Page Contents
- 1 Gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnancy: a description of the disease
- 2 Causes of the disease and its features
- 3 Risk factors
- 4 Diagnostic methods - test results
- 5 Treatment of
- 6 Diabetes in gestational diabetes during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the most important anda crucial stage in the life of any woman. This is the period when a real miracle is happening inside - a small life develops. But often, when the child is born, old "sores" make themselves felt, which the future mother forgot long ago. This is due to the fact that against the background of hormonal changes in the body immunity often weakens and the body can no longer actively resist infections and diseases. Sometimes in this critical period there are quite serious failures associated with violations of carbohydrate metabolism and specialists diagnose gestational diabetes mellitus during pregnancy.
Most often the pathological condition begins to develop, starting from 15-16 weeks. It is noted in 4-6% of women bearing a child. As a rule, after the birth, symptoms of gestational diabetes disappear, but the risk of developing normal diabetes in the future increases. How dangerous is the disease, why is it developing, and are there any measures to prevent it?
Gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnancy: a description of the disease
 Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease of the endocrine system caused by the relative or absolute lack of the hormone insulin. As a result, there is a persistent increase in blood glucose( hyperglycemia), which is accompanied by a violation of carbohydrate, fat, protein and water-salt metabolism. That is, this ailment affects almost all organs and systems of the body.
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease of the endocrine system caused by the relative or absolute lack of the hormone insulin. As a result, there is a persistent increase in blood glucose( hyperglycemia), which is accompanied by a violation of carbohydrate, fat, protein and water-salt metabolism. That is, this ailment affects almost all organs and systems of the body.
Diabetes mellitus is divided into two types:
- Type 1 diabetes - the body produces insufficient amounts of insulin or is unable to produce it at all.
- Type 2 diabetes - the pancreas retains its functions and produces insulin, but as a result of damaging insulin receptors, tissue cells are unable to absorb it. This type is typical for people with excessive body weight and lack of physical activity, people of advanced age.
Diabetes during pregnancy is called "gestational", as it is first detected when the baby is born and is directly related to the position of the future mother. In prenatal practice, diabetes is difficult to describe as a common phenomenon - only 4% of pregnant women are diagnosed with this type of diagnosis. But knowledge about him will not be superfluous in preparing for the birth of a child.
Causes of the disease and its features
 The main factor that causes gestational diabetes is a violation of carbohydrate metabolism, resulting in a persistent increase in blood sugar levels. In the context of pregnancy, there are two main reasons for this phenomenon:
The main factor that causes gestational diabetes is a violation of carbohydrate metabolism, resulting in a persistent increase in blood sugar levels. In the context of pregnancy, there are two main reasons for this phenomenon:
- Growing fetus. The child continuously develops in the mother's body for 40 weeks. All this time he daily needs energy, the supplier of which is carbohydrates. Glucose is a necessary food for a future child. The mother's body has to spend tremendous efforts on its production, since glucose is necessary for the development of the fetus.
- Progesterone. Steroid hormone, responsible for the safety and successful course of pregnancy, affects the amount of insulin in the body, in part interfering with its production. In response to these measures, the pancreas produces insulin with redoubled strength, in order to maintain the required level of sugar in the blood. The load on this organ reaches an impressive scale, and if the pancreas does not cope with it, then the symptoms of diabetes mellitus appear.
