
It is generally accepted that added sugar has negative health effects, and this is especially true for peripheral neuropathy. Eating large amounts of food raises blood sugar levels, which often damage the nerves and blood vessels that feed them.
Refined grains and cereals
Processed grains have a high glycemic index, and therefore increase sugar levels. Monitoring blood glucose levels is the best thing to do to prevent diabetes-related polyneuropathy, so these foods should be avoided. Improving the glycemic index of food intake is an important measure. This can be achieved by replacing refined grains and cereals with whole grains whenever possible.
Trans and saturated fats
Known as "unhealthy fats," they are found in most fatty meats and full-fat dairy products.  When consumed in excess, they lead to the development of chronic inflammation and exacerbate the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy.
When consumed in excess, they lead to the development of chronic inflammation and exacerbate the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy.
Salty snacks
Foods high in sodium can be a serious source of problems because high amounts of salt restricts blood flow to the extremities, causing numbness, and thereby exacerbating the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. Potato chips, meats, and fast food are especially high in sodium and should be avoided whenever possible. All industrially processed and canned foods are high in salt and are considered hazardous.
Certain foods increase the risk of elevated levels of unsafe metals in the body (most commonly mercury). Mercury is found in many popular ocean fish species found in polluted waters. Eating large amounts of it will lead to a build-up of heavy metals in the body, so it is imperative to be careful when choosing a product. Oily fish with a shorter lifespan should be chosen to minimize risks.
Spicy and pungent food
Eating stinging and spicy foods with polyneuropathy can lead to excessive sweating and heart palpitations, serious gastrointestinal ailments, bowel problems, lazy bladder syndrome, and the like. Nerve fibers that transmit impulses to these organs can be damaged and cause severe painful symptoms. Therefore, you should avoid chili and other such peppers, hot sauces (such as Tabasco and Shriracha), spicy noodles and similar foods.
Foods that increase inflammation
Certain foods cause inflammation in most people.

The most common irritants are:
- trans and saturated fats;
- sources of omega-6, such as corn oil, soybean oil, and safflower oil;
- sugar;
- alcohol.
However, there is a more significant list of foods that are considered to provoke an increase in inflammation and cause painful symptoms:
- dairy;
- wheat;
- citrus;
- corn;
- caffeine;
- meat of all types and varieties;
- nuts;
- eggs;
- nightshade vegetables, including potatoes, tomatoes, eggplant, and peppers
- products fried to a dark crust (in a pan or grill).
What can replace prohibited
Eaten processed carbohydrates are usually processed into more sugar than the body can absorb. Their sources include not only processed foods and industrial sweets, but also certain fruits (bananas), starchy vegetables (potatoes), and cereals (white rice). It is recommended to exclude the first group of products from the diet completely, the second - to limit the serving size to 0.5 tbsp.
In addition, there are safe alternatives to white sugar such as stevia and other natural sweeteners that do not affect glucose levels in the body. It is recommended to replace sweets and other sweets with fresh fruit.
Fatty sources of protein should be replaced with leaner options (for example, include chicken instead of pork on the menu). Moderation of healthy oils (such as avocado and coconut) is a good alternative to saturated fat.
Main menu
The diet for polyneuropathy of the lower extremities requires the elimination of any foods containing gluten from the diet. In addition, there are indications of the advisability of avoiding many other types of food, which are listed as capable of provoking the development of inflammation. There are even opinions that an effective diet for polyneuropathy should consist of a vegetarian or vegan menu.
Such strict restrictions are not binding on everyone. It is required to exclude from the diet only gluten and food groups that are not suitable for a low-carb diet (saturated and trans fats, fast carbohydrates, alcohol).
Other types of food can be consumed if they do not cause individual unwanted reactions in the body. When in doubt, it is recommended that you start keeping a food diary to determine which foods make you feel better or worse.
