 Liquorrhea is an uncontrolled flow of cerebrospinal fluid( CSF, cerebrospinal fluid).
Liquorrhea is an uncontrolled flow of cerebrospinal fluid( CSF, cerebrospinal fluid).
Cerebrospinal fluid provides stable intracranial pressure, protects against mechanical influences, supports water-electrolyte regulation, serves to provide an exchange process between the brain and blood.
Cerebrospinal fluid forms in the brain. The usual location of the cerebrospinal fluid is the area between the bones of the spine and the spinal cord, the central canal of the spinal cord, the ventricles of the brain, the area between the skull bones and the brain envelopes, the cerebral grooves, the subarachnoid space.
The flow of cerebrospinal fluid occurs as a result of a violation of the integrity of the dura mater, as a result of traumas of the spine, skull, after surgical interventions.
What provokes the problem
The main factor influencing the development of cerebrospinal fluid is trauma or defects of the dura mater. Damage is due to:
- craniocerebral injuries, in which the skull base bone is damaged( the pyramid of the temporal bone, the bottom of the anterior cranial fossa);
- craniocerebral injuries in which the bones of the cranial vault( frontal sinus) are damaged
- neurosurgical intervention in the spine, spinal cord or brain( CSF expires through the postoperative sutures)
- growth of pathological neoplasms located in the brain region;
- congenital anomalies of the central nervous system( hernia in the region of the spinal cord or brain);
- congenital or acquired anatomical defects of the skull( defect in the wedge sinus, latticed bone, sitovid plates, posterior wall of the frontal sinus, pyramid of the temporal bone, posterior and middle cranial fossa, roof of the tympanic cavity);
- injuries of the sinuses of the latticed bone, as a result of ENT manipulation( drainage, rinsing, extraction of foreign objects, removal of polyps);
- connective tissue diseases( Marfan syndrome), which cause a significant thinning of the hard shell of the brain, hyperplasticity of the joints;
- pathological processes in the brain and skull bones( dysembryogenetic, tumor, inflammatory origin).
The cerebral edema in children is caused by a congenital abnormality of the development of the labyrinth, which favors the appearance of deafness and meningitis. In adults, it is caused by the bulging of the arachnoid medulla due to a defect( congenital) in the upper wall of the tympanic cavity or a defect( acquired due to dynamic factors) of the arachnoid.
Clinic of the disease
It is possible to determine the presence of liquorrhea according to the following symptoms:
- liquor leakage( clear, clear liquid, sometimes with blood veins, or pale pink color).The expiration of
 of cerebrospinal fluid has a periodicity and lasts up to 2 minutes, can be abundant and lean, jet and drip. Nasal liquorrhea - comes from one nostril, and mostly with the head tilted forward. Exhaustion from the ears - occurs when the head is tilted to the side. Expulsion from the sites of trauma to the spine or skull bones( in the case of craniocerebral trauma, a cerebrospinal fluid is mixed with blood).
of cerebrospinal fluid has a periodicity and lasts up to 2 minutes, can be abundant and lean, jet and drip. Nasal liquorrhea - comes from one nostril, and mostly with the head tilted forward. Exhaustion from the ears - occurs when the head is tilted to the side. Expulsion from the sites of trauma to the spine or skull bones( in the case of craniocerebral trauma, a cerebrospinal fluid is mixed with blood). - Cough , mainly during sleep, caused by the ingestion of cerebrospinal fluid into the bronchi and trachea.
- Headaches ( dull character) due to a decrease in intracranial pressure caused by leakage of cerebrospinal fluid. May occur with minimal physical exertion, with a change in the position of the body.
- Dehydration of - occurs with a long flow of liquorrhea. It is manifested in the form of dry skin, mucous membranes, weight loss.
- Decreased sense of smell, sight, hearing .
Forms of violation
Classify this condition can be depending on various characteristics: from the form of manifestation, from the place of expiration, from the cause.
According to the form of manifestation, cerebrospinal fluid is divided into apparent( spinal fluid is secreted) and latent( the liquor is not secreted out, swallowed).
Depending on the cause of development, it can be divided into primary( develops after surgery, trauma) and secondary( occurs after a while because of the liquor fistula).
Depending on the localization of cerebrospinal fluid leakage, a liquorrhea happens:
- spinal - the bleeding occurs from a defect, spinal injury;
- wound( postoperative) - fluid flows through the postoperative wound;
- ear - flow of liquid from the ears( due to fracture of the pyramid of the temporal bone);
- nasal - the liquor is secreted through the nose( due to injuries to the bones of the skull).
Diagnostic criteria
Liquorrhea is detected during examination and after examination. The methods of diagnosis include:
- anamnesis collection - helps to determine the time of appearance of the first signs of the condition( flow of clear liquid);identify
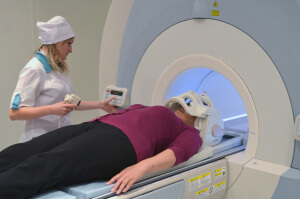 actions that could cause the development of a condition( trauma, surgery);
actions that could cause the development of a condition( trauma, surgery); - examination with the neurologist - is aimed at the detection of defects and injuries of the spine, skull, fracture of the base of the skull, leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the nose and ears;
- test for glucose in the fluid ( cerebrospinal fluid contains a large amount of glucose);
- test for the content of tau protein ( contained only in cerebrospinal fluid);
- is used computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging - allow to detect damage to the bones of the skull by layer-by-layer study of the structure of the brain;
- cisternography with the use of radiopaque preparations;
- sample of oil stain - with a handkerchief soak the leaky liquid( cerebrospinal fluid leaves oil stains, after drying the handkerchief remains soft).
It can also be recommended to visit and consult a neurosurgeon, an otolaryngologist, a traumatologist.
Aims and methods of therapy
Patients with cerebrospinal fluid need hospitalization in a neurological or neurosurgical hospital, treatment includes conservative and operational methods.
Often the process of treatment begins with the use of conservative methods that can reduce the allocation of CSF, reduce the liquor pressure, create conditions for stopping liquorrhea. Non-surgical methods include:
- prevention of stress in the abdomen, marking;
- maintaining the head in an elevated position to stop the exit of the cerebrospinal fluid;
- use of diuretics that reduce intracranial pressure;
- lumbar drainage - allows to reduce the cerebrospinal fluid pressure in the skull by reducing intracranial pressure;
- reception of antibiotics for the purpose of treatment and prevention of infectious diseases;
- reception of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
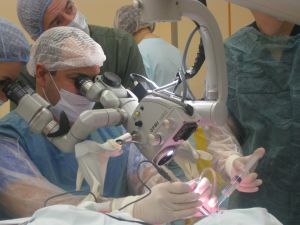 In case when conservative treatment does not bring a positive result, resort to surgical methods of therapy. Shunt, transcranial and transnasal operations are performed. Often, endoscopic methods are used, but they are rarely used for auric liquorrhea.
In case when conservative treatment does not bring a positive result, resort to surgical methods of therapy. Shunt, transcranial and transnasal operations are performed. Often, endoscopic methods are used, but they are rarely used for auric liquorrhea.
Operative therapy is aimed at surgical removal of trauma or defect of the skull and hard shell of the brain, stitching the wound;removal of the cavity with cerebrospinal fluid from the brain or spinal cord.
What is dangerous?
The danger of liquorrhea is the possible complications. To such consequences carry:
- meningitis - occurs due to infection from the nasal cavity along with the cerebrospinal fluid into the brain cavity;
- headache - due to the expiration of the cerebrospinal fluid, intracranial pressure decreases;
- pneumaticcephalus - ingress of air into the cerebral membranes, the ventricles of the brain, the substance of the brain;
- pneumonia and bronchitis - due to penetration of cerebrospinal fluid into the respiratory tract;
- gastritis, dysfunction or inflammation of the intestine - are caused by the ingress and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the stomach.