Thrombocytopenic purpura is a common cause of hemorrhages and hemorrhages in adolescents and young children. In such a situation, it is important not to get lost and try to find answers to the questions, why it happened and what to do with it further.
What is it?
Thrombocytopenic purpura is a pathology characterized by a tendency to develop bleeding due to a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood. This is one of the most common diseases of the hemorrhagic diathesis group.
The first manifestations of the disease begin to worry the patient already in childhood. The disease is equally common in boys and girls of young children, but after 10-12 years this pathology affects mostly female representatives.
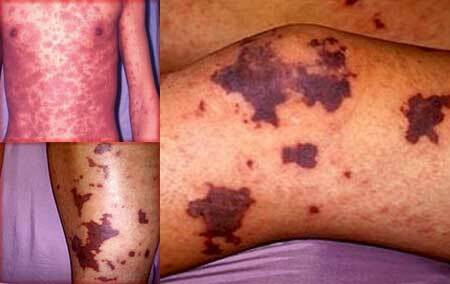
Thrombocytopenic purpura, photo 1
The exact cause of the development of this problem is not fully understood. The provoking factors are infections, hormonal crises, etc. There are immune and non-immune mechanisms of the disease development.
Content
- 1 Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- 1.1 Types thrombocytopenic purpura in humans
- 2 Thrombocytopenic purpura in children
- 3 treatment of thrombocytopenic purpura
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
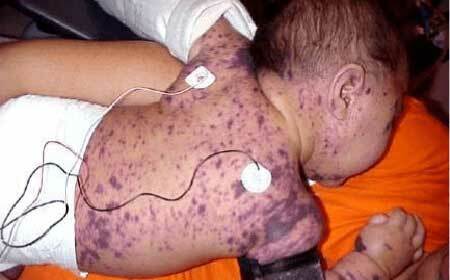
photo 2
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura( ITP), the second name thrombocytopenic purpura disease - is one of the first known haemorrhagic disease. The word "thrombocytopenia" suggests that in this pathology a decrease in the number of platelets occurs. These are cells of the blood coagulation system that participate in the reactions of thrombosis and stop bleeding.
The term "idiopathic" means that the cause that triggered this process is unknown. The factor that initiates the beginning of the ITP may be trauma, excessive exposure to ultraviolet light, stress, medication, vaccinations, etc., but in more than a third of patients the disease develops for no apparent reason.
- What happens with this pathology?
The human immune system begins to consider its own platelets an alien substance. In response, it develops special antiplatelet immune complexes that settle on platelets.
In the spleen, there is destruction and death of such platelet-labeled immune complexes and their absorption by macrophages. In the blood, the platelet count drops and the body begins to intensively produce them, which gradually leads to depletion of the stock of these cells and their qualitative deformation.
It turns out a kind of vicious circle: on the one hand, the immune system itself destroys platelets, and itself tries to restore their number through enhanced synthesis, which leads to sad consequences.
Types of thrombocytopenic purpura in humans
Two pathologies are distinguished by the development mechanism:
- Autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. It runs chronically with frequent relapses, the cause of development is unclear. On their own unchanged platelets produced antibodies. In addition, such antibodies can attack the precursors of these cells, as well as other blood elements and stem cells.
- Hetero-immune. In these cases, antibodies are attacked only by those platelets that have changed their structure under the influence of viruses, bacteria, allergens or the action of the drug. Such immune thrombocytopenic purpura has a more favorable course, since after the elimination of the causative factor everything is normalized and the antibodies stop producing. It is this form that usually occurs in children.
The disease can occur in acute( up to six months) and chronic form( over six months).Chronic form occurs with frequent and rare relapses. Although thrombocytopenic purpura in adults is often acute, a persistent recurrent chronic form of ITP occurs.
Depending on the number of platelets and clinical symptoms, mild, moderate and severe severity of the disease is isolated. In addition, according to clinical signs, it is divided into:
- "dry" - subcutaneous hemorrhage predominates;
- "wet" - a combination of bleeding and hemorrhage.
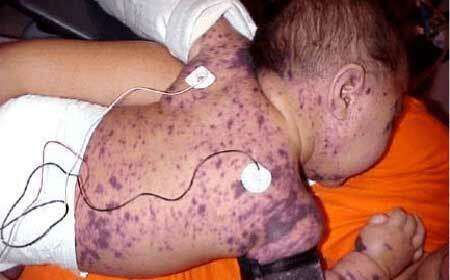
Thrombocytopenic purpura in children
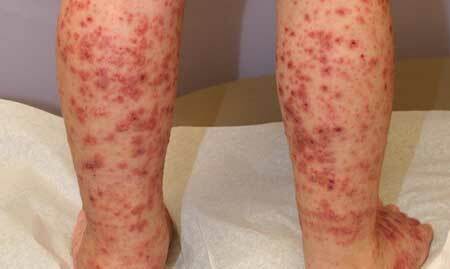
purpura thrombocytopenic, photos in children
In most cases, thrombocytopenic purpura in childhood begins acutely. The first manifestations of the disease may not be noticed by parents, because children are very mobile due to age and are prone to injuries and abrasions.
After the doctor begins to collect anamnesis, it is possible to establish that signs of pathology and damage to inadequate injuries have occurred in the child for a long time.
Clinically, the disease manifests itself:
1. Skin hemorrhagic syndrome. Its signs:
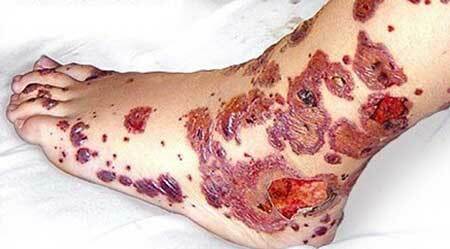
- Spontaneous appearance of subcutaneous hemorrhages( hemorrhages).They are formed usually at night under the influence of minimal traumatic forces: mild compression, compression, bruising;
- The variety of sizes of such hemorrhages: from point to large, merging with each other;The disparity between the size and nature of damage to the injuring force, i.e.a minor bruise can cause extensive hemorrhage;
- Some patients have hemorrhages in the mucous membranes or sclera. This is an unfavorable sign, as the risk of a serious complication of ITP is increasing - hemorrhage to the brain;
- Polychrome - this means that their appearance differs by prescription of appearance: there are fresh bright red elements and blue-green ones at the stage of reverse development;
- They are formed almost everywhere, there are no favorite places for localization of hemorrhages.
2. Bleeding. Their characteristics:
- Develop together with skin hemorrhagic manifestations;
- Often there are nasal, gingival and uterine bleedings, less often esophageal, gastric, renal. In girls, the disease may manifest as prolonged, excessive menstruation;
- Hemorrhage in the brain and other severe bleeding can cause death.
Important! Bleeding after tooth extraction is serious in patients with undiagnosed thrombocytopenic purpura. Such bleeding begins immediately after the intervention and does not stop for a long time, causing the development of acute anemia.
In addition to this tendency to increased bleeding, the general condition of the child is not violated. He does not have a fever, no chills, no other signs of intoxication. In rare cases, there is an increase in the size of the spleen and liver.
In addition, with frequent prolonged bleeding, the symptoms of anemia develop, which can be eliminated by taking appropriate medications.
Depending on the period, two forms of the disease are distinguished:
1. Acute( haemorrhagic crisis).The hemorrhagic syndrome is expressed and laboratory parameters of blood are changed.
2. Remission:
- clinical. According to laboratory data, there is a decrease in the number of platelets, but there are no clinical manifestations of the disease;
- clinical-hematological. There are no symptoms of the disease, no changes in blood tests.
The diagnosis is based on the history, laboratory indicators and the exclusion of other possible variants of thrombocytopenia.
Treatment of thrombocytopenic purpura
Treatment of thrombocytopenic purpura depends on the form and stage of the disease. The acute phase is recommended for bed rest and activities aimed at stopping bleeding: blood transfusion, hemostatics, etc.
All remedies are aimed at preventing the development of another bleeding during the remission period.
One of the controversial methods of treatment has been and