Diseases of the thyroid gland occupy an honorable second place in the prevalence among endocrine pathologies after diabetes mellitus. Very often people do not even know about the presence of the disease. The reason for this is the low severity of the first signs of ailment, especially with organ hypofunction, which is mainly manifested by fatigue, drowsiness and apathy. To verify the diagnosis, patients need to take specialized tests to determine the levels of the following hormones:
- thyroxine( T4),
- triiodothyronine( T3),
- thyreotropic hormone( TSH).
These are the most common tests that are necessary to confirm or refute the diagnosis of thyroid pathology.
Baseline characteristic of

Patients who donate blood for analysis often think that all of the above hormones are produced in the thyroid gland. Even doctors sometimes habitually call them all thyroid. However, this is not true. Indeed, T3 and T4 are biologically active substances that are synthesized by thyrocytes and take part in the metabolism of the organism. Their main functions are:
- regulation of basal metabolism,
- participation in the process of growth, strengthening of bone tissue and the whole body,
- stimulation of human mental development,
- support of normal heart rhythm,
- catabolic action that provides energy release during the breakdown of fats and glycogen.
Both hormones are iodine-containing. This microelement is absorbed with food, enters the thyroid gland and is used as a chemical basis for the creation of these biologically active substances. It is worth saying that there is a concept of free and bound T3 and T4.It all depends on the attachment to a particular protein, which acts as a transporter. Nevertheless, the main work is carried out by a free type of hormone. He is sought in the patient's blood.
TTG is a pituitary hormone. It plays a major role in maintaining adequate functional organ activity. With its increased amount of iron stimulated and begins to throw out large doses of T3 and T4 in the blood. It works on the principle of negative feedback. If iodine-containing hormones are sufficient in the body, the pituitary gland "knows" about it and does not excrete the tropic substance. If their levels fall, then it is activated and synthesizes additional portions of TSH.
Reasons for reduced T4
In the practice of modern endocrinology, examples of thyroid dysfunction are often encountered, which can manifest as hypo- and hyperactivity, with a corresponding drop and an increase in the concentration of free T4 in the blood. This hormone is reduced in the following situations:
- Incorrect treatment of thyrotoxicosis with excess doses of thyreostatics or radioactive iodine. As a result, the tissue of the thyroid gland is inhibited too much, and it loses the ability to actively act.
- Autoimmune lesion of the organ structure. The most common example of such a pathology is Hashimoto's goiter - a special disease that develops as a result of the destruction of its own thyocytes by antibodies. The level of free T4 is usually low for such a disease.
- Operative removal of the organ. If a patient suffers from a malignant neoplasm in the thyroid gland, he may be recommended to completely eliminate it. This will lead to the impossibility of synthesizing one's own homons, but it will save a person's life. For substitution therapy, patients should receive synthetic analogues of biologically active substance for life. Accuracies in the work of the laboratory. There are situations when relatively healthy people without any manifestations of the thyroid pathology show reduced rates of free T3 and T4.Very often the reason for this can be mechanical or technical errors of laboratory assistants in determining the number of these compounds in the blood. Repeated tests usually correct such errors.
The normal value for free thyroxine in human blood is 9-20 pmol / l.
Reasons for decreased TSG
Because TTG and iodine containing hormones are regulated by the principle of negative feedback, the concentration of the tropic substance decreases with too violent activity of the thyroid gland. This happens with various pathologies of the organ. Its normal value is 0.4-4 μIU / ml. The most common situations when TSH is down are:
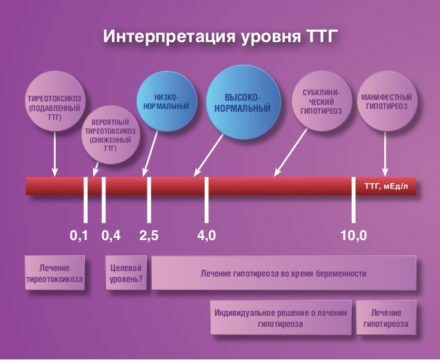
- Thyrotoxicosis. It is a consequence of diffuse toxic goiter.
- The phase of thyroid activation in the autoimmune lesion. There is a special term "hashitoxicosis", which characterizes such a phenomenon that it develops relatively infrequently.
- An increase in the amount of free T4 due to pregnancy and an increase in chorionic hormone is the so-called trophoblastic thyrotoxicosis.
- Thyroid cancer with activation of its function( follicular adenocarcinoma).
- Acute or subacute thyroiditis is an inflammation of the organ tissue.
- Overdose of drugs in the treatment of hypothyroidism. The most frequent "culprit" of this situation is L-thyroxine.
- Pathology of other organs and systems. The thyroid can compensate for additional portions of free thyroxine in order to influence metabolism. As a result, the TSH level falls.
- Euthyroid pathology. Special condition when there is a decrease or a jump in TSH without thyroid dysfunction. This happens when the pituitary gland reacts to stress or an attack of some other disease. An example is the drop in TSH in the acute phase of myocardial infarction. Thyroid hormones remain normal, and the level of the tropic substance is significantly reduced.
All these situations are factors that lead to a decrease in the amount of the hormone of the pituitary gland. Nevertheless, they arise only in the pathology of the gland itself.
Additional causes of reduced TSH
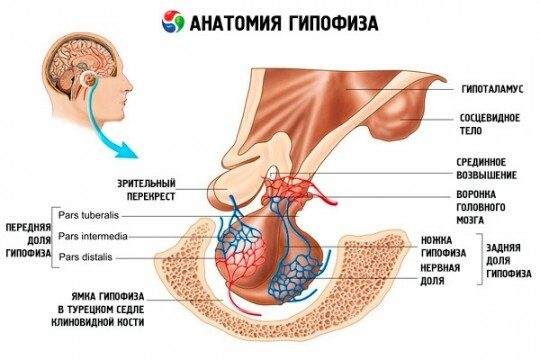
Separately, it is worthwhile to talk about pathology, which affects the pituitary itself. Such a drop in the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone is called secondary and occurs much less often than the primary. However, it is necessary to know that the problem develops because of the following diseases:
- tumor in the hypothalamus or pituitary tissue,
- tumor in the main brain that mechanically squeezes the main "regulator" of the endocrine system,
- hemorrhages and bruises in the cranial cavity,
- radioactive brain irradiation andhead tissue,
- surgical interventions in this area,
- empty Turkish saddle syndrome,
- autoimmune and infectious pituitary lesions( very rare phenomena).
Well it becomes clear that situations when the concentration of TSH falls, there are a lot. Nevertheless, do not worry. In the general population, this pathology takes a relatively modest place. Not many people suffer from such diseases.
Adequate and timely diagnosis with the correct course of treatment can solve the problem with maintaining a good quality of life for the patient. The main thing - will turn to a specialist at the first manifestations of the disease. The same goes for the pathology of the thyroid gland with a drop in the level of free T4 and T3.Curing the disease in the early stages is always much easier than dealing with it in the active development phase.