Stones in the bladder( cystoliths) are formed during the fusion of minerals into small solid formations. Suitable conditions arise with incomplete emptying of the bladder, which causes the urine to become concentrated - this leads to crystallization of the dissolved minerals contained in it.
Sometimes these stones come out( while they are small), sometimes they are fixed to the wall of the urinary or urethra, gradually increasing in size.
Often, the cystoliths stay in the bladder for a long time without causing any symptoms and are found out by chance, while undergoing a survey on other health problems.
Contents
- 1 Causes of stones in the bladder
- 1.1 Kinds and composition of stones
- 2 Symptoms of stones in the bladder
- 2.1 Features in women
- 3 Diagnosis
- 4 Treatment of stones in the bladder
- 4.1 Possible complications
- 5 Prevention and recommendations
Causes of stones in theurinary bladder
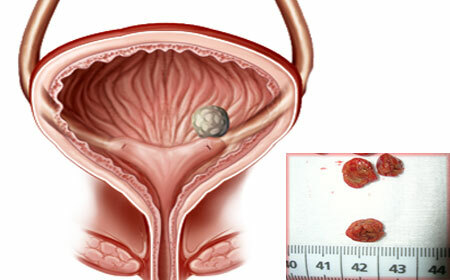
So, as the cystoliths begin to form in the residual urine, which is not completely excreted from the bladder, the search for the causes of the formation of stones is related to the definitiondiseases will impede the full emptying. To such pathologies belong:
- Neurogenic bladder - is observed when the nerves that connect the bladder with the spinal cord and the brain( for example, after a stroke or spinal injury) are damaged.
- Enlarged prostate - an enlarged prostate compresses the urethra.
- Medical devices - catheters, suture material, stents, third-party bodies in the bladder, devices for contraception.
- Inflammation of the urinary bladder.
- Kidney stones - they can migrate through the ureters into the bladder and grow in size.
- Diverticula of the bladder - they accumulate and stagnate urine.
- Cystocele - in women, the wall of the bladder can fall into the vagina, which breaks the emptying.
Kinds and composition of stones
Not all stones consist of the same minerals. Their various types include:
- Calcium stones - composed of oxalates, phosphates and calcium hydroxyphosphates.
- Stones from uric acid are the most common type in adults.
- Struvites - this type of stone is found most often in women with urinary tract infections.
- Cystins - occur in patients with a hereditary cystinuria disease, in which the amino acid cystine is released from the kidneys into the urine.
The cystoliths have different sizes and texture - they can be single or grouped, rounded or have outgrowths.
The largest stone found in the bladder weighed 1899 g and measured 17.9 x 12.7 x 9.5 cm.
Symptoms of stones in the bladder
 Sometimes the symptoms of stones in the bladder do not appear for a long time. But, as soon as they begin to irritate the walls, there are characteristic signs. So, the symptoms of a stone in the bladder can be:
Sometimes the symptoms of stones in the bladder do not appear for a long time. But, as soon as they begin to irritate the walls, there are characteristic signs. So, the symptoms of a stone in the bladder can be:
- Discomfort or pain in the penis in men.
- More frequent urination or intermittent flow of urine.
- Slow onset of urination.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Pain and discomfort during urination.
- Blood in the urine.
- Turbid or abnormally dark urine.
Features in women
The cause of the formation of cystolites in women can be cystocele( prolapse of the urinary in the vagina), contraception, migrated to the bladder, vaginal reconstructions.
Cystocele is manifested by the sensation of an external body in the vagina, unpleasant sensations during sex.
Because the urethra in women is shorter than in men, its infectious inflammation( urethritis) is more prone to progression to cystitis( inflammation of the bladder).Repeated cystitis is a risk factor for the formation of cystolites and a sign of their presence in women.
Diagnosis of
The presence of cystolites is detected using the following methods:
- Urinalysis - Determines the presence of blood, bacteria and minerals crystals.
- Computed tomography.
- Ultrasound examination.
- Radiography( with this survey not all types of cystolites can be seen).
- Intravenous pyelography - intravenously injected with a special contrast, which through the kidneys is released into the bladder.
Treatment of stones in the bladder
With a small size of stones, their natural excretion is facilitated by increased water intake. If they are too large to pass through the urethra, the treatment is divided into two groups: crushing stones and surgical removal.
It is important to note that there is no scientific evidence that confirms the effectiveness of treatment with folk remedies.
Stone crushing
Cystolitholapaxia( crushing stones) consists in placing a thin tube with a camera at the end through the urethra in the bladder, through which the doctor sees the stones and can break them.
For this, laser, ultrasound or mechanical crushing is used, after which the debris is washed out or sucked. This procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia.
Surgical removal of
If the stones are so large that they can not be broken with cystolitholapaxy, another option is treatment. The surgeon makes a cut in the abdominal wall and bladder, through which the cystolite is extracted.
Possible complications of
Despite the fact that some of the cystolites do not cause any complaints, they can still lead to a number of complications:
- Chronic bladder dysfunction( frequent urination, pain and discomfort associated with it).Over time, cystolite can completely block the opening of the urethra, blocking the exit of urine from the bladder.
- Urinary tract infection.
Prevention and recommendations
Since the formation of stones is usually caused by the presence of a disease, no fail-safe and specific prevention methods do not exist.
However, if a person has any impairment from the urinary tract( for example, pain when urinating, changing the color of urine), it is advisable to seek medical help immediately. The use of a sufficient amount of liquid also helps dissolve the minerals.
If a person has an infectious disease of the urinary tract and incomplete emptying of the bladder, he should re-try to urinate 10-20 seconds after the first attempt. This technique is called "double emptying", it helps to prevent the formation of cystolites.
There is an opinion that the sitting position during urination helps to completely empty the bladder in patients with an enlarged prostate. This, in turn, prevents or slows the formation of cystolites.