Among a variety of diseases of a urological nature, cystitis in women is the most common pathology. Etymology is caused by the damage of the upper mucous layer of the inner walls of the bladder by an inflammatory process. Sometimes the submucosal and muscular layer is involved in the lesion, causing changes in the tissue structure of the organ and impairing its functions.
Women are much more likely to develop cystitis( up to 80% of all patients).This is due to the peculiarity of the female anatomical structure of the urethral canal. It is wider and shorter than the male urethra, which does not cause difficulties in advancing in infectious agents.
The clinical picture of the disease can manifest itself in an acute or chronic course, with various symptoms and signs.
Contents
- 1 Causes of cystitis
- 2 Forms of cystitis and features of manifestation
- 3 Signs and symptoms of cystitis in women
- 4 Cystitis - which doctor should a woman refer to?
- 5 Diagnosis - Detection of the disease
- 6 Than to treat a cystitis in women?- drugs and medicines
- 7 Measures for the prevention of cystitis
Causes of cystitis
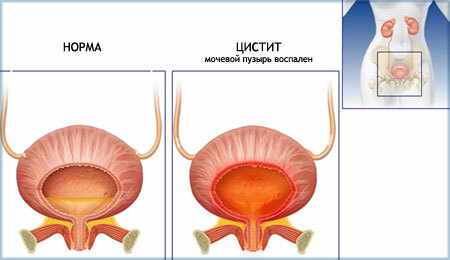
Cystitis itself refers to the classification of infectious diseases. Its genesis is associated with bacterial carriers: intestinal bacillus bacteria( 70%), globular staphylococci and other bacteria. The main role in the occurrence of cystitis in women is attributed to the spread of infection from possible foci of lesions in the body:
- In the underlying organs( different forms of vulvovaginitis);
- Downward pathway with urine flow from foci of inflammation in the kidneys and upper ureter;
- Hematogenous pathway of the pathogen( with blood flow).
Often, acute cystitis in women develops as a result of a structural underdevelopment of the urinary system or cancerous tumors that interfere with the normal process of urine output, contribute to its acute retention in the urinary system and the development of infection.
Various factors contributing to the development of pathology contribute to a decrease in the overall resistance( resistance) of immunity:
- Acute and chronic infectious diseases in the anamnesis( previously transferred) - inflammation of the appendages, fallopian tubes or ovaries, acute or purulent pyelonephritis, inflammation of the urethra;
- Subcooling and prolonged sedentary work;
- Conditions and diseases that reduce protection of immunity( pregnancy and diabetes);
- Chronic foci of infection - angina, rhinitis or caries;
- Immunosuppressive drugs, stress and instability of the nervous system;
- Back injury;
- Early sexual relations;
- Neglect of hygiene;
- The age factor.
Forms of cystitis and features of the manifestation
Cystitis in women can manifest itself in various forms, caused by a morphological change in the cavity wall of the bladder.
- The catarrhal pathology is characterized by hyperemia and swelling of the mucous layer of the organ membrane provoked by the action of the inflammatory process.
- With hemorrhagic form, bleeding lesions appear on the mucous membrane. There is an increase in erythrocytes and macrohematuria( dark or red urine).
- In necrotic( ulcerative) form, deep grooves in the form of furrows, penetrating into the muscle tissue of the membrane, are noted.
- The follicular form of the disease is characterized by the tuberosity of the mucous layer, caused by the formation of follicular tubercles under the mucous coating, which do not change the cavity surface itself.
- Fibrous appearance - the surface of the mucous layer is covered with a purulent or fibrin film of whitish or purple color. The walls of the bladder become inflamed, the upper membrane of the cavity is compacted and wrinkled.
- Bullous cystitis is manifested by prolonged excessive reddening and a significant accumulation of infiltration( swelling) of the upper layer of the inner membrane of the bladder.
- Polyposis manifestation is characterized by a long inflammatory process, which provokes the development of polyps on the mucous layer and in the cervical area of the organ.
- In cystic pathology, under the layer of the mucous coating of the bladder, single or group cystic neoplasms are formed, filled with lymphatic tissue and surrounded by a modified epithelium.
- The inlaying appearance of the pathology is distinguished by a prolonged course. A characteristic symptom is the formation of phosphate deposits( incrustations) on the walls of the cavity of the bladder, which subsequently promote the formation of stones. The transformation of carbamide( urea) into alkali occurs through the fault of bacterial microorganisms, capable of metabolism.
Signs and symptoms of cystitis in women
Bright symptoms of cystitis and severe signs of illness in women are noted in acute course, accompanied by: general intoxication( malaise, weakness, chills, vomiting or nausea, slight increase in temperature).
When the disease, after a remission( apparent recovery) periodically recurs( more than 2 times a year), it goes to the stage of chronic course. Symptoms of chronic cystitis in women can be manifested, less pronounced.
Inflammation processes alternate with the stage of remission and acute clinical course. Cystitis in the stage of remission does not show external signs and symptoms. When the disease worsens, the symptoms manifest themselves by a number of characteristic symptoms:
- Increased number of urge to urinate( every 20 minutes);
- Soreness, burning and cutting on the urethral throat at the time of urine output;
- Tenderness in the suprapubic zone( may be an independent symptom or accompany urinary output);
- Unpleasant odor and turbidity of urine, the formation of flakes, purulent, or blood clots in it;Sensation of residual urine in urine collection;
- Soreness in the lumbar and renal region;
- Possible development of enuresis( urinary incontinence).
Chronic cystitis in women has various signs of clinical course of the disease.
- Latent flow is stable, with rare or frequent exacerbation processes. The symptomatology is "erased", or completely absent.
- The persistent appearance is manifested as a characteristic symptom of chronic pathology. In this case, the functions of the urinal are not violated. There are alternations of remission and exacerbation, signs of hemorrhage within the body.
- Interstitial flow is characterized by stable painful signs of manifestation with significant symptoms. The spread of inflammation into the tissues, the disruption of the reservoir function( enuresis) is noted. This is the most severe type of disease course.
With timely treatment of the disease can be coped quickly, otherwise - do not avoid complications.
Probability of complications of
Absence of treatment, or incorrectly selected therapy, leads to relapse and complication of the disease:
- Transition of inflammatory processes in the muscular structure of the wall of the bladder - the development of the interstitial type of pathology.
- Ascending spread of infection, affecting the overlying organs of the urinary system, which contributes to the formation of accompanying background pathologies - defeat of renal pelvis, purulent inflammation of the kidneys, etc.
- Intraperitoneal rupture of the bladder( not excluded) followed by the formation of peritonitis.
Cystitis - which doctor should a woman address?
 With the manifestation of signs of the disease, to confirm the diagnosis, you need to contact a urologist. It is this doctor that solves the problems of a urological nature.
With the manifestation of signs of the disease, to confirm the diagnosis, you need to contact a urologist. It is this doctor that solves the problems of a urological nature.
To avoid the consequences of STDs, a gynecologist is needed. You may need a smear on the flora of the vagina, which will help to identify the disease and determine its stage of development.
Diagnosis - Detection of the disease
To diagnose the disease, various types of diagnostic tests are used, from rapid diagnostics to routine examination methods, including:
- blood and urine tests;
- revealing of hidden inflammatory processes in the urinary system( according to the Nechiporenko method);
- diagnosis of infectious diseases by PCR analysis;
- tank-seeding on the flora - detection of UPM( bacteria);
- revealing background diseases - ultrasound of the genitourinary system;
- analysis for vaginal dysbiosis;
- biopsy;
- endoscopic examination of the internal cavity of the bladder( cystoscopy)
Than to treat a cystitis in women?- drugs and medications

On the correctly written protocol of treatment depends on how quickly it is possible to cure cystitis in women. Therapeutic tactics include various therapeutic techniques.
Medical therapy - prescribes the appointment of appropriate antibiotics, with chronic cystitis in women who suppress co-infection - a class of cephalosporins and combinations of protected penicillins.
- They are prescribed immediately, without waiting for the identification of the pathogen, followed by correction of the drugs.
The main treatment is tableting. In the treatment of cystitis in women, pills are prescribed to relieve symptoms. These include anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating agents, antispasmodics and uroseptics based on nitrofurans and sulfonamides.
As an additional treatment may be prescribed antispasmodics and natural uroseptics( herbs, collections, etc.).
Specific drugs are prescribed exclusively individually. Since many of them have a number of contraindications and limitations in admission. The treatment will be complete if the sparing regimen and balanced diet are observed, since the diet plays an important role.
- it is necessary to use more liquid( water without gas, juices);
- more products with vitamin C content;
- to exclude from the ration of smoked meat, spices, fried foods, dishes saturated with potassium( dishes from cottage cheese, cheese and milk);
- is not allowed to drink alcohol.
Measures for the prevention of cystitis
To prevent the recurrence of the disease should be strictly adhered to the recommendations of the attending physician. Basic rules:
- avoid overcooling and prolonged sitting;
- use up to 1.5 liters.liquid per day;
- not to allow stagnation of urine( do not tolerate urge);
- use intimate proximity protection methods;
- does not neglect personal hygiene( especially during the menstrual cycle).
Observance of such not tricky rules, will protect from repeated treatment of illness.