Menu for a week without restriction of animal products
| Breakfast | Dinner | Dinner | |
| Monday | 1 poached or scrambled egg, a quarter of a small avocado puree, 2 slices of gluten-free bread (toasted), 1 tbsp. low fat milk or herbal substitute | 2 tbsp. red lentil soup, mixed green salad, 1 tbsp. l. easy refueling | 2 tbsp. (500 ml) tofu stew with spring vegetables, 1 tbsp. (125 ml) cooked quinoa |
| Tuesday | 1 tbsp. gluten-free rice flakes, 0.5 tbsp. berries or fruits, 1 tbsp. skim milk or herbal substitute | baked fennel stuffed with apple, 1 tbsp. berries or 1 medium fruit, 0.5 tbsp. low fat yogurt | 1 serving of white fish baked with garlic and lentil puree, 1 medium fruit |
| Wednesday | 1 egg omelet with vegetables (spinach, mushrooms, etc.), 2 slices of toasted gluten-free bread, 2 tbsp. l. soft sandwich margarine and 1 tbsp. skim milk or herbal substitute | large bowl of tomato and black bean salad, with crumbled gluten-free tortilla chips (about 20 slices) | 1 serving of cheese shepherd's pie, 1 tbsp. fruit, green mixed salad with crumbled feta cheese |
| Thursday | 1 tbsp. water-cooked gluten-free oatmeal with 1 tbsp. l. peanut butter, 0.5 tbsp. skim milk or herbal substitute | 1 tbsp. cabbage, beets and chickpeas | 1 serving chicken breast, pan-stewed with tomatoes, 0.75 tbsp. boiled brown rice and green salad with 1 tbsp. l. easy refueling |
| Friday | 1 tbsp. strawberries, 2 toasted slices of gluten-free bread, 2 tsp. l. soft sandwich margarine | shawarma in gluten-free pita bread with 50 g of boiled chicken fillet, 2 tbsp. l. light ranch dressing, green salad, 1 tbsp. l. salsa and 2 tbsp. l. grated cheddar cheese, 1 medium fruit | 1 serving salmon baked with lemon-ginger sauce, 1 tbsp. boiled quinoa, 1 tbsp. cooked broccoli |
| Saturday | 1 poached or scrambled egg, a quarter of a small avocado puree, 2 slices of gluten-free bread (toasted), 1 tbsp. low fat milk or herbal substitute | grilled cheese sandwich made from 2 slices of gluten-free bread with 50 g of cheddar cheese, chopped tomato and 2 tsp. l. soft margarine, 1 medium fruit | 125 g baked pork loin, 1 tbsp. baked sweet potato, 1 tbsp. boiled green beans |
| Sunday | 1 tbsp. water-cooked gluten-free oatmeal with 1 tbsp. l. peanut butter, 0.5 tbsp. skim milk or herbal substitute | 1 serving of vegetable frittata, 2 slices of gluten-free toast, and 2 tsp. l. soft margarine, 1 medium fruit | 125 g baked chicken fillet with potato wedges with 2 tsp. l. mixture of olive oil with mild spices (1 root vegetable), green salad and 1 tbsp. l. easy refueling |
 In addition to the main meals, you should include one or more of the following snacks in your daily menu:
In addition to the main meals, you should include one or more of the following snacks in your daily menu:
- 1 medium apple or banana and peanut butter
- 0.5 tbsp. low-fat yogurt with 0.5 tbsp. berries;
- 3 tbsp. popcorn cooked without fat;
- 8 dried apricots and some almonds (or other nuts).
Vegan menu for the week
| Breakfast | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner | |
| Monday | green smoothie with baby spinach, frozen raspberries, avocado, nut milk, pea protein and fresh mint or matcha tea | mixed green salad with avocado, hemp seeds, lupine seeds, various non-starchy vegetables, olive oil and vinegar | celery slices with nut butter | zucchini noodles with vegan pesto (basil, walnuts and garlic) and chopped cherry tomatoes |
| Tuesday | tofu salad with tomatoes and spinach | broccoli cream soup cooked in fatty coconut milk and vegetable broth with herbs | avocado and cocoa powder chocolate mousse sweetened with stevia | zucchini spaghetti with caramelized onions, sauteed Brussels sprouts, lupine seeds and plenty of olive oil |
| Wednesday | chia pudding made with high-fat nut or coconut milk, berries, and unsweetened coconut flakes | salad of chopped cucumbers, tomatoes, olives, edamame, olive oil and vinegar | almonds and unsweetened coconut | roast broccoli and tempeh |
| Thursday | raspberries, a handful of walnuts, and matcha tea with coconut oil | cauliflower rice cooked with green onions, ginger, baby peas, chopped carrots, sesame seeds, and tofu | red bell pepper slices with guacamole or avocado puree | cauliflower pizza with tomato sauce or vegan pesto, mushrooms, peppers and onions |
| Friday | plain plant-based yogurt topped with unsweetened gluten-free muesli and blueberries | thinly sliced purple cabbage with sesame oil and rice vinegar, sprinkled with edamame and sunflower seeds | slices of cucumber, celery, or bell pepper dipped in vegan nut-based cream cheese | shirataki noodles with vegetables, tofu, almond butter and coconut sauce |
| Saturday | tofu salad with tomatoes and spinach | broccoli cream soup cooked in fatty coconut milk and vegetable broth with herbs | red bell pepper slices with guacamole or avocado puree | roast broccoli and tempeh |
| Sunday | chia pudding made with high-fat nut or coconut milk, berries, and unsweetened coconut flakes | mixed green salad with avocado, hemp seeds, lupine seeds, various non-starchy vegetables, olive oil and vinegar | almonds and unsweetened salad of chopped cucumbers, tomatoes, olives, edamame, olive oil and coconut vinegar | zucchini noodles with vegan pesto (basil, walnuts and garlic) and chopped cherry tomatoes |
Efficiency
With proper menu design and strict and continuous adherence, low-carb diets are highly effective not only for weight loss, but also to control and maintain sugar levels in the body, reduce inflammation and remove painful symptoms caused by neuropathy.
However, a restrictive diet can be a trigger for those with a history of an eating disorder, so caution should be exercised in people with such problems. Despite the fact that the vegan version is often called the most effective in the fight against polyneuropathy of the lower extremities, however, it long-term adherence can lead to nutritional deficiencies, especially if no additional supplements are included in the diet.
Video about a diet for polyneuropathy of the extremities
Polyneuropathy of the lower extremities: