Content
- Etiology
- Research
- Types
- Fluent (receptive, sensory, Wernicke)
- Motor (expressive, slow, Broca)
- Semantic
- Amnestic
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Forecast
- Complications
- Video about aphasia
Under aphasia in speech therapy speech dysfunction is understood, which most often includes a distortion of understanding or verbal expressions, as well as non-verbal symbols. Pathology can develop due to the development in the cerebral cortex of the affected speech centers, basal nuclei or white matter. Diagnosis is based on an assessment of symptoms, as well as information obtained from neuropsychological and neuroimaging examinations, in particular, CT and MRI.
This assessment is in direct proportion to the nature and level of violations. The age category of the patient also directly affects. Until now, no specific treatment methods have been developed for aphasia, but methods are used that are used for similar diseases, which often contributes to the correction and partial restoration of speech and its understanding.
Etiology
The concept of "aphasia" comes from the Greek word "fasio", which means "I say" in translation, as well as the addition of the prefix "a" (translated as "not"). That is, literally this word means "I do not speak." Since with this pathology speech can be partially preserved, some speech therapists suggest calling this disease "dysphasia".
But in speech therapy studies, most often Western ones, "dysphasia" is called various pathologies of speech development in children, by analogy with the fact that, in particular, underdevelopment of sound pronunciation is attributed to dyslalia, although it is proposed to attribute partial underdevelopment of speech or alalia.
In right-handers and in about 2/3 of left-handed people, the regions of the brain that are responsible for speech are located in the left hemisphere. 1/3 of left-handers - in the right.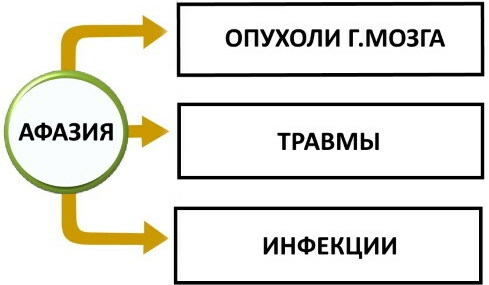
Areas of the cortex that form speech include:
- The posterior superior temporal lobe (including Wernicke's center).
- The adjacent inferior parietal lobe.
- The posteroinferior part of the frontal cortex, which is located in front of the motor cortex (Broca's area).
- Subcortical connections between these departments.
Disruptions in the activity of any of the above areas of the brain (in particular, in stroke, severe trauma, heart attack or tumor) can lead to pathologies of speech functionality.
Also, speech therapists sometimes note pathologies in isolated disorders of the subdominant hemisphere of the head brain, which entails dysfunction of prosody (intonational side of speech, which is significant for understanding).
Aphasia in speech therapy is a disease that differs significantly from dysarthria. Dysarthria is a pathology of speech development associated with disorders of the motor pathways and muscles that are responsible for articulation.
However, sometimes pathology can be the result of disorders that can progress. These can be tumors or dementia. In these cases, the condition will worsen.
It is the reasons due to which aphasia began to develop that determine its appearance, course and development. This is very important to consider when diagnosing and prescribing treatment.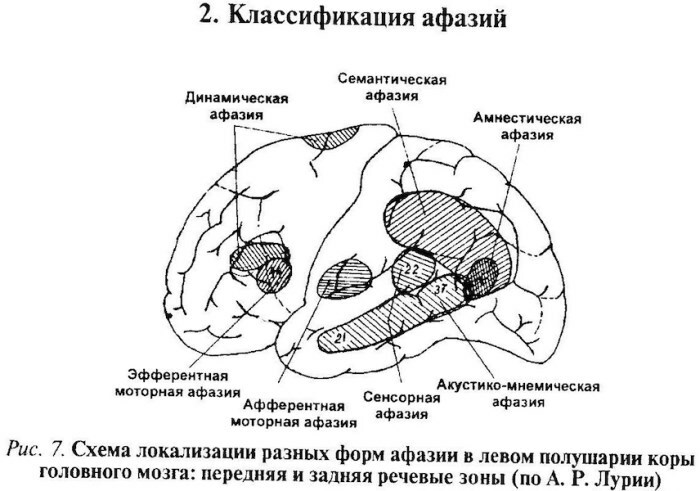
Aphasia is most often a consequence of pathological changes that do not cause damage that can progress, in particular, after a heart attack, brain injury. In these cases, the patient's condition will not worsen. Etiology in speech therapy is of paramount importance, and the pathology that is caused by a particular disease or injury will be different at different levels of development of the underlying disorder.
For example, with aphasia, which is caused by a brain tumor, will lead to a negative change intellectual and mnestic functions, as well as other mental changes resulting from focal brain lesions.
In vascular diseases, aphasia directly depends on the specifics of the stroke, which can be hemorrhagic or ischemic, as well as on the strength of the development of the atherosclerotic process.
If aphasia was caused by trauma, then its characteristics are more associated with focal brain damage. In this case, the pathology often has the property of a qualitative reverse development, because the changes that have developed after injury more often of all are in children or young people, when the integrity of the cerebral vessels is preserved, as well as the possibility of compensating for some functions.
Research
For the first time, aphasia was diagnosed in ancient Egyptian papyri, from which you can learn about people with brain lesions who have lost the ability to speak. However, significant and scientific studies of pathology were recorded only in the 19th century by European scientists and researchers.
In the 1860s. neuroscientist Paul Broca, who lived in France, described his observations of 2 patients with brain lesions who were almost completely unable to speak. However, one of these patients was able to pronounce the syllable “tan,” which is why he was nicknamed Monsieur Tan.
An autopsy showed that both patients had lesions of the posterior part of the inferior frontal gyrus. This site was named after the doctor - Broca's zone, and the characteristic type of aphasia, in which it is almost impossible for the patient to speak, is Broca's aphasia.
There are several similarities between aphasia in children and adults:
- Serious difficulties of already formed speech are diagnosed.
- For the most part, the causes of the pathology are similar. These can be injuries, inflammations, tumors. However, strokes are very rare in children.
- Early development is most often normal.
- Clinical symptoms and signs of pathology are similar.
The difference in the course of the disease in children and adults is especially visible in the following factors:
- Regardless of the severity, childhood pathology can often be cured much more quickly than in adult patients.
- The varieties of pathology in children are not as diverse as in adults. This is due to the fact that children's speech is not fully developed.

Childhood aphasia has similar features to alalia:
- negative changes in all speech elements;
- the relationship between speech disorders and mental systems associated with it;
- general and specific directions of speech therapy work.
However, there are significant differences between these 2 diseases:
- alalia is the initial, often congenital underdevelopment of speech systems, and aphasia is a violation of the formed;
- the goal of correction for alalia is the formation of speech systems and functions, with aphasia - restorative work.
Types
Aphasia in speech therapy is a disease that is divided according to the level of severity into:
- partial (in this case, full-fledged speech functions may occasionally appear);
- total (in this variant, significant negative changes and almost complete absence of speech are noticeable).
Also, pathology is divided into fluent and motor.
Fluent (receptive, sensory, Wernicke)
In this case, patients do not have the ability to understand words, and they also do not have the ability to recognize various symbols and elements:
- auditory;
- visual;
- tactile.
This symptomatic picture is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the posterior superior temporal gyrus of the leading hemisphere of speech, otherwise called the Wernicke center. This type of pathology is often accompanied by alexia, which is a negative change in the perception of written speech.
Patients with this type of pathology can usually pronounce simple words without much difficulty, but often use phonemes that are devoid of any meaning. However, sometimes even easily pronounced words by them lose their meaning for such patients, they cannot understand them. The result is a meaningless set of words both for those around them and for the patients themselves. But the patients themselves are not able to understand that those around them do not understand them.
With this type of aphasia, written speech is also impaired, it is usually fluent, but full of many mistakes, for example, the absence of nouns is characteristic. This picture speaks of fluent agraphism.
Motor (expressive, slow, Broca)
Aphasia in speech therapy is a pathology in which negative changes in the ability to form speech are diagnosed, but at the same time its meaningful understanding is partially preserved. These signs are the result of disorders that affect the left frontal or fronto-parietal zones, including Broca's area. In this case, writing and reading disorders are often diagnosed.
Patients with this type of pathology are almost always able to understand and comprehend their own and someone else's speech, but at the same time they cannot correctly form coherent words themselves. Most often, such a pathology affects the correct and meaningful education of both written and oral speech (not fluent agraphia and dysgraphia). At the same time, attempts to communicate are practically difficult.
