Often happens such that in the kidneys begins the process of stone formation, which has many names - urolithiasis, nephrolithiasis, urolithic or nephrolithiasis, etc. Stone formation can be observed onlyin the cavities of the kidneys( pelvis, cups) or extends to the ureter and bladder. Concrements of small sizes are called sand, and large ones are already stones.
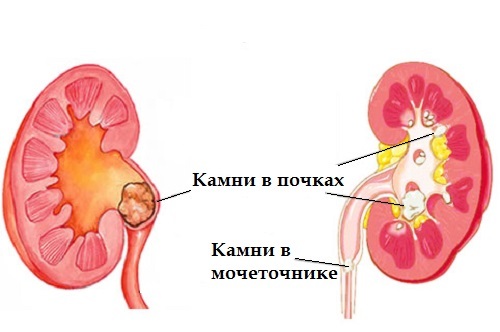
Pathology can affect even a newborn baby, but is more common in adults 25-50 years of age, the older we become, the higher the risk of calculus formation. The disease is somewhat more likely to affect the male population. Treatment of kidney stones is often aimed at crushing concrements without surgery, although stones can be removed and surgically.
Classification of formed stones
Typical accessory of stones depends on the age group of the patient. In elderly patients, patients tend to form concrements based on uric acid salts( urate stones), and pebbles based on protein in these patients are very rare. The size of the stones can vary significantly from the smallest grains to 5-centimeter pebbles. In kidney tissues, stones can be formed, based on oxalates( based on oxalic acid salts) or phosphates( based on phosphoric acid salts).Concrements with a phosphate base differ in their propensity for rapid growth and formation into coral-like stones. Practice shows that the stones have a predominantly mixed base.
That's interesting! Medicine knows the case when the size of the kidney stone reached a 15-centimeter diameter, and its weight was several kilograms.
Depending on the course of renal stone pathology, there is a classification for the primary and secondary etiology of stone formation. Primary etiology is characterized by the absence of internal predisposing endogenous factors, whereas primary forms develop precisely under the influence of factors associated with disturbances of the urino-drain or leading to these disorders. Regardless of the basis, stones tend to move - they move along the urinary tract, changing their location. Usually the process of movement is accompanied by an acute pain syndrome.
Clinical picture of renal stone pathology
 The clinical picture is largely determined by the size of the stones. Practically there is no symptomatology in case of formation of the smallest stones which else name sand. Such a course of pathology can be accompanied by minor painful sensations in the area of the affected kidney. Painful discomfort is characterized by a constantly-aching character, and becomes more intense after severe shaking or physical overstrain, overeating or drinking alcohol. In the urine may be found small bloody impurities, inconspicuous without a microscope, or in urine, there are no changes at all.
The clinical picture is largely determined by the size of the stones. Practically there is no symptomatology in case of formation of the smallest stones which else name sand. Such a course of pathology can be accompanied by minor painful sensations in the area of the affected kidney. Painful discomfort is characterized by a constantly-aching character, and becomes more intense after severe shaking or physical overstrain, overeating or drinking alcohol. In the urine may be found small bloody impurities, inconspicuous without a microscope, or in urine, there are no changes at all.
During an attack, the pain syndrome in men can irradiate to the area of the penis and scrotum. Some men notice in the urine the presence of sand or pebbles, which directly indicates the development of urolithiasis. And after the departure of concrements, the patient's condition improves significantly( until the next attack).
A pronounced clinic is present with significant stone sizes, especially when the movement of the calculus or the overlap of the urethral lumen occurs. Then the patient begins to worry about the signs characteristic of renal colic: a sharp attack of pain in the kidney, accompanied by hematuria and vomiting and vomiting symptoms. Patients often begin to run to the toilet, they are pained by painful urination, in which there can be a sudden interruption of the jet and its subsequent resumption. The general symptomatology is supplemented by a strong puffiness, high temperature and pressure. The patient is periodically tormented by severe painful seizures with periods of calm in a few days. If the formed stones blocked the passage of the two ureters, then the excretion of urine is completely absent( anuria).This condition is very dangerous, therefore requires immediate intervention of a urologist or nephrologist. To prevent such a complication, it is necessary to periodically check for concrements.
Etiological factors
Kidney stone formation belongs to the group of polytheological pathologies, therefore several reasons are singled out for explaining the development of such a disease. The most significant factors provoking the formation of calculi in the kidneys are metabolic disorders, especially those associated with urate metabolism. A similar phenomenon is characteristic of gout, in which the uric acid content in urine and blood increases many times. Therefore, the causes of kidney stone formation include pathogenetic factors that provoke the development of gout. Among such factors, the wrong food leads, consisting in the abuse of wine and beer, fatty dishes and meat.
 The process of kidney stone formation can last for months and even years, the main thing is that the content of protein and salts is significantly exceeded. When the concentration of uric acid increases in the body, the risk of formation of urate calculi grows. The formation of stones occurs when the urinary salts settle on the protein microparticles, which in this situation act as the framework of the future calculus. If the body increases the content of phosphates and oxalates, then phosphoric and oxalate stones are formed. The formation of phosphate stones is often promoted by pathologies of the endocrine nature, which are characterized by redundancy in the blood of vitamin D. Provoking the emergence of phosphate stones can also abuse mineral waters. Stones are formed mainly in the urinary tract, so their formation is affected by the mucous kidney, in the case of infectious damage, the risk of formation of calculi in the pelvis increases substantially.
The process of kidney stone formation can last for months and even years, the main thing is that the content of protein and salts is significantly exceeded. When the concentration of uric acid increases in the body, the risk of formation of urate calculi grows. The formation of stones occurs when the urinary salts settle on the protein microparticles, which in this situation act as the framework of the future calculus. If the body increases the content of phosphates and oxalates, then phosphoric and oxalate stones are formed. The formation of phosphate stones is often promoted by pathologies of the endocrine nature, which are characterized by redundancy in the blood of vitamin D. Provoking the emergence of phosphate stones can also abuse mineral waters. Stones are formed mainly in the urinary tract, so their formation is affected by the mucous kidney, in the case of infectious damage, the risk of formation of calculi in the pelvis increases substantially.
In general, the causes of kidney stone formation are divided into several groups:
Endogenous
Endogenous factors act within the body and include chronic gastrointestinal pathologies( ulcers or gastritis), a deficiency of any enzyme substances( enzymes), hyperthyroidism( hyperparathyroidism), disorders of protective hepaticfunctions, trauma in the bone system.
Local
These causes are caused by pathological conditions or abnormalities that form directly in the kidneys. This includes inflammatory kidney processes such as pyelonephritis, renal omission( nephroptosis), stagnation of the urine against the background of prostate adenoma or hydronephrosis, disorders of renal circulation against a background of various bleeding, trauma or shock.
Exogenous
Exogenous factors are external unfavorable and pathogenetic influences including inappropriate climate( heat dehydration, vitamin D and ultraviolet deficiency), lack of mobility or hard work in harmful production, malnutrition( abuse of acidic or spicy dishes), poor qualitydrinking water( excessive calcium content).
There is also a hereditary factor, since the risk of such diseases increases significantly for people whose immediate relatives suffer from urolithiasis or kidney stone pathology. In the hypodynamic way of life, the flow of phosphate-calcium processes is disrupted, which provokes stone formation in the kidneys.
Methods of therapy of pathology
Treatment of kidney stones is carried out in several ways, including urgent help for relief of renal colic and subsequent systemic treatment, the purpose of which is to prevent the development of recurrent cases of kidney stone pathology. For relief of colic, antispasmodics such as baralgina, spasmalgon or no-shpa are used, which relax the ureter and facilitate the movement of the calculus into the bladder.
Practice shows that the maximum therapeutic effect is achieved when injecting spasmolytic drugs intravenously, although some doctors recommend still intramuscular injection.
Therapy of an attack of renal stone pathology also involves corrective techniques like a hot water bottle on the affected area or a hot bath. Thermal action similar to spasmolytic drugs helps to stop renal colic and to alleviate the patient's condition. But the procedures that remove pain syndrome are temporary and do not get rid of the pathology itself, and kidney stone formation is known to be characterized by a recurrent course. To completely get rid of the stones, they should be removed, which modern medicine allows you to do in several ways.
Removal of large pebbles is carried out through classical nephrotomy. Although experts are aware of all the shortcomings of this technique, with large amounts of concrements, it is considered the most preferable and effective. A modern way to remove kidney stones is lithotripsy, which involves crushing concretions directly in the kidney with ultrasound. Particles of the crushed stone later leave with urine, which is not highly traumatic and highly effective.