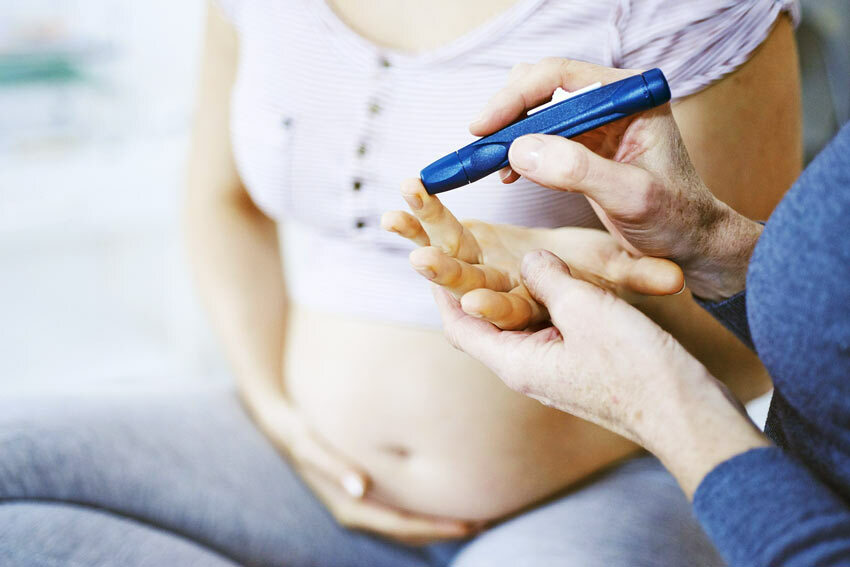 During pregnancy, the placenta produces special hormones necessary for the proper development of the fetus. If they block the production of insulin, there is a state of insulin resistance, that is, the cells become insensitive to insulin and the blood glucose level rises.
During pregnancy, the placenta produces special hormones necessary for the proper development of the fetus. If they block the production of insulin, there is a state of insulin resistance, that is, the cells become insensitive to insulin and the blood glucose level rises.
In the process of childbirth, sudden jumps of blood sugar can occur, associated with physical and emotional tension, aimed at the appearance of a child. After delivery( within 1-2 weeks), the test results are usually normalized. However, there remains a high risk of developing diabetes in the future.
Risk Factors
It is not necessary that during pregnancy a woman will be diagnosed with "diabetes mellitus".But there is such a thing as "risk factors", in the presence of which favorable conditions for the development of the disease are created. When planning a pregnancy, any woman can determine in advance whether she is at risk. For this, it is necessary to pay attention to the following features:
-
 Weighed heredity - the presence of close relatives suffering from diabetes mellitus, significantly increases the risk of developing the disease;
Weighed heredity - the presence of close relatives suffering from diabetes mellitus, significantly increases the risk of developing the disease; - Overweight, a tendency to obesity before pregnancy( especially if the amount of excess kilograms exceeded the norm by 20 or more percent).
- Polyhydramnios based on ultrasound data.
- Weighed obstetrical anamnesis - a severe pregnancy in the past, pathologies of child development, spontaneous abortions, frozen pregnancies, intrauterine fetal death.
- The birth of a large child - more than 4 kilograms.
- Late pregnancy( over the age of 30).
- The violation of the organism's tolerance to glucose is a periodic increase in the levels of sugar in the blood.
- Nationality. According to the doctors' observations, gestational diabetes is most often detected in a certain ethnic group( Hispanics, Asians and Africans).
If there is at least one of the above factors in the patient's history, a special test should be performed to determine the level of insulin production in the body and the degree of increase in sugar in the blood. This will allow you to make an accurate diagnosis and take timely measures when finding a malaise.
Symptoms of
 You can only give an unambiguous diagnosis based on the results of laboratory tests. It is not accidental that during pregnancy, before every scheduled visit to the doctor, a woman is supposed to pass an analysis of urine and blood - in terms of the level of glucose in them one can judge the risk of the disease.
You can only give an unambiguous diagnosis based on the results of laboratory tests. It is not accidental that during pregnancy, before every scheduled visit to the doctor, a woman is supposed to pass an analysis of urine and blood - in terms of the level of glucose in them one can judge the risk of the disease.
Paying attention to the results of the tests, it is important to take into account that in women in the position a slightly different standard of glucose in the blood. On average, this is 0.7 to 1 mmol / L higher than that of a healthy adult and is normally up to 7 mmol / l. Data above this figure is a clear sign of gestational diabetes, requiring confirmation of the diagnosis by performing additional tests and testing. Even before the next testing, you can suspect this ailment, focusing on a number of signs of diabetes:
- Constant dryness in the mouth, unceasing thirst;
- Frequent urge to urinate, profuse urination;
- Increased fatigue, weakness;
- Insomnia, psychoemotional instability
- Decreased visual acuity;
- Problems with appetite;
- Skin itching, localized in the perineal region of
The difficulty is that the above symptoms are also characteristic of a number of other diseases, which delay the moment of detection of diabetes and the adoption of measures for its treatment. Therefore, today the only reliable method of detecting diabetes in pregnancy is laboratory diagnosis.
 Diagnostic methods - analysis parameters of
Diagnostic methods - analysis parameters of
 Even if from the first weeks of pregnancy in the state of the future mother there were no factors indicating the possibility of developing diabetes, it must necessarily pass an analysis for diabetes mellitus during pregnancy. The blood test for glucose is prescribed in each trimester of pregnancy. If the blood sugar level exceeds the index of 5.1 mmol / l, the doctor will prescribe an additional test for glucose tolerance.
Even if from the first weeks of pregnancy in the state of the future mother there were no factors indicating the possibility of developing diabetes, it must necessarily pass an analysis for diabetes mellitus during pregnancy. The blood test for glucose is prescribed in each trimester of pregnancy. If the blood sugar level exceeds the index of 5.1 mmol / l, the doctor will prescribe an additional test for glucose tolerance.
What does this study consist of? On the appointed day on an empty stomach the pregnant woman is in a medical facility where she is taking blood from a vein. Immediately after this, she will need to drink a highly sweetened liquid, which contains about 50 grams of sugar.
An hour later, the doctor will again take venous blood for analysis. Then, after another 60 minutes, the analysis will repeat, that is, in total, the blood will be taken three times. A laboratory study of the material taken will show how successfully the body is able to metabolize the sugar solution and absorb glucose.
The diagnosis of "gestational diabetes" is confirmed if the analysis results are as follows:
- Sugar level "fasting" - more than 5.1 mmol / l;
- After 1 hour - more than 10 mmol / l;
- After an hour - more than 8.5 mmol / l.
To confirm the result, the test is repeated after 2 weeks.
Treatment of
 In the process of bearing a child, the expectant mother must constantly be under the supervision of a qualified specialist. The treatment of a pregnant woman with gestational diabetes is reduced to diet and physical activity. In 70% of cases this gives a positive effect. But if these measures do not bring tangible results, resort to injections of insulin.
In the process of bearing a child, the expectant mother must constantly be under the supervision of a qualified specialist. The treatment of a pregnant woman with gestational diabetes is reduced to diet and physical activity. In 70% of cases this gives a positive effect. But if these measures do not bring tangible results, resort to injections of insulin.
And, pregnancy with type 1 diabetes requires advance preparation - even at the planning stage, a woman should take insulin preparations. Pregnancy in type 2 diabetes also requires constant medical supervision.
For type 1 diabetes, the dosage of the drug depends on the severity of the condition. The doctor's task is to calculate the daily dose of insulin necessary for a pregnant woman, and, based on this figure, to write out the amount of injection for one application. In addition to insulin therapy with gestational diabetes, the following activities will help to cope:
-
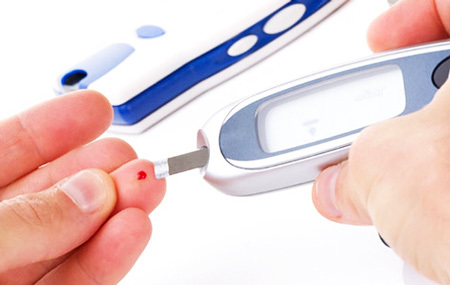 Regular urinalysis. If the results show ketone bodies, this indicates an uncontrolled course of diabetes.
Regular urinalysis. If the results show ketone bodies, this indicates an uncontrolled course of diabetes. - Control of blood sugar level. Using special devices and test strips, monitor the condition 4 times a day on an empty stomach or a couple of hours after a meal.
- Control over body weight. The rate of weight gain for the entire pregnancy should not exceed 12 kg. A woman should strictly follow this indicator.
- Blood pressure monitoring.
If the pathological condition is diagnosed in mild form, diet therapy and herbal medicine will be a salvation. Additionally, moderate physical activity and daily exercise are recommended for a pregnant woman. Long walks in the open air, swimming are useful. In addition, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of the doctor for adjusting the diet. Also, a completely natural drug that can be consumed by pregnant women - Diabenot - is not bad at all. Read more here.
