According to statistics, diabetes ranks second in the world in the frequency of occurrence, after cardiovascular pathologies.
The disease tends to rejuvenate: if before insulin-dependent diabetes was the lot of people over 35 years old, today this pathology is diagnosed even in young children.
Contents
- 1 Type 1 diabetes mellitus - what is this disease?
- 2 Causes of type 1 diabetes mellitus
- 3 Symptoms of type 1 diabetes
- 4 Diagnosis of type 1 diabetes
- 5 Treatment of type 1 diabetes
- 6 Complications of type 1 diabetes
- 6.1 Diabetes nutrition of type 1
- 7 Diabetes mellitus type 1 MKB 10
Diabetes mellitus 1type - what is this illness?
 Type 1 diabetes mellitus( or insulin dependent diabetes) is an endocrine disease characterized by inadequate production of the hormone insulin by the pancreas. As a result, a person has an elevated level of sugar in the blood plasma and concomitant underlying symptoms - constant thirst, causeless weight loss.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus( or insulin dependent diabetes) is an endocrine disease characterized by inadequate production of the hormone insulin by the pancreas. As a result, a person has an elevated level of sugar in the blood plasma and concomitant underlying symptoms - constant thirst, causeless weight loss.
The disease is incurable, so when diagnosing diabetes, patients have to take life-long medications that lower blood sugar levels and carefully monitor their condition.
Life expectancy in type 1 diabetes mellitus, with competent treatment and follow-up of the doctor's recommendations, is quite high - more than 30-35 years.
Causes of type 1 diabetes mellitus
There are no exact causes of the development of the disease. It is believed that the most predisposing factor of insulin-dependent diabetes is a genetic predisposition.
In addition to heredity, other factors may lead to the development of the disease:
- Obesity or excessive weight;
- Disturbance of the diet - the constant use of baking, chocolate, simple carbohydrates, resulting in the human body is violated carbohydrate and fat metabolism, which in turn provokes a malfunction in the pancreas;
- Chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic necrosis;
- Stress;
- Alcoholism;
- The use of drugs that are destructive to pancreatic cells responsible for the production of the hormone insulin( the so-called islets of Langerhans);
- Postponed infectious diseases and gland failures in the thyroid gland.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes

Symptoms of type 1 diabetes, photo 1
The first signs of type 1 diabetes are the following:
- Rapid weight loss;
- Increased thirst;
- Increased appetite;
- Increased urination( polyuria);
- Lethargy, fast fatigue, drowsiness;
- Feeling of hunger, which is accompanied by pallor of the skin, tachycardia, cold sweating, lowering of blood pressure;
- Tingling sensation in the fingertips and muscle weakness.
In women , one of the first signs of diabetes is severe itching of the perineum and external genitalia, which is caused by the presence of sugar crystals in the urine.
After going to the toilet, the drops of urine remain on the skin and mucous membranes, causing severe irritation and unbearable itching, which forces women to consult a doctor.
In men, , the first clinical manifestation of type 1 diabetes is sexual dysfunction( erectile dysfunction) and lack of sexual desire.
The disease may take a while to go latently or the patient simply does not attach importance to the developing clinical picture.
To cautions and become an occasion for immediate medical attention, non-healing scratches and minor wounds on the surface of the skin, the formation of boils and ulcers, as well as a sharp deterioration of immunity, frequent colds and general malaise should be observed.
Diagnosis of type 1 diabetes
Diagnosis of insulin-dependent diabetes is usually not difficult, if a patient is suspected of a disease, it is prescribed to take a blood test to determine the level of glucose.
In order for the results of the study to be reliable, blood must be taken on an empty stomach, and 8 hours before the procedure, the patient should not eat sweets, eat, drink coffee, smoke and take medications.
The optimal blood sugar is 3-3.5 mmol / l, in pregnant women these values can reach 4-5 mmol / l, which is not a pathology. With diabetes, the blood glucose level on an empty stomach will be 7.0-7.8 mmol / l.
For the reliability of the diagnosis, the patient is given a glucose tolerance test: first, the blood is taken on an empty stomach, then the patient is given a glucose solution and recommended to retake the assay after 2 hours. If the result after 2 hours is more than 9.0-11.0 mmol / l, then this indicates a type 1 diabetes mellitus.
The most informative method of diagnosing the disease is a test for glycosylated hemoglobin A1C, which allows to correctly diagnose and does not require long preparation of the patient.
Treatment of type 1 diabetes
 When a diagnosis of insulin-dependent diabetes is confirmed, the doctor gives the patient an individual treatment regimen - these are drugs that lower the blood glucose level that the patient must take for life.
When a diagnosis of insulin-dependent diabetes is confirmed, the doctor gives the patient an individual treatment regimen - these are drugs that lower the blood glucose level that the patient must take for life.
The dose of the medicine can be adjusted depending on the characteristics of the patient's body, the course of the disease, the parallel use of other drugs, the presence of complications.
At the initial stage of treatment, the patient is prescribed insulin preparations in tablet form, but if the effect is insufficient or poorly expressed, and diabetes mellitus progresses, then insulin injections are used.
The dose of the hormone is calculated strictly individually, it must be administered to the patient subcutaneously( in the area of the shoulder, the external part of the thigh, the anterior abdominal wall).
Places of injection should be constantly alternated, because when injections of insulin into one and the same place in the patient, lipodystrophy develops rapidly.
Depending on the ability and quantity of insulin production, the patient is prescribed background preparations( injected several times per day) or prolonged action( enough 1 injection per day) to the islets of Langerhans.
Each patient with diagnosed type 1 diabetes should carry a special glucometer - a pocket device that will allow you to quickly measure the blood glucose level.
Insulin pump
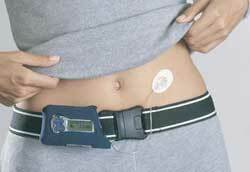
Insulin pump, photo 3
Patients in whom the pancreas practically does not work and does not produce an insulin hormone, an insulin pump is installed.
The pump is a small device through which the patient continuously receives insulin at a given dosage through a special tube with a needle. The needle is inserted into the anterior abdominal wall and is replaced every few days.
The advantage of this method of treatment is the abolition of the need to constantly inject insulin injectively and better control of the course of the disease, but the lack of a pump is its high cost, as a result not all diabetics can afford to install it.
Complications of type 1 diabetes

Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus is cunning because the disease is rapidly progressing and the patient's condition can rapidly deteriorate.
In case of untimely detection of pathology and sudden changes in blood serum glucose levels, the patient may develop complications:
- Diabetic angiopathy - the blood vessels of the eyes, limbs, heart, kidneys and other vital organs are affected, as a result of which their work is disrupted;
- Insufficient blood supply and nutrition of the heart muscle, heart attack;
- Gangrene - develops as a result of the appearance on the surface of the skin of small wounds and sores that do not heal and can constantly fester;
- Diabetic foot - changing the shape of the foot, reducing the sensitivity of the skin, fungal lesions and the formation of microscopic cracks;
- Hepatitis;
- Osteoporosis;
- Obesity of the liver.
The most dangerous complication of type 1 diabetes is coma:
- Hypoglycemia - caused by an overdose of insulin;
- Ketoacidotic - is caused by a high level of glucose in the blood and the accumulation of ketone bodies.
Both conditions pose a threat to the life of the patient, and in the absence of skilled, timely care, death is caused.
How many people live with type 1 diabetes, depends largely on the clinical picture of the disease and the ability to control blood glucose levels.
When performing all the medical recommendations, following a diet and leading a healthy lifestyle, patients live to their old age without complications.
- More about complications in diabetes mellitus
Nutrition for type 1 diabetes
In addition to medical treatment, the patient must always follow a diet with a sharp restriction on the amount of carbohydrates and fats( potatoes, animal fats, sweets, chocolate, coffee, beans, cakes and pastries, fatty cottage cheese, alcoholic beverages, pasta, fresh white bread).
The basis of the ration consists of porridges, bran, fresh fruits and vegetables, lean meat, sour-milk products.
Diabetes mellitus type 1 MKB 10
In the international classifier of diseases, type 1 diabetes mellitus is:
Class IV - Endocrine system diseases, eating disorders and metabolic disorders( E00 - E90)
Diabetes mellitus( E10-E14)
- E10 Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. This item excludes: diabetes associated with malnutrition( E12.-), neonates( P70.2), during pregnancy, during labor and in the puerperium( O24.-), glycosuria: RDU( R81), renal(E74.8), impaired glucose tolerance( R73.0), postoperative hypoinsulinemia( E89.1)