In a population living in the basins of large rivers( the Urals, the Volga, the Irtysh and others), a particular type of helminthiosis, opisthorchiasis, is often diagnosed. However, you can also become a helminth owner on a trip to Thailand, Ukraine, Kazakhstan. This is due to the fact that the source of infection is found in freshwater fish.
Opisthorchiasis is a rather dangerous disease, with a long course leading to severe consequences, up to the development of cancer. That is why it is necessary to diagnose as early as possible the presence of helminthiosis and to start antiparasitic treatment.
Contents
- 1 Opisthorchiasis - what is it?
- 1.1 Pathways of opisthorchiasis transmission
- 2 Symptoms of opisthorchiasis in adults, photos
- 3 Chronic opisthorchiasis
- 4 Analyzes and diagnostics of opisthorchiasis
- 5 Treatment of opisthorchiasis in adults, preparations
- 6 Prevention of opisthorchiasis
Opisthorchiasis - what is it?

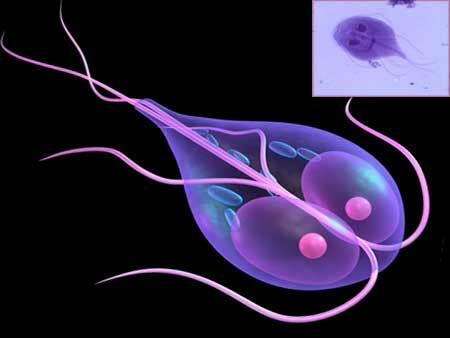
Opisthorchiasis is a hard-working parasitic lesion of the body caused by flat worm-flukes( cat litter) of the genus Opisthorchidae. Worm-flukes get into the human body or carnivorous animal( cats, dogs, foxes, etc.) when eating insufficiently processed fish( see photo).
Helminth parasitizes in the bile excretory system( gallbladder, hepatic passages, bile ducts).Already after 2 weeks the parasite begins to lay to 1000 larvae a day.
Damaging effect of worm-flukes on the human body:
- Attaching to the walls of the bile duct with two suckers, worms cause mechanical damage to the epithelial layer and provoke the development of inflammation.
- In case of a massive invasion, the squamming of the epithelium and the unregulated cell division can lead to the development of oncopathology.
- The products of the life of the opisthorchus have a toxic effect not only on the digestive tract, but also on the brain and heart.
- Large populations of parasites block the outflow of bile and spread to the adjacent sections of the gastrointestinal tract - stomach, pancreatic duct, 12-colon. All this leads to a violation of digestion.
Opisthorchiasis gives polymorphic symptoms, the detection of helminth often occurs already at the chronic stage of the disease. Without adequate therapy, flatworms live in a person up to 25 years. Even effective treatment of opisthorchiasis does not completely eliminate the damage done to the body.
Paths of transmission of the opisthorchiasis

Initially, the helminth larvae from water contaminated with the faeces of the diseased animal get into the mollusks( at this stage the parasite is not contagious to humans) and then into freshwater fish.
Mass infection is recorded among carp fish: roach, bream, rudd, golyan, tophole, gudgeon, czechoni, yaz, white-eyed and others.
However, cases of infection with opisthorchiasis from pike, ruff, burbot, perch and other predatory fish are recorded, having one habitat with the family of cyprinids.
Ways of infection:
- Use of invasive fish cooked with non-compliance with processing rules;
- A sample for the taste of fish minced meat( this is the "sin" of many housewives);
- Close communication with domestic animals( this applies mainly to children), when the feces with parasite eggs fall into the hands of a person.
It is absolutely impossible to catch opisthorchiasis when swimming in a pond infected with opisthorchia larvae. Once introduced into the skin, the larvae quickly die and can cause only an itch and a brief rise in temperature.
Also opisthorchiasis is not transmitted from person to person, provided that elementary hygiene standards are observed. The larvae of the parasite in the soil die within a few hours. But the freezing of the invaded fish in the refrigerator does not prevent human infection.
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis in adults, photos of
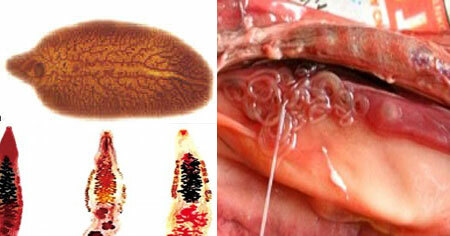
opisthorchiasis photos of
The duration of the incubation period of opisthorchiasis depends on the number of larvae caught, averaging 2-4 weeks. Further, depending on the state of immunity, suddenly there are signs of acute parasitic lesion. Acute opisthorchiasis in adults can proceed according to the following scenarios:
- The mild course lasts 1-2 weeks, the patient complains of fever at 38 ° C, weakness, fatigue, headache.
- Medium-severe course - an infected person has an itchy urticaria rash like urticaria( toxic effect on the vascular bed), muscle and joint pains, vomiting, diarrhea, temperature up to 39 ° C.Decreased appetite, perhaps weight loss. Symptoms last 2-3 weeks.
- Severe course - against the backdrop of an extremely serious condition of the patient due to severe intoxication, inhibition or psychomotor agitation, signs of lesion of separate departments of the digestive tract, insomnia are observed. Perhaps the development of acute epidermal necrosis( Lyell's syndrome), acute myocarditis, Stephen-Johnson syndrome, and Quincke's edema.
Forms of acute opisthorchiasis:
- Hepatocholangitis - is associated with extensive damage to the gallbladder and liver. The patient complains of spastic pain, localized in the right hypochondrium and imitating hepatic colic. The signs of stagnation of bile are fixed: icterus of the skin and sclera.
- Pancreatic-like signs of pancreatitis often accompany the involvement of the bile ducts. There are girdling pains, flatulence, indigestion.
- Gastroenterocolitis - symptoms of opisthorchiasis are dominated by signs of inflammatory and ulcerative lesions of the duodenum and, often, of the stomach. At the same time intoxication is most often expressed weakly.
- Typhoid-like - in the foreground in a symptomatic picture, skin rashes, hyperthermia, sometimes a cough appear.
In residents of dysfunctional areas of epidemiology of the opisthorchiasis in Western Siberia, the disease often proceeds in a latent form, without giving a vivid symptomatology.
Chronic opisthorchiasis

symptoms in the adult
Gradually pronounced symptoms of opisthorchias subside, and the disease goes to a chronic stage: against a background of temperature normalization there are symptoms of dyskinesia of bile ducts, cholecystitis, hepatitis, pancreatitis.
Often the patient is diagnosed with gastroduodenitis or stomach ulcers. And only the data of laboratory and instrumental studies allow to reveal helminthiasis.
Chronic opisthorchiasis is also characterized by toxic damage to other organs:
- of the central nervous system - permanent headaches, twitching of the eyelids, tremor of hands, irritability and depressive state;
- of the heart - heart pain, arrhythmia, signs of myocardial dystrophy appear on the ECG;
- depletion of the adrenal glands is an asthenic-vegetative syndrome.
Absence of treatment is fraught with the development of cirrhosis or liver cancer, pancreatic cancer, peritonitis.
Analysis and diagnosis of opisthorchiasis
The diagnosis of "opisthorchiasis" at an early stage of the disease is quite difficult: eggs of helminths in fecal masses and bile are found after 4-6 weeks.after infection. Diagnostic methods that detect the presence of flatworms in the body:
- A blood test with the definition of a leukocyte formula - eosinophillosis( indicates the presence of any helminths and the development of sensitization to a foreign protein);
- Biochemistry - an increase in hepatic enzymes( ALT, AST), a change in protein values;
- Feces on eggs worm - it is carried out repeatedly( eggs are allocated sporadically), up to 100 eggs per 1 g - mild degree, more than 30 thousand - massive invasion;
- Immunological analysis - blood for opisthorchiasis reveals antibodies to the opisthorchis protein;
- PCR - detection of helminth DNA in feces;
- Instrumental studies confirming opisthorchiasis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, CT, MRI - detection of damage to the liver and biliary tract;
- Duodenal sounding - detection in the harvested bile of opisthorchis eggs;
- Retrograde pancreocholangiography and percutaneous cholangiography - endoscopic techniques allow to identify clusters of helminths.
Treatment of opisthorchiasis in adults, drugs
Therapeutic tactics for opisthorchiasis involves the phased use of various medications. Antiparasitic treatment is preceded by a preparatory stage: the body should be prepared for a course of toxic drugs that destroy opistrochis.
Restorative course after antiparasitic treatment is also mandatory.
Preparatory course
With the beginning of opisthorchiasis treatment, the symptoms are eliminated in the first place, as well as the developing pathological processes:
- The maintenance of bile outflow - choleretic( Holensim, Holosas, Tsikvalon, Galstena), traditional spasmolytics( No-shpa, Buskopan, best - Duspatalin),cholepysmolithics( Platyphylline, Atropine);
- Restoration of digestion - enzymes( Mezim forte, Pancreatin, Creon), prokinetics( Motilium, Motilac);
- Elimination of cholestasis - Heptral, Ursofalk, Urososan;
- Elimination of sensitization - antiallergic agents( Tavegil, Suprastin), with severe allergic manifestations, corticosteroids( dexamethasone) are advisable;
- Detoxification of the body - sorbents( activated carbon, Prolisor, Enterosgel, Lactofiltrum), hepatoprotectors( Karsil), infusion therapy;
- Leveling of inflammatory phenomena - antibiotics( Amoxicillin, Ampicillin), Metronidazole, course - no more than 10-14 days.
The course of drug preparation takes 10-20 days.
Degelmentation of
The destruction of flatworms is carried out by the course of taking toxic anthelmintic drugs: Albendazole, Chloksila, Prazikvantela( the best).The treatment regimen for opisthorchosis in adults - dosage of medications, frequency of admission per day, and duration of the course - is determined individually.
With care, anthelmintic chemotherapy drugs are prescribed for elderly people and patients with severe heart, kidney and liver damage. These medications are contraindicated in pregnant women( 1 trimester), nursing mothers and children up to 4 years.
Against dehelmmentization, pains occur in the right upper quadrant, headache, nausea, weakness and dyspepsia increase. Sometimes in the first 2-3 weeks of taking anthelmintic drugs, there is a worsening of liver tests, possibly a skin rash.
On the 2nd day of dehelmmentation blind duodenal probing with xylitol or mineral water is conducted to excrete the products of the breakdown of worms into the intestine. An increase in the outflow of bile is achieved by using electrostimulation and a pulsed magnetic field.
Use of home remedies( popular - garlic with celandine) at the stage of dehelmmentation and replacement of prescribed anthelmintic medicines by the doctor are unacceptable!
Self-medication can lead to a worsening of the condition and definitely will not kill all parasites.
Rehabilitation stage
Medical therapy restores the normal functioning of the damaged parts of the digestive tract. For 3-4 months, antispasmodics, hepatoprotectors, cholagogue preparations are used.
It is at this stage that the treatment of opisthorchiasis is possible by folk remedies: the broths of St. John's wort, plantain, calendula, elecampane.
- Successful cure for opisthorchiasis is confirmed with negative studies of feces and duodenal contents 1, 3 and 6 months after the end of the treatment course. In each of these terms the study is carried out three times.
Prevention of opisthorchiasis
To avoid infection with opisthorchias, the following recommendations for the preparation and consumption of freshwater fish should be strictly observed:
- It is strictly forbidden to eat bad fish, not sufficiently processed, and, moreover, to sample the raw product.
- Refuse from fresh-salted fresh-water fish, stroganina.
- Thorough washing of dishes( cutting board, knife), which comes into contact with raw fish.
- Effective freezing: -28ºС - 32 hours, -35ºС - 14 hours, -40ºС - 7 hours.
- Cooking fish: pieces - 20 min., Fish semi-finished products( pelmeni) - 5 min. From the beginning of the boil.
- Fry: small fish whole - 15-20 minutes, large pieces and cutlets from minced fish - 20 minutes, fish cakes - in the oven for 1 hour.
- Salt in strong saline solution: large - 40 days, fish up to 25 cm - 21 days, small fish - 10 days.
- Ambassador before drying( 10 kg of product requires 2 kg of salt): 2 weeks.salting and drying on request, 3 days of pickling and drying 3 weeks.
- Smoking: hot + 70-80ºС - 2-2,5 hours, cold smoking type - salting 2 weeks or freezing.
Because of possible infection from animals, contact with wildlife( foxes, foxes) should be avoided. Home pets( cats, dogs) should be fed only well-boiled fish.