Thyrotoxicosis and pregnancy rarely occur at the same time. Such a combination is found only in single cases per thousand, and yet, it is not a reason obliging to interrupt pregnancy, as there are modern and fairly loyal methods of treatment.

Description of the disease
Thyrotoxicosis refers to a patient's condition in which there is an increase in the concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood plasma. The term also means a constant increase in the level of free thyroid units in the blood.
Often the term hyperthyroidism is used to describe such a clinical picture, but it should be understood that this term means not only an increase in the concentration of hormones in the blood, but also the activation of excessive synthesis and secretion. Hyperthyroidism can occur with pregnancy often enough, in contrast to thyrotoxicosis.
What happens in the body
The clinical picture of thyrotoxicosis can indicate several types of diseases. In particular, two large groups of hormonal abnormalities are distinguished, which are manifested by severe symptoms of this disease.
The first group includes thyrotoxicosis, which is combined with hyperthyroiditis. It can be a multinodular goiter, toxic goiter, tyrotropinoma, ovary proliferation due to an adenoma or with its atrophy.
The second group includes a disease not burdened by hyperthyroidism. This subacute form of thyroiditis, radiation and painless thyroiditis, as well as disorders caused by long-term use of interferon.
The first group is more common in pregnancy. Most often the disease is caused by a diffuse toxic goiter. This disease is also called Graves' disease.
As a matter of fact, this pathology means the development by the immune system of antibodies that destroy the receptors of the thyroid-stimulating hormone, which is manifested in the change in the shape and size of the thyroid gland.
Today, such a diagnosis is not a contraindication for pregnancy and is not a reason for abortion. If a woman has a severe form of autoimmune pathology, in ninety percent of cases, infertility is possible before the disease is eliminated.
Symptoms of
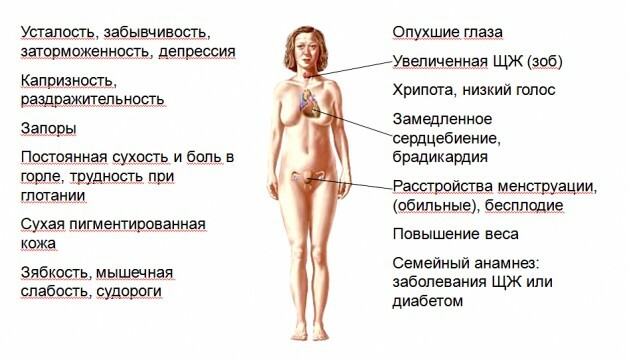
The first symptom that indicates hyperthyroidism is vomiting and nausea. But since in pregnancy such phenomena are observed and without autoimmune pathologies, the diagnosis becomes more complicated.
Specific signs are sweating, fast fatigue, palpitation, emotional instability, an increase in the thyroid gland in size. But such symptoms are also observed during pregnancy.
Therefore, the diagnosis of the disease is possible only with the laboratory diagnosis, otherwise the doctor simply takes symptoms for toxemia in pregnancy. It should be noted that a prolonged course of thyrotoxicosis without appropriate treatment can lead to early childbirth or spontaneous abortion, as well as to the development of congenital abnormalities in the child.
Diagnosis of the disease
For the correct diagnosis, the patient is referred for the thyroid hormone assay. In particular, blood is shed from the vein, and endocrinologists are interested in such indicators as the level of TSH, T3, T4 and AT-TPO.
Sometimes diagnosis during gestation is hampered by gestational hyperthyroidism, which is common among pregnant women and goes untreated as the gestation period increases.
Methods of treatment
In the first trimester of pregnancy, the use of drugs is virtually impossible, as many of them are able to overcome the placental barrier, enter the bloodstream. With mild thyrotoxicosis, antithyroid drugs are not prescribed, in addition, the state of pregnancy already in itself positively affects the dynamics of treatment.
Basic principles of drug treatment during pregnancy:
- The form of the preparations, mainly oral, in the form of tablets.
- Active substances - derivatives of imidazole or propylthiouracil, trade names: Mercazolil, Thiamazole.
- Pregnant often prescribed is propylthiouracil, since it is less able to penetrate the placenta.
- The dose of the drug should be selected to maintain the T4 level at the upper limit of the normal range or slightly higher than it, otherwise, when prescribing too large doses of drugs, it is possible to achieve fetal preparations and develop goitre.
General principles of therapy of thyrotoxicosis in pregnancy:
- Each month the patient should undergo a laboratory blood test for the concentration of free thyroxin.
- The most gentle preparation is propylthiouracil.
- With primary thyrotoxicosis and with mild forms, two hundred milligrams of the drug are prescribed four times a day.
- If the next blood test reveals a decrease in thyroxine levels, the dosage of the drug is reduced to fifty milligrams per day.
- There is no need for frequent research and a decrease in the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone.
- Many patients are shown substitution therapy, which is the administration of levothyroxine, but during pregnancy it is strictly forbidden to use substitution therapy.
- If there is a sharp drop in the level of thyroxin in the blood, the drug is canceled and prescribed only after relapse.
- In the postpartum period, one hundred per cent of women giving birth is found to have a relapse of the disease, which is cured by the appointment of similar drugs.
- With the increase in the duration of pregnancy, the severity of the disease decreases and the dependence on thyreostatics, in the third trimester many women lose the need for taking the drug.

- During breastfeeding, it is allowed to take low doses of propyluracil, up to one hundred milligrams per day, which will not affect feeding and will not harm the baby.
Surgical treatment of
The only indication for the operation is immunity to derivatives of imidazole or propyluracil, as well as other thyreostatics, if it is possible to regulate their dosage and concentration.
Most often the disease lends itself to medical treatment, and if necessary, the operation is performed only starting from the twelfth week in the second trimester. Previously, the doctor must test any ways of conservative treatment.
Treatment features
If a disease is detected in a moderate form of severity, the maximum primary dose of propylthiouracil should be two hundred milligrams per day, with the administration divided four times.
In this treatment regimen, a decrease in the level of free thyroxin to the upper limit of the norm is observed after a month. Then the dosage is reduced to maintenance, in the amount of not more than one hundred milligrams a day.
The concentration of free thyroxine in the blood is analyzed every month. It is noted that in this case the dosage of the drugs gradually decreases and reaches no more than twenty-five milligrams per day.
It is possible to explain such a course of the disease by the fact that during pregnancy, the formation of antibodies to the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptors decreases, and the binding of free hormones by protein-vectors increases, which naturally reduces the concentration in the blood of the latter.
Possible complications of
In the absence of adequate treatment, for the misapplication of a regimen or drug, it is possible to develop quite dangerous complications. First of all, the mother organism suffers, in which hypertension, early childbirth, flaking of the placenta or leakage of amniotic fluid can be observed.
Possible development of anemia, heart failure and a crisis state, which requires immediate treatment and hospitalization of the patient.
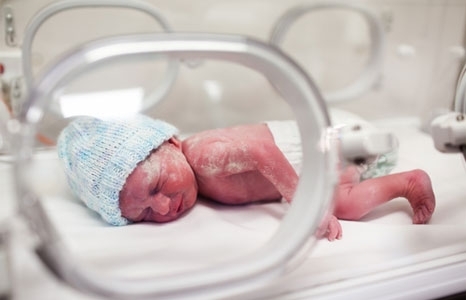
The fetus may have much more serious complications, since the thyroid gland is already formed and begins to function, but largely depends on the hormonal background of the mother.
In particular, the fetus may develop thyrotoxicosis, anomalies in the development of organs and vices. Children are born with low weight, expressed in utero developmental delay. It is not ruled out stillbirth.
In contrast, it is worth noting that only 1% of children born to women with thyrotoxicosis during pregnancy suffer from such complications. Therefore, if a pronounced toxicosis is found, it is better to take the tests in advance and begin treatment as early as possible.