This type includes several types of pathology, their common unifying feature is the impossibility of realizing active speech function orally:
| views | characteristic |
| Efferent | This is a negative change in articulation when the patient is unable to move from sound to sound without difficulty. Such a violation is characterized by speech almost without control. It usually consists of a set of sounds or syllables, pronounced at random. At the same time, a monologue or dialogue is scarce, a person does not use prepositions and conjunctions, and also uses only one case. With severe degrees, the ability to read aloud disappears. |
| Afferent | It is an articulation dysfunction where the patient is unable to determine how to pronounce a particular sound. A person begins to confuse sounds similar in pronunciation ("m" and "n", "t" and "d" and others). Also, in the process of speech pronunciation, patients rearrange sounds, syllables and words in places or skip them altogether. |
| Dynamic | Patients are diagnosed with long pauses between words, they do not use prepositions and conjunctions. There is a confused rhythm, blurred articulation, uncontrollable whispering. Patients have decreased speech activity, usually they do not seek to conduct a dialogue. |
 Also, this type of aphasia sometimes includes prosodic disturbances, as well as changes in the ability to repeat.
Also, this type of aphasia sometimes includes prosodic disturbances, as well as changes in the ability to repeat.
Semantic
With this type of pathology, dysfunction is usually localized in the parietal cortex of the brain and adjacent nerve endings. The disease is characterized by difficulties in understanding complex words and categories, as well as a lack of ability to explain them. But at the same time, a person can still maintain a dialogue.
Amnestic
This form of the disease appears after violations of the internal system of the brain lobes located in the temporal lobes. A person is usually able to maintain the ability to conduct a dialogue, but he cannot name any objects or phenomena himself, but after being prompted he is still capable of this.
A person is usually able to maintain the ability to conduct a dialogue, but he cannot name any objects or phenomena himself, but after being prompted he is still capable of this.
Symptoms
In a symptomatic picture, it is necessary, first of all, to note the most common symptom - this is difficulty or inability to remember a specific word. Every person has experienced this feeling at least once in his life: the word is familiar, but for some reason there is no way to apply it in a dialogue or monologue at the right moment. Patients with aphasia experience this sensation regularly.
Other signs are characteristic and occur only depending on the type of violation. For example, in the case of non-fluent types, which are detailed in Brock, patients are diagnosed with fluency. Such people try to speak less, they are characterized by stuttering, and in severe forms and stages, they are not at all able to pronounce something. When communicating, they can use a particular word or several, and even - be limited to a syllable.
In particular, the researchers described cases where only minimal profanity was present in the patients' boring vocabulary. Such forms are characterized by the difficulty of combining words into meaningful phrases. Patients swap words and use incorrect grammatical forms. For example, a patient tries to say: "My child was given a toy car," but can only say: "A child, a toy car."
The fluent forms that Wernicke studied are characterized by the fact that patients can speak quite quickly, avoiding stuttering, however, the structure of phrases resembles a set of words in which words are used that do not match the meaning or do not at all exists.
For example, the desired phrase "My child was presented with a toy car", such a patient can replace with: "My mother was presented with lapamasin." Moreover, people with such a diagnosis often have difficulty understanding someone else's speech. Hearing functions are normal, but the native language sounds like a foreign language or even meaningless.
With any type of pathology, people may have difficulty with the ability to clothe their own thoughts in words, as well as understanding the semantic load of other people's words. Cognitive functions are normal, memory is preserved and knowledge about the structure of the world is not changed.
That is, the patient sees a spoon, he may call it a fork or a spoon, or he may not find the words at all. But at the same time, he clearly understands that the spoon belongs to the dishes, they take it in the hand and eat it with the help of it. The remembrance of the world order is preserved and can expand, only the verbal shell disappears.
Diagnostics
Aphasia in speech therapy is a disease that is most often diagnosed through verbal communication. But it can be easily confused with communication problems associated with dysarthria, hearing or vision impairment. Also, when diagnosing, it should be borne in mind that Wernicke's aphasia is only a change in speech, it is not characterized by a delusional state (for example, hallucinations).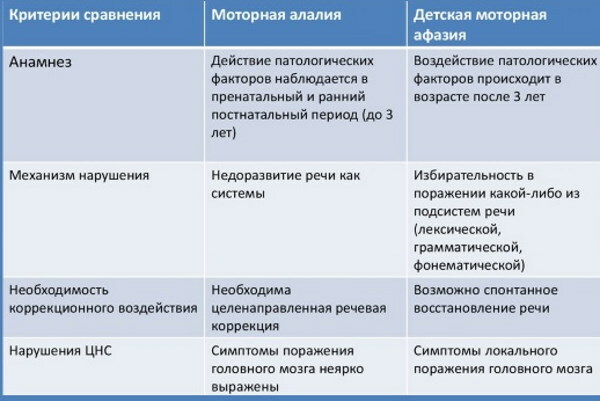
A study to determine specific forms and types of pathology includes an analysis of the following signs and symptomatic picture:
| function | characteristic |
| Spontaneous speech | Speech ability is assessed by fluency, the number of words per unit of time, the ability to initiate a dialogue, or monologue, the presence of uncontrolled speech disorders, the speed of the selection of lexemes, doubts and prosodic optimization. |
| Naming | The subject should name objects. Those experiencing difficulties with this test may resort to verbose characteristics (for example, "device to find out the time" - "clock"). |
| Repetition | The examinee must repeat grammatically complex sentences or just phrases. |
| Understanding | The subjects indicate objects, called a speech therapist or a doctor, follow simple commands, and answer “yes” or “no” questions. |
| Reading and writing | The subjects should write any phrase and read it aloud. In this case, not only comprehension and pronunciation are assessed, but also the ability to write under dictation. |
Neuropsychological diagnostics can be carried out by a neuropsychologist, as well as a speech therapist to identify the degree of impairment. It helps in making plans for adjustment and analyzing the potential for cure.
When diagnosing, different tests are used:
- Boston Name Test;
- Action names test;
- Nominative test;
- Boston Diagnostic Study;
- Western block of tests for detection and others.
Neuroimaging techniques may include MRI with or without angiography and CT. Such diagnostic methods are usually used when it is necessary to clarify the nature of the lesion. In the future, the diagnosis is carried out to determine the etiology of the pathology in accordance with the indications.
Treatment
At the first stage, a specialist (usually a speech therapist) must establish the nature of the patient's speech disorders in order to correct them in the future with the help of training. For example, if it is established that the ability to select words is impaired, then exercises are selected for the development of this zone. If a lack of understanding of the grammar of sentences is diagnosed, then it is necessary to train dialogical speech.
The next stage is rehabilitation measures, which can be carried out by a neuropsychologist or speech therapist.
They are engaged in the study of the state and correction of disorders of higher mental functions:
- memory;
- speech;
- perception;
- thinking;
- praxis.
Often people with aphasia need osteopathic treatment, as well as courses of therapeutic massage and / or physiotherapy.
Modern physiotherapy methods include transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). It is very effective for people diagnosed with organic brain damage. This method is non-invasive. It allows you to stimulate nerve cells that are located in areas of the brain that have undergone negative changes. This, in turn, activates them and is included in the process of understanding and supporting speech functions, as well as all accompanying higher mental functions.
It is a painless method with no side effects and is easily tolerated by people, making it effective for even the most severe patients. Corrective work, combined with transcranial magnetic stimulation, becomes even more effective, and allows you to get unique results.
Patients with a severe form of pathology, as well as people who care for them, have access to special devices for communication. These include computerized devices, as well as communication boards or books that contain pictures or symbols that represent the patient's regular needs.
Forecast
The possibility of a partial or complete cure depends on the factors:
- the reasons for the appearance of pathology;
- volumes and localization of violations;
- the level of speech disorder;
- reaction to correction;
- age category;
- the level of education;
- health status.
In almost all preschoolers, speech can be restored completely, even as a result of a serious violation of any part of the brain. For older children, the fastest cure is 3 months, but most often up to 1 year. Adults, especially the elderly, may not fully recover.
Complications
If you do not start correcting aphasia in a timely manner, then the following consequences may be:
- stable changes in which the patient ceases to understand other people's words and form his speech;
- complexes and psychological trauma associated with the inability to communicate.
Despite the fact that aphasia has been studied for decades, currently there are no generally accepted methods of diagnosis and correction, speech therapists cannot accurately predict the success of treatment for both mild and severe forms of this diseases.
Video about aphasia
Motor aphasia. Exercises: