Content
- Determination of the color index of blood
- Norms for women, men, children by age
- Possible deviations
- Hypochromic anemia
- Moderate hypochromia of erythrocytes
- Hyperchromia
- Normochromia
- Calculation formula
- What analysis is used to determine how
- Decoding the results
- Reasons for the lowered level
- Reasons for increasing the value of the color index
- What affects the reliability of the study
- Blood color index video
The color index is determined during clinical analysis. blood along with other erythrocyte indices. Comparison of the obtained figures with the established norm is of great diagnostic value in the presence of anemia, since it gives an idea of its cause.
Determination of the color index of blood
Red blood cells are saturated with oxygen in the lungs and deliver it to all organs and tissues, taking carbon dioxide from there and transferring it back to the lungs. The main constituent of the dry matter of erythrocytes is hemoglobin (Hb), the "respiratory enzyme" of the blood.
Its structure includes four heme molecules, which have an iron atom in their composition, and a globin protein. Since the iron atom has a large number of free electrons, it easily attaches or gives up an oxygen molecule. In the form of various complexes, hemoglobin circulates in the arterial and venous bed, transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide. Thus, respiration of tissue and organ cells is ensured.
When the hemoglobin content decreases, the supply of oxygen to the tissues decreases. Anemia develops. It is the hemoglobin compounds that give the blood color: bright scarlet - arterial, darker - venous.
The color index is an index that reflects the degree of saturation of erythrocytes with hemoglobin, that is, its relative concentration in red blood cells. Another name that is used in medicine: farb-index (from the word farb - color). For its designation in diagnostic laboratories, the abbreviation "CP" is used.
The CPU is somewhat outdated today. In modern laboratories, more and more often they resort to another calculated indicator - MCH (the average hemoglobin content in 1 erythrocyte cell, Mean Cell Hemoglobin). This index is expressed in picograms. Nevertheless, the old parameter is still used in the differential diagnosis of anemia.
Norms for women, men, children by age
When establishing the CP norm, it was conventionally assumed that the ideal farb-index is equal to one (1.0). This value is achieved when the amount of hemoglobin is 16.7 g% (gram percent), and the number of erythrocytes is 5 million.
Each calculated case is compared to this ideal metric: the resulting analysis, the average amount of hemoglobin in the erythrocyte is compared with its content in normal erythrocyte.
The color index of blood, the norm of which is ideally 1.0, in practice fluctuates in values close to unity. The physiological norm is considered to be CPU fluctuations in the range from 0.86 to 1.05. If the laboratory uses an analogue of the color indicator - MCH, then its norm is in the range of 27.0-31.0 pg.
Age and gender do not affect these values: numbers in the range of 0.86-1.05 in the lines of the analysis form are normal for children, men and women. Some sources still point to some age differences in the norm.
The difference is reflected in the table:
| Age | CPU Rate (Units) |
| Adults | 0,86–1,05 |
| Children from 0 to 5 days | 0,9–1,3 |
| Children from 5 days to 15 years old | 0,85–1,0 |
 The increase in CP in newborns is attributed to fetal hemoglobin (F), which was present in fetal blood during pregnancy. In the first days after birth, it remains in large quantities. In adults, this type of hemoglobin makes up only 1-2% of the total amount of pigment. Hemoglobin F has a high affinity for oxygen, which protects fetal tissue from hypoxia.
The increase in CP in newborns is attributed to fetal hemoglobin (F), which was present in fetal blood during pregnancy. In the first days after birth, it remains in large quantities. In adults, this type of hemoglobin makes up only 1-2% of the total amount of pigment. Hemoglobin F has a high affinity for oxygen, which protects fetal tissue from hypoxia.
Possible deviations
Anemia is a condition in which there is not enough hemoglobin in the circulating blood to properly supply oxygen to tissues. This usually occurs as a result of a decrease in the amount of Hb in erythrocyte cells. In this case, anemia also develops in the case of a normal or even increased content of Hb in the erythrocyte, when the total number of erythrocytes is greatly reduced.
Separation of types of anemia by color index:
| Hypochromic | CPU below normal |
| Hyperchromic | CPU above normal |
| Normochromic | Hemoglobin saturation remains within the normal range |
The color index of blood, the norm of which is in the range from 0.86 to 1.05 units, reflects the saturation erythrocytes with hemoglobin, which stains these blood cells red after binding an iron ion with a molecule oxygen.
At high saturation, red blood cells are considered overly colored; at low - insufficiently colored.
Hypochromic anemia
The pale color of red blood cells indicates a low content of hemoglobin in them. If the CPU numbers are below 0.8, they speak of hypochromia. It is mostly found in iron deficiency anemia, which is associated with the depletion of iron stores in the body. Fe deficiency causes a decrease in the synthesis of hemoglobin and its concentration in the blood.
A strong drop in the index (up to 0.5 units) occurs with significant blood loss.
Moderate hypochromia of erythrocytes
If the CP index is between 0.5 and 0.8, they speak of moderate hypochromia. The condition is characteristic of iron deficiency anemia of pregnant women, as well as cancer or infectious intoxication.
In some cases, undersaturation of erythrocytes with red pigment is not associated with Fe deficiency. The cause is a disturbance in the mechanism of hemoglobin formation. So, in some hereditary diseases (porphyria), hypochromia causes a failure in the formation of the non-protein part of hemoglobin - heme. In hemolytic anemia (thalassemia), the synthesis of protein chains of globin is disrupted.
Lead poisoning affects several levels of the process: it disrupts heme synthesis, reduces the rate of globin biosynthesis and leads to a shortening of the life of red blood cells.
Hyperchromia
Erythrocytes are considered hyperchromic if the CP is above 1.05. The volume of the red blood cell increases, which allows it to contain more red pigment. Excessive saturation of erythrocytes with hemoglobin creates the impression of "thick" and "heavy" blood.
Enhanced color of red blood cells characteristic of anemias caused by vitamin B deficiency12 (cobalamin, cyanocobalamin) and folic acid. CP values above 1.3 occur in severe pernicious anemia caused by impaired hematopoiesis due to a lack of vitamin B in the body12.
Normochromia
The color index of the blood is normal. This condition indicates health, but not always. With a proportional decrease in erythrocytes and hemoglobin, their ratio remains (1: 1) - while anemia is observed.
Pathological normochromia occurs due to significant blood loss.
Normal CP may be in hemolytic anemia, in which red blood cells are destroyed at a high rate. Accordingly, the total amount of hemoglobin also decreases.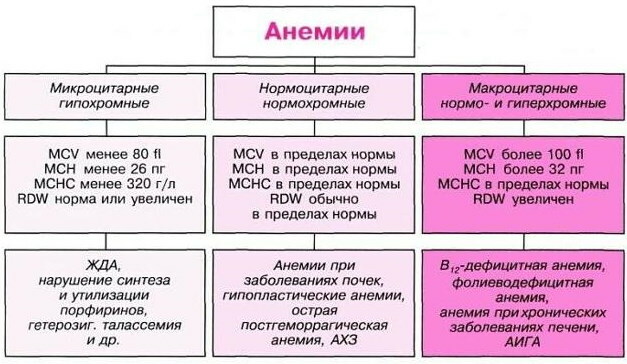
Normochromia is characteristic of the blood picture in sickle cell anemia caused by a hereditarily transmitted abnormality of the globin structure.
A decrease in the number of red blood cells is observed with viral infections, toxic and autoimmune effects on the body. The cell membranes (walls) of erythrocytes are actively destroyed, and massive lysis of red blood cells occurs.
Normochromic anemia is caused by long-term kidney disease. In healthy kidney tissue, erythropoietin is produced, which is necessary for the formation of new red blood cells. In the chronic course of the disease, the renal tissue is scarred, as a result of which the synthesis of erythropoietin is disrupted.
A decrease in the number of red blood cells occurs in chronic diseases due to the activity of cytokines. Constantly circulating in the blood, they act on the cell wall of erythrocytes, destroying it and thereby affecting the exchange of hemoglobin.
Calculation formula
The color index is a relative value that characterizes the percentage of hemoglobin and red blood cells.
CPU is the result of the following relationship:
(Hb% in the test blood / Hb% normal) / (number of red blood cells in the test blood / number of normal red blood cells).
In practice, two formulas are used to calculate CPU. One of them is for hemoglobin, expressed in gram percent; the other is in Sali units.
- (Hb g% x 3) / (Er).
- Hb unit Sali / (Er x 2).
Er is the first 2 digits of the red blood cell count per mm3.
The color index of blood, the norm of which is close to 1.0, was calculated based on the ideal amount of hemoglobin (16.7 g%) and erythrocytes (5 million). These numbers are taken for the following examples in order to demonstrate the calculations using the formulas most clearly.
So, if the hemoglobin content is expressed in gram-percent, then its amount is tripled and the resulting figure is divided by the first two digits of the erythrocyte number indicator. For example, the number of Hb is 16.7 g%, the number of erythrocytes is 5 million. Calculation example: 16.7x3 / 50 = 50.1 / 50 = 1.
16.7 g% corresponds to 100 units. hemoglobin on the Sali scale. Therefore, with the same indicators as in the previous problem, the ratio will be equal to one: 100 / (50x2) = 100/100 = 1.
The need to calculate the color index by the formula arises if the analysis is carried out manually. In the case of using a similar index (MCH), calculations are made automatically using a hematology analyzer.
What analysis is used to determine how
The color indicator, along with other erythrocyte indices, is included in the general (or clinical) blood test (CBC). Their comprehensive assessment gives an idea of the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of erythrocytes and, in particular, allows one to judge the etiology of anemia.
The study is carried out both in the number of planned activities and before surgery. The analysis is prescribed during the examination of patients suffering from various diseases. Reassessment of CP and other erythrocyte indices is required for persons receiving treatment for anemia. The goal is to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy.
A blood test is performed prior to physiotherapy. The need to take medications is agreed with the attending physician.
For research, capillary blood is taken from a finger. To take a biomaterial, a scarifier is used to puncture the skin, a test tube, alcohol and cotton wool. In some cases, according to the instructions of the attending physician, blood is taken from a vein.
It is recommended to donate blood in the morning, after 8 hours of fasting. All this time, it is allowed to drink only non-carbonated water. Alcohol intake should be excluded.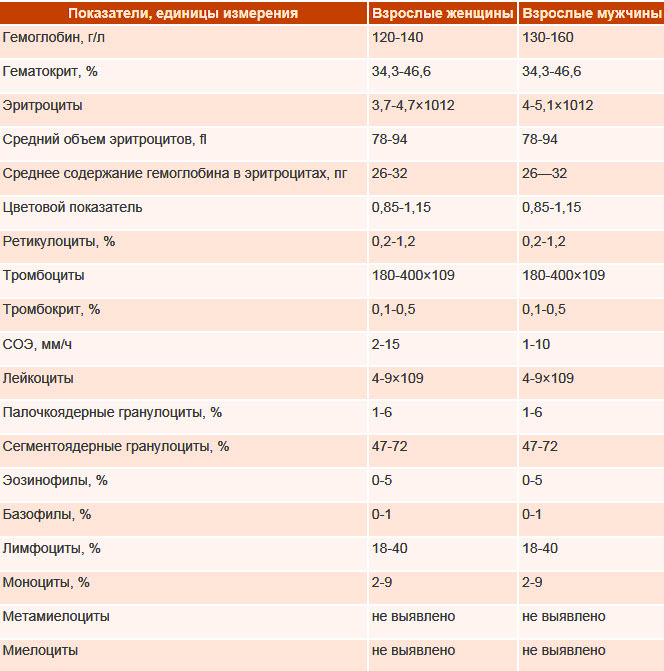
Research in the laboratory is carried out manually or using a special analyzer. Manual blood smear microscopy improves the accuracy of the results. As a rule, it is carried out if any deviations are found.
Decoding the results
The interpretation of the test results is carried out by a doctor who focuses not only on the values of the color indicator. The rest of the indices, the clinical picture of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient are taken into account.
The blood color index, the norm of which has the same standards for children and adults of both sexes, suggests exceptions. In newborns, this index is higher and varies within 0.9–1.3 units, while in adults, an increase in CP to 1.3 is characteristic of the development of pernicious anemia.
Any deviation of the CP from the norm is a sign of anemia, but with different types of anemia it manifests itself in different ways. For the differential diagnosis of anemia, the doctor needs to take into account many factors.
Thus, the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia is established based on a low farb-index with a reduced level of hemoglobin. The trophic signs characteristic of iron deficiency states are taken into account: brittle nails, hair loss, dry skin. Low ferritin and serum iron levels are critical for diagnosis.
With hypochromia, but with an increased level of iron in the blood serum and without trophic disorders, thalassemias and anemias occur, associated with a violation of porphyrins.
CP levels above 1 are commonly associated with megaloblastic anemia due to inadequate intake of B12 into the body. Other signs are also taken into account: a high volume of red blood cells (macrocytosis), a decrease in the level of platelets and neutrophils.
Atrophic changes are noted in the gastrointestinal mucosa. There are symptoms of glossitis, in which the tongue is inflamed and painted in a bright red color - the so-called "polished" tongue. In severe cases, disorders of the nervous system develop in the form of funicular myelosis, or sclerosis of the spinal cord. The same blood picture is characteristic of folate deficiency anemia, but glossitis and funicular myelosis are absent.
To establish what led to the deviation of the CP from the norm, the doctor takes into account the rest of the indicators of the study. The shape and size of erythrocytes, the number and basic characteristics of other blood cells are important.
With established anemia, a biochemical blood test is prescribed. Other types of laboratory tests may be needed, such as a serum iron test, ferritin, and a study of the level of porphyrins in erythrocytes. An occult blood test will allow you to verify the presence of latent bleeding as a source of anemia in a patient.
To find out the deep etiology of anemia and prescribe adequate treatment, instrumental diagnostic studies are often required. So, deficiency B12 can be combined with stomach cancer. To exclude a malignant process, gastroscopy or radiography is performed.
Reasons for the lowered level
With a reduced color index, the hemoglobin level falls to a greater extent than the number of red blood cells. This usually indicates iron deficiency anemia, although there may be other causes.
CPU decreases in the following situations:
- Blood loss due to surgery and trauma.
- Latent blood loss in gastrointestinal ulcers, hemorrhoids, "chocolate" ovarian cysts.
- Abundant menstruation with uterine fibroids, polycystic ovaries.
- Insufficient intake of iron from food.
- Initially low Fe levels in the baby due to iron deficiency in the mother during pregnancy.
- Iron deficiency anemia due to a chronic inflammatory process (chronic pyelitis, sepsis).
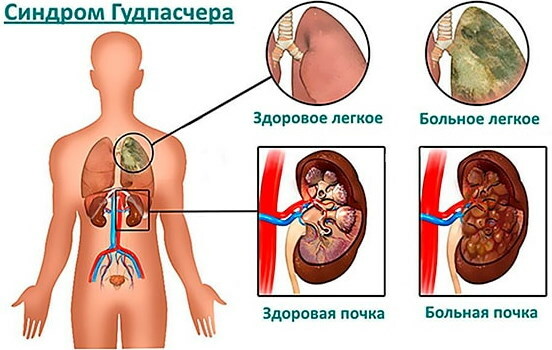
- Goodpasture's syndrome is a lesion of the pulmonary vessels and renal endothelium by immune complexes. The clinical picture consists of a combination of glomerulonephritis and hemoptysis.
- Heavy metal poisoning.
- Bone marrow damage.
- Hereditary anemias associated with impaired protoporphyrin synthesis.
- Increased death of red blood cells in thalassemia.
There are situations in which a decrease in Hb is a normal physiological phenomenon. For example, during pregnancy, the volume of the bloodstream increases (mother and child), and with it the total blood volume increases. In this case, the increase in the number of blood cells lags behind, and the blood becomes thinner.
The color index of blood, the norm of which coincides with the result on the test form, may indicate anemia in acute blood loss, hemolytic anemia and chronic kidney disease. In these cases, red blood cells and hemoglobin may decrease in parallel.
Reasons for increasing the value of the color index
With an increased farb-index, the number of erythrocytes decreases to a greater extent than the level of red pigment. The most likely cause is megaloblastic anemia, the etiology of which is a lack of folic acid or vitamin B12. A violation of the absorption of these substances in the gastrointestinal tract is of critical importance.
CPU values are increased in the following cases:
- Inadequate intake of dietary vitamin B12. Deficiency is associated with impaired glycoprotein production and is common in older people. The glycoprotein combines with the vitamin and ensures its absorption.
- Impaired absorption B12 in the small intestine after the transferred enteritis.
- Inventory depletion B12 in the liver with hepatitis.
- Wide tapeworm infestation that absorbs large amounts of vitamin B12.
- Polyposis of the stomach and decreased acidity of gastric juice make it difficult for the absorption of vitamin B12 and folic acid.
- Long-term use of drugs to reduce stomach acidity (omeprazole, famotidine).
- Alcohol intoxication, when it is accompanied by damage to the gastric mucosa.
- Imerslund-Gresbeck syndrome, in which multiple lesions of the epithelium of the kidneys, skin and intestines occur.
- Total gastrectomy. The symptoms of iron deficiency anemia develop 5 years after surgery. Until that time, patients make do with vitamin B stores.12 in the liver, replenishing them through insignificant absorption in the small intestine.
- Small intestine resection.
- Stomach cancer.
- Long-term use of anticonvulsant drugs (phenobarbital) and cytostatics (anticancer drugs).
- Folic acid deficiency in pregnant women.
What affects the reliability of the study
The following factors can affect the reliability of the analysis result:
- the patient's pregnancy;
- the presence of concomitant diseases;
- taking alcohol or drugs before testing;
- non-compliance with the usual drinking regime, which causes thickening or thinning of the blood;
- the introduction of heparin and an increased level of blood lipids (overestimate the index);
- violation of the technique of sampling biomaterial.
If the test results deviate too much from the norm, it will be advisable to retake it. The most reliable are studies that are carried out in dynamics. This allows you to find out the individual characteristics of the norm of a particular patient.
The color index of blood is an important diagnostic characteristic, signaling any changes in the ratio of red blood cells and hemoglobin. Deviation of CP values from the norm to a greater or lesser extent allows one to establish the presence of anemia and make an assumption about its etiology.
Blood color index video
Blood color index:



