Content
- Stages and types
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
- Drug therapy
- Vitamins
- Chondroprotectors
- Muscle relaxants
- Glucocorticosteroids
- NSAIDs
- Exercise therapy, massage
- Surgical intervention
- Videos about Spina Bifida
Spina bifida S1 is a developmental anomaly in which the posterior arch of one or more vertebrae is absent. In adult patients, this disease is quite rare. The occult form of pathology at the initial stage of development is often asymptomatic. Signs of illness may appear after a strong blow or other mechanical injuries.
Stages and types
There are several main forms of the disease: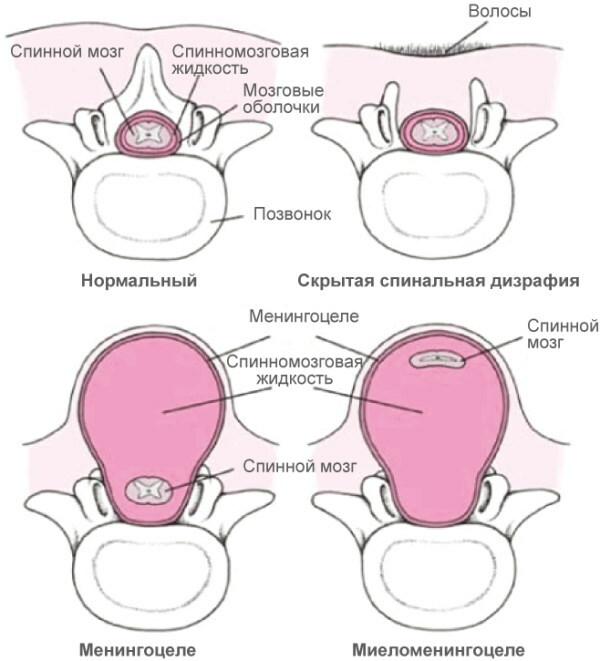
| Types of pathology | Description |
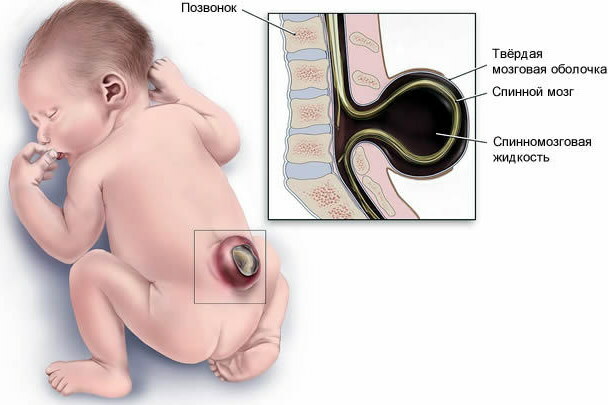
| Myelomeningocele (spina bifida custica) | This type of pathology occurs most often in medical practice. Myelomeningocele is accompanied by the formation of a cerebral hernia - the spinal cord and spinal roots grow through the vertebrae of the column. The "pouch" is formed from connective tissue and covered with skin. In severe cases, the spinal cord may be visible with the naked eye. The severity of the symptom complex directly depends on the location of the cerebral hernia. If it is located closer to the coccyx, then patients complain of violations of the functional activity of the intestines and bladder. Localization of a hernia in the lumbar or thoracic spine is accompanied by paralysis of the extremities (mainly the lower ones). |
| Meningocele | In a healthy person, the spinal cord is located inside the spinal column. With meningocele, as the most severe form of pathology, part of the brain tissue grows through the vertebrae. The "pouch" is formed from the soft, cobweb and hard spinal cord. With meningocele, the hernia is localized in the thoracic, cervical or lumbar spine. This type of pathology is classified as moderate. With meningocele, there is a high risk of loss of physical activity. |
| Latent form (spina bifida occulta) | This is the easiest type of cleavage. Most often, the form is diagnosed in adult patients. In this case, there are no defects in the development of the spinal column. The slit diameter does not exceed 4-5 mm. The disease is usually asymptomatic. Patients may occasionally experience mild leg and lower back pain. |
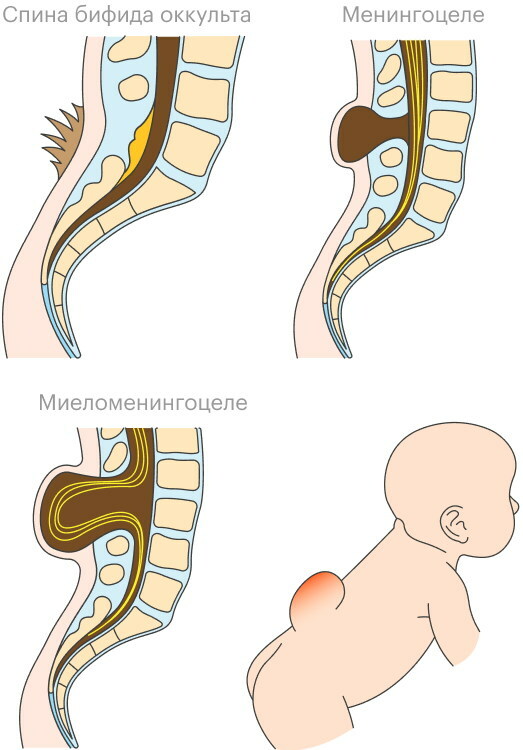 It is impossible to identify the occult form of the disease during a visual examination of the patient. Splitting is not diagnosed by palpation. In order to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an x-ray.
It is impossible to identify the occult form of the disease during a visual examination of the patient. Splitting is not diagnosed by palpation. In order to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an x-ray.
Symptoms and Signs
Spina bifida S1 in adults is a pathological condition characterized by a fracture of the spinal column. Light (occult, latent) form of pathology has no characteristic symptoms. After a severe blow or other mechanical injury, a person with spina bifida may complain of weakness in the legs, recurrent pain in the lumbar region and rapid fatigue.
Also, the occult form of spina bifida is characterized by various disorders of the neurological type, especially if, upon impact or fall, the nerve roots at the site of the cleavage were damaged.
Signs of defeat endings:
- decreased visual acuity;
- headache;
- noise in ears;
- balance and coordination disorders;
- numbness of the upper and lower extremities;
- tingling sensation;
- tic, tremor;
- sleep disorders.
Symptoms of neurological disorders are mild and intermittent.
With latent spina bifida, patients may also complain of impaired functional activity of the urinary system:
- retention of urine;
- feeling of fullness in the bladder;
- nocturia (frequent urge to urinate at night).
The main sign of the development of meningocele and myelomeningocele is the formation of a hernia. Bulging can be accompanied by dysfunction of the urinary tract and intestines.
Causes
Spina bifida S1 in adults is formed during the period of intrauterine development. Spina bifida is a congenital anomaly. In an adult, it cannot suddenly develop. Fetal pathology occurs 26-28 days after conception. During this period, the fetal neural tube is actively formed. The back of the bifida develops against the background of incomplete closure of the nerve groove.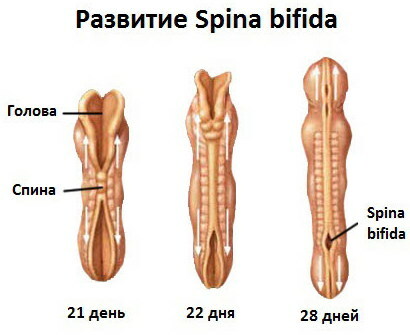
The risk of developing an occult form of spina bifida increases if a pregnant woman has close relatives suffering from this disease.
Factors predisposing to the development of spina bifida:
- the parents have close relatives, Hispanics;
- the onset of pregnancy in women over 40-45 years old;
- long-term use of drugs during pregnancy that have a teratogenic effect;
- penetration of infection into the body of a pregnant woman;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- long-term use of antiepileptic and antineoplastic drugs;
- folate deficiency during pregnancy.
Women who abuse alcohol during conception are at high risk of having a baby with spina bifida.
Diagnostics
Spina bifida S1 in adults is diagnosed in several ways.
Patients are prescribed:
- Electroneurography. A diagnostic study is aimed at studying the activity of nerve endings. The thinnest electrodes are inserted under the patient's skin and an electric current is supplied through them. The procedure is completely painless. Electroneurography allows you to identify the degree of damage to the nerve roots in spina bifida.
- Myelography. The method of instrumental diagnostics is aimed at examining the subarachnoid cavity. Using a thin long needle, a preparation containing iodine is injected into the lumbar spinal canal. The patient is then sent for x-ray. Also, the patient may be prescribed pneumomyelography. In this case, air is injected into the spinal cord instead of a contrast solution. The procedure is quite painful, therefore, it is prescribed only in extreme cases. It is important to properly prepare for myelography. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
-
Computed tomography. A non-invasive diagnostic method allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of various parts of the spine. X-rays are directed at the split sections of the column. Scanning is carried out in layers. The image is displayed on the monitor of the tomograph. In the process of research, a contrast agent can be used.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. The diagnostic method allows you to examine the vertebrae and soft tissues of the spinal column. Using MRI, a specialist assesses the condition of joints, cartilage, nerve endings, blood vessels, spinal cord and intervertebral discs of all departments. The procedure with almost 100% accuracy will allow the specialist to determine the localization of the cleft.
- Radiography. The procedure reveals the location of the hernia and its size. The patient is placed on his side on a couch and X-rays are directed at different angles. The clinical picture is displayed in the image in several projections. Also, the procedure helps to identify various changes in the bone structure.
Methods of neuroimaging diagnostics are considered the most informative.
Treatment methods
Spina bifida S1 in adults is a treatable disease. There is no specific therapy. With a latent form, the patient can be assigned massage and physiotherapy exercises. The mode of exercise therapy and the type of exercise are selected individually, depending on the age of the patient and the presence of accompanying hernia pathologies.
Drug therapy
The following drugs may be included in the composition of drug therapy for spina bifida:
- Vitamins. Medicines help restore the functional activity of cells in the affected area. Thanks to drugs, metabolic processes are accelerated.
- Chondroprotectors. Medicines of this category are prescribed to a patient with spina bifida in order to restore the cartilage of the intervertebral discs.
- Muscle relaxants. Medicines can have a relaxing effect. The drugs help relieve acute pain.
- Glucocorticosteroids. Medicines have an analgesic effect. They are prescribed in extreme cases, if weaker pain relievers do not work.
NSAIDs can also be included in drug therapy. Usually they are prescribed to patients at the initial stage of treatment in order to relieve inflammatory processes and eliminate spasms.
Vitamins
With spina bifida, drug therapy includes:
-
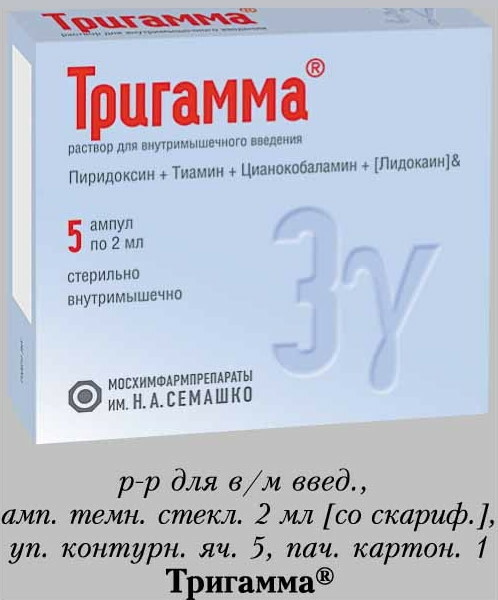
Trigamma. The preparation contains lidocaine chloride, pyridoxine, cyanocobalamin, thiamine, disodium edetate. It goes on sale in the form of a solution. It has anesthetic, anti-inflammatory and metabolic effects. When the spine is pinched, the drug is prescribed in order to restore metabolic processes at the cellular level in the affected area.
- Milgamma. The active ingredients are lidocaine, cyanocobalamin, thiamine, pyridoxine. The drug has a neurotropic effect, restoring blood flow in the affected area. Also, vitamins are actively involved in metabolic processes. The drug comes on sale in the form of a solution.
Milgamma and Trigamma help relieve mild spasms. For drugs in this category, a local analgesic effect is characteristic.
Chondroprotectors
With the latent form of spina bifida, the patient may be prescribed chondroprotectors.
The most effective drugs in this category are:
- Don. The medication has several forms of release: tablets, injection solution, granules for preparing a suspension. The drug has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. The positive effect is achieved due to the ability of the drug to restore the permeability of the capsules of the joints, cartilage and cell membranes.
- Rumalon. The active ingredient is glucosamine peptide. Release form - solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration. The drug is characterized by protective properties. Thanks to Rumalon, metabolic processes are restored in the tissues and catabolic processes are inhibited.
Medicines for spina bifida should only be taken as directed by a doctor. It is strictly forbidden to independently select the dosage regimen and application regimens.
Muscle relaxants
For drugs in this category, a membrane stabilizing effect is characteristic.
With spina bifida, drug therapy includes:
-
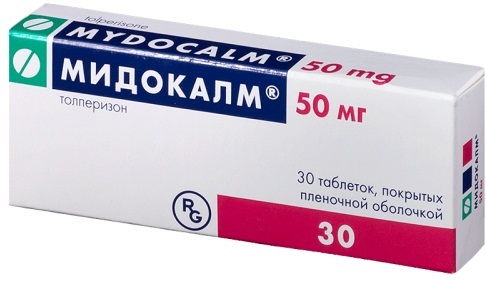
Midocalm. The drug is marketed in tablet form. The active ingredient is tolperisone hydrochloride. The drug has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. Also, a muscle relaxant restores peripheral blood flow in the affected area, simultaneously reducing muscle tone.
- Sirdalud. Comes on sale in the form of tablets. The active ingredient is tizanidine hydrochloride. The muscle relaxant has a beneficial effect on the muscular skeleton, eliminating tone and spasm. The drug is also characterized by an analgesic effect.
The above drugs should be taken with caution in elderly patients. It may be necessary to adjust the dosage regimen in the direction of decreasing it.
Glucocorticosteroids
Glucocorticosteroids are potent drugs. They are prescribed for severe pain caused by a protrusion of a spinal hernia. With spina bifida, patients are shown injections of Prednisolone or Dexamethasone.
Medicines have a number of contraindications, therefore, they can be used as directed only with the permission of the attending physician. Any ailments that occur during treatment require immediate discontinuation of drugs.
NSAIDs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) will help stop spasm spasm.
Patients are prescribed:
-
Ibuprofen. The active ingredient is the substance of the same name. The drug comes on sale in the form of a gel, ointment, suppositories and suspensions. The drug is characterized by analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory effect. Ibuprofen restores physical activity and relieves stiffness.
- Diclofenac. For spina bifida, it is best to use the drug in the form of a solution - it will work faster this way. The drug contains sodium diclofenac. The solution eliminates inflammation, providing a mild analgesic effect.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of infusion solutions are administered intramuscularly. The course of treatment is selected on an individual basis.
Exercise therapy, massage
An S1 bifida back with minor spina bifida in adults can be corrected with non-surgical methods. Experts do not recommend performing vacuum massage for spina bifida. It is necessary to dwell on the mid-depth study of muscle fibers.
Therapeutic massage includes several stages:
- Kneading. The masseur gently kneads the lower back with his fingers or palm, trying to slightly stretch the muscle fibers. In the process of kneading, you need to carefully fold the skin into a fold.
- Stroking. Using the palm of your hand, gently, in a circular motion, work out the problem area. For better glide, you can use analgesic gels, massage oils or honey.
With spina bifida, you cannot tap the lower back.
Physiotherapy is also well established as a method of restoring physical activity. You can do the exercises at home using a variety of available tools. Lying on your back, on a flat surface, you need to forcefully raise your arms and legs up. Movements should be smooth and measured.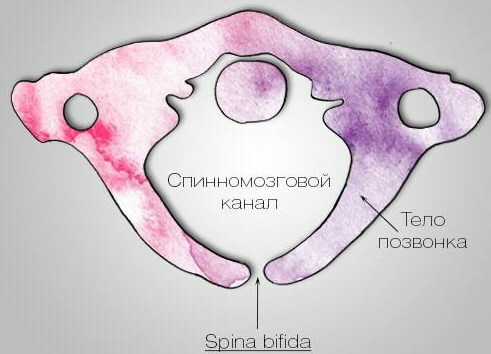
With spina bifida, you can exercise 2-3 times a day. Exercise helps to strengthen the muscle frame. Sitting on a chair, you need to bend your elbows and lean on a flat surface. Raise both legs above the floor by 15-20 cm and fix the position for 10 seconds. Up to 15 approaches are performed per day.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is indicated for patients in a number of situations:
- the development of complications characterized by increased curvature of the spine;
- formation of a fistulous course;
- compression of the spinal roots or spinal cord.
Most often, the operation is performed in order to:
- stabilize the vertebrae;
- correct scoliosis;
- eliminate the pathological process caused by pathologies accompanying cleavage.
During surgery, microinstruments, an operating microscope and other special devices are used. Such operations are less traumatic.
Spina bifida S1 is a pathological condition that often occurs in adults. Treatment should be selected by a doctor depending on the patient's age and condition. It is strictly forbidden to independently adjust drug therapy by increasing or decreasing the dose of prescribed drugs.
Videos about Spina Bifida
Back Bifida: