 Seizures - uncontrolled contraction of muscle tissue due to overexertion;the nature of the seizures is paroxysmal.
Seizures - uncontrolled contraction of muscle tissue due to overexertion;the nature of the seizures is paroxysmal.
As a rule, cramps are not permanent. Their appearance and disappearance are sudden, but the duration is not more than a minute.
Depending on the cause, seizures may be frequent or rare, short or prolonged. Pain is usually not typical, but children and the elderly can clearly feel the muscle contractions, which are manifested by pain syndromes.
The most common time of seizures is night. This is due to the fact that during sleep all muscles are in a relaxed state. Also, seizures are not uncommon in healthy people after an active muscle load.
Seizures are not clearly localized. Muscle contraction can affect one muscle and the whole group. The most common muscle groups are: calves, femoral, abdominal region, back and neck.
Content
- seizures
- tonic convulsions
- typical position during
- attack clonic seizures
- typical position during
- attack tonic-clonic spasms
- Atonic attacks
- Short atonic
- Prolonged
- focal and generalized seizures
- Myoclonic seizures - seizures
- reasons convulsive manifestations
- Epileptic seizures and seizures
- Focal seizures
- Generalized
- Sedoroand other neurological diseases
- Cramps in other diseases and conditions
- First aid for seizures and convulsions
- assist concept
seizures
seizures( syndrome), or in other words, an attack of violent motions that manifests itself strong enough uncontrolled muscle contraction.
The reason for convulsive attacks in most cases is a violation of calcium metabolism. An important feature of the convulsive attack is that the patient is constantly in consciousness, even though the spastic pain can reach high rates.
The development of an attack can be wavy or single. Duration can also vary greatly. Pain syndrome depends on the disease and individual characteristics of a person.
With mild cramps, there is usually a slight tingling in the muscles - very dangerous muscle cramps that are near the spine and large arteries. Pain will be felt not only in the place of spasm, but also throughout the nerve or vessel.
In the chronic course of convulsive attacks, fragility of nails and bones, hair loss is observed. This is due to the leaching of calcium. This pathological process worsens the state of tooth enamel, promotes the development of conjunctivitis and the progression of cataracts.
All seizures are characterized by involuntary contraction of muscle fibers and unpleasant pain. However, despite the similarity of symptoms, there is a difference.
Any seizures and attacks occur due to the negative effects of certain factors, most often the internal environment. Despite the fact that the movement itself during the seizures is generalized, only a small part of the muscle groups are spasmodic.

Tonic convulsions
Tonic convulsions are characterized by:
- shortening process;
- the rise in spasm peak occurs gradually;
- is provoked by muscle tension.
The most common location is the area of hands and feet. The areas of the abdomen, face and neck can also be prone to spasm. To a lesser degree of localization is the musculature of the respiratory tract.
Typical position during an attack
Extension is prevalent, so the lower and upper limbs are in the open state. The head appears to be thrown back, the teeth are closed, the whole body is stretched out because of the muscle tension. Possible loss of consciousness.

Clonic convulsions
Characteristic signs of clonic convulsions:
- the periods of contraction are followed by periods of muscle relaxation;
- appears characteristic twitching of body parts;
- self-determination of this type of seizures is not difficult.
The location is the same as for tonic convulsions.
Characteristic position during attack
Upper and lower limbs are bent, the spine is bent. Naked eye markedly calm twitching of spasmodic muscles. The peculiarities include stuttering, which arises from the spasm of the muscles of the respiratory system.
Tonic-clonic spasms
Combine both the mechanisms of tonic convulsions and clonic ones. There are three stages of development, which end in fainting or coma. 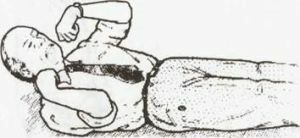
The first stage - tonic spasms, which are characterized by:
- pupil dilated;
- by rolling the eyes;
- voltage of all muscles.
The second stage - clonic convulsions, a change in periods of contraction and relaxation.
The third stage is a twilight consciousness disorder. It is possible to separate foam from the mouth due to the bite of the tongue and a large amount of saliva secretion.
Atonic attacks
These seizures refer to epileptic attacks. The main feature is the fall in muscle tone and / or loss of consciousness. Spasm can be both regional( local) and generalized. They are very rare.
There are two types of seizures.
Short atonic
The period of reduction in muscle tone is very short and affects either the muscles of the neck and head, or the muscles of the lower extremities.
Prolonged
Sudden loss of consciousness and loss of muscle tone lasts a few minutes. After falling to the ground the patient is not able to say anything or move. Due to a sudden fall, severe bruises and fractures often occur.
Partial atonic attacks:
- Drop-attack , or in another attack of falling. Occur due to epileptic seizures, or because of symmetrical or asymmetric rigidity.
- Focal atonic attacks .It is characterized by paresis or paralysis of one or more parts of the body. Negative Myoclonus .
Focal and generalized convulsions
 Focal( partial) convulsions are those in which the focus is localized in one part of the brain( focal fit of the frontal lobe).
Focal( partial) convulsions are those in which the focus is localized in one part of the brain( focal fit of the frontal lobe).
With this seizure, the patient remains conscious. However, if the situation is complicated, then there may be a confusion of consciousness, frequent blinking, constant performance of the same type of actions. Before the attack itself, unusual sensations may arise.
Generalized convulsions are most often a pathology of neuronal activity. It provokes loss of consciousness, sharp muscle atony or generalized spasm.
Possible following manifestations:
- muscle twitching of symmetrical and asymmetric limbs;
- look at one point;
- muscle tension of the back, limbs;
- uncoordinated lowering of the head.
Myoclonic seizures - seizures
Their main feature is that they are painless. Spasmodic one or more muscles. Externally, you can see a slight twitching.
Most often occur at night or during daytime sleep. Duration of more than a minute. Perhaps the appearance of myelonic fright, which is provoked by a flash of light, a loud knock, a cry.
The manifestation of myoclonic seizures depends on their type: benign and negative.
In benign course there is:
- numbness in the muscles of the head;
- eye teak;
- involuntary contraction of the muscles of the neck, limbs, back.
With negative, a slight tremor of the arms in the extended position is observed.
Causes of convulsive manifestations of
The causes depend on the type of seizures.
Epileptic seizures and seizures
These seizures are very short-lived and rarely exceed 10 seconds. Their appearance is provoked by external irritating factors, such as flashes of light, shock, eating, and internal - the process of memorizing, reading.
Focal seizures of
Differ from generalized ones because their approach can be felt by a person. It can be the appearance of some kind of smell, visual images, music. 
Focal seizures are divided into:
- sensitive;
- motor;
- fits of laughter or crying;
- reflex;
- secondary generalized.
Generalized
Appears due to symmetrical discharges in the cerebral cortex. Appear suddenly.
Seizures are subdivided into:
- tonic-clonic;
- is tonic;
- is clonic;
- atypical;
- myoclonus;
- reflex generalized.
Seizures in other neurological diseases
Neurological diseases that provoke the development of convulsive syndrome:
- epilepsy;
- krampi( periodic spasms of gastrocnemius muscles of unknown etiology);
- radiculitis;
- neuropathies due to injuries, tumors;
- polyneuropathy of an infectious-allergic nature;
- poliomyelitis;
- sclerosis;
- amyotrophy;
- myositis;
- Becker's dystrophy;
- myotonia;
- Parkinson's disease.
Seizures in other diseases and conditions
Diseases that provoke the development of convulsions:
- deficiency of calcium or magnesium;
- insufficient maturity of the brain( in children);
- psychophysiological disorders;
- varicose veins;
- thyroid disease;
- poisoning by products of nitrogen decomposition;
- cirrhosis;
- diabetes;
- kidney disease;
- atherosclerotic vascular lesion;
- malignant neoplasms;
- pathology of the musculoskeletal system.
Provoking conditions:
- insufficient blood supply in muscles( with physical activity);
- overstrain( insufficient blood supply or stress factors);
- pregnancy;
- increased sweating, diarrhea and loss of salt;
- monotonous, often repetitive movement in the brush( typing on the computer);
- pregnancy;
- alcohol intoxication;
- insufficient intake of micro and macronutrients for fasting and improper diets.
First aid for convulsions and seizures
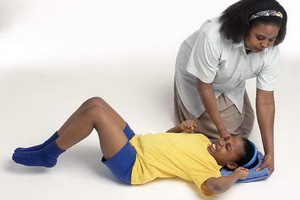
In case of convulsive seizures, it is necessary:
- to put the patient on a flat but soft surface, if necessary, use outer clothing, pillows, blankets;
- to free the person from the fettering clothes, accessories;
- with the loss of a person's consciousness put on their side so that the tongue does not tilt and does not inhale saliva and vomit;
- of the limb should be gently held, as excessive force can provoke fracture or dislocation;
- give the patient medication or water during an attack is prohibited.

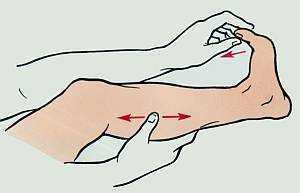
What to do if the leg cramps:
- use self-massage or ask another person to stretch the spasmed muscle;
- stretch the muscles;
- Raise the limb for high blood flow;
- use warming ointments and compresses;
- take a warm bath.
The concept of assisting
Any treatment should begin with a diagnosis, only after that a diagnosis is made and a plan of further therapeutic actions is chosen.
If the convulsions are caused by diseases of organs and systems that are not related to neurology, then the treatment will be directed to this body.
 If the cause is a specific neurological condition, then it is important to apply measures aimed at eliminating or compensating for this condition.
If the cause is a specific neurological condition, then it is important to apply measures aimed at eliminating or compensating for this condition.
So convulsions for infectious diseases or febrile conditions pass independently, but only after the treatment of the underlying disease and without the development of complications.
General concepts for the treatment of convulsive seizures:
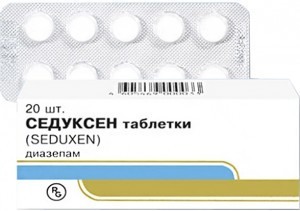
- Assignment of sedatives and muscle relaxants , which will help relax the muscles and reduce nervous system activity. Examples of such drugs are Seduxen and Andaxin.
- Intravenous administration of droperidol or sodium oxibutyrate with severe seizures or seizures.
- Nootropics for inhibition of nerve impulse transmission.
- Proper nutrition .Appointed by a doctor individually, taking into account the characteristics of the patient and concomitant diseases. It is important to fill the deficiency of missing substances( lack of calcium, magnesium, salts, macronutrients).
- Surgical treatment of ( for tumors and epilepsy with the identified focus of epileptic excitation).