Diet for gestational diabetes during pregnancy
 Diabetes in pregnancy is the main therapeutic method that helps to lower blood sugar levels. Its essence lies in a sharp limitation of the amount of carbohydrates and an increase in the proportion of proteins, vegetable fats and fiber.
Diabetes in pregnancy is the main therapeutic method that helps to lower blood sugar levels. Its essence lies in a sharp limitation of the amount of carbohydrates and an increase in the proportion of proteins, vegetable fats and fiber.
In the diet should be as much as possible to limit the "light" and starchy carbohydrates contained in sweets, flour and confectionery products, potatoes. Contraindications for gestational diabetes during pregnancy - eating bread, pastries, pasta. It is necessary to limit consumption of tomatoes, onions, sweet fruits.
A day can be eaten a handful of sour berries, one orange, an apple or half a grapefruit. On your table there should not be sweet fruits( bananas, grapes, melons).It is strictly forbidden to drink sweet fizzy drinks.
Favorite products for pregnant women with this diagnosis should be:
-
 lean meat,
lean meat, - fish,
- seafood,
- cheeses,
- milk,
- soy products,
- lentils.
The daily menu should be porridge, fresh vegetables and fruits. The diet should consist of protein foods( 30-60%), vegetable fats( 30%), complex carbohydrates( 40%).
Forbidden: 
- fried and fatty foods,
- semi-finished products,
- fast food,
- canned food,
- most meat products( dumplings, sausages, sausages).
Fatty dairy products( sour cream, cream, butter, cheese) are allowed in a minimal amount.
Many women in the position do not represent their life without ice cream. During this period, it acts not only as a favorite sweetness, but also as a wonderful home remedy for heartburn. It does not have to be abandoned if you have enough strength to learn how to do it yourself, replacing sugar with any natural sweetener.
It is important that the future mother should eat moderate portions, and not overeat. The ideal option is 6-8 times a day. Also, a profitable drink of clean water will bring benefits - at least 2 liters per day.
Phytotherapy
 Phytotherapy for diabetes can normalize blood sugar levels, improve the general condition and prevent the development of complications. Of course, before applying any prescription, you should consult your doctor and get his approval.
Phytotherapy for diabetes can normalize blood sugar levels, improve the general condition and prevent the development of complications. Of course, before applying any prescription, you should consult your doctor and get his approval.
- Well a decoction of herbs: 60 grams of blueberry leaves pour a liter of boiling water, insist 20 minutes, drain. Take up to 5 times a day for 100 ml.
- Functions of the pancreas well stimulates the substance secretin, which is contained in cabbage, artichoke, carrots. Improve the condition will help freshly squeezed plant juice.
- Against diabetic complications, vitamin doses( berries of raspberries, sea buckthorn, cranberries, cowberry, nettle leaves and sporrows) are used. It is useful to take forest berries, blueberries, make broths based on clover, chamomile, licorice or violets. These plants act as strong biostimulants, fight inflammation and promote the regeneration of renal tissues.
Possible consequences of
 What is dangerous for gestational diabetes in pregnancy ?The severity of the disease lies in the fact that it disrupts the metabolism, and this negatively affects the functioning of the woman's organism and provokes a shortage of nutrients for the fetus.
What is dangerous for gestational diabetes in pregnancy ?The severity of the disease lies in the fact that it disrupts the metabolism, and this negatively affects the functioning of the woman's organism and provokes a shortage of nutrients for the fetus.
According to statistics, only 15% of women suffer latent diabetes during pregnancy. They learn about its presence only after the test, not feeling any symptoms and anxiety. Unfortunately, not everyone is lucky in this way. The most common complications of gestational diabetes:
- . Malfunctions in the reproductive system. In the future, this results in miscarriages, premature births and even intrauterine fetal death.
- Mother's death. A similar prospect awaits half of the women diagnosed with ischemic heart disease.
- Gestosis - late toxicosis, manifested in puffiness, increased pressure, convulsions, loss of protein in the urine. Gestosis diabetes in pregnancy is at risk of developing pre-eclampsia, when irreversible damage occurs in the vascular system and circulation. Preeclampsia can be transformed into eclampsia, the outcome of which is coma and subsequent death.
- Polyhydramnios, which can cause premature birth.
-
 Diabetic fetopathy of the fetus and newborn, characterized by its large size( over 4 kg), pathology of the body's organs and systems, neurological and respiratory disorders, cardiovascular diseases, cyanotic limbs, hemorrhages in the face and body, swelling, lethargy, hypoglycemia.
Diabetic fetopathy of the fetus and newborn, characterized by its large size( over 4 kg), pathology of the body's organs and systems, neurological and respiratory disorders, cardiovascular diseases, cyanotic limbs, hemorrhages in the face and body, swelling, lethargy, hypoglycemia. - Development of a jaundice in a child in the first hours after birth. From physiological jaundice, it is distinguished by the degree of severity and duration of treatment.
- The death of a newborn is the most terrible variant of all possible. If a woman needed treatment during pregnancy, but for some reason did not receive it or did not follow the doctor's advice, in 80% of cases her newborn child is at risk of death in the first days of life. In time, the selected therapy helps to reduce this risk to 15%.
 If a woman has a history of diabetes, this does not mean that she can not give birth. It is recommended to plan pregnancy in advance. At the preliminary stage, you need to undergo the necessary examination and then carefully monitor your own condition and carefully follow all the recommendations of the treating doctor.
If a woman has a history of diabetes, this does not mean that she can not give birth. It is recommended to plan pregnancy in advance. At the preliminary stage, you need to undergo the necessary examination and then carefully monitor your own condition and carefully follow all the recommendations of the treating doctor.
If during a previous pregnancy a woman already had gestational diabetes, special attention should be paid to the diet, maintain her weight in norm and regularly perform physical exercises. These measures will help to avoid adverse effects and reduce the risk of developing a permanent form of diabetes after childbirth.
Childbirth with gestational diabetes
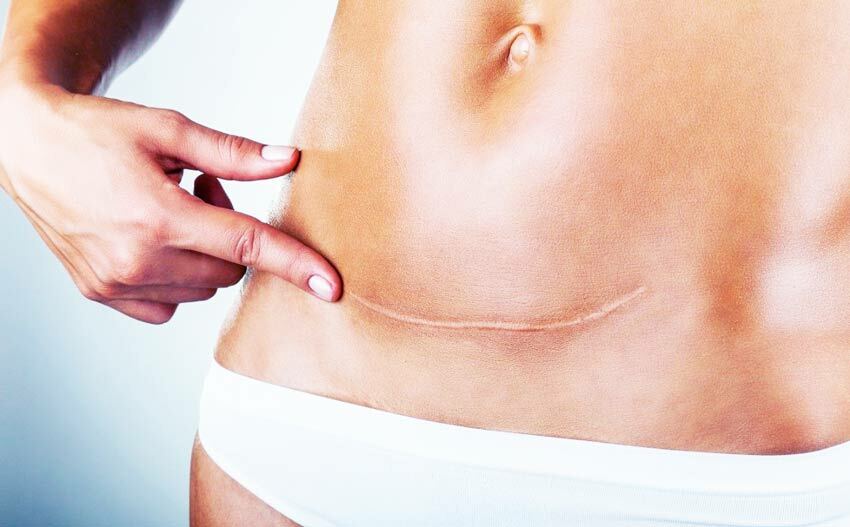 With this diagnosis, certain complications may occur during labor. Due to the developmental features, the child can be very large. In this case, you have to do cesarean section.
With this diagnosis, certain complications may occur during labor. Due to the developmental features, the child can be very large. In this case, you have to do cesarean section.
If a mother has gestational diabetes, the baby is born with a low blood sugar level. But this feature does not need a medical correction. During breastfeeding, the glucose level will return to normal. Until then, blood counts should be monitored by a laboratory.
A woman after childbirth should continue to adhere to a low-calorie diet, this will help get rid of hyperglycemia and avoid the development of diabetes in the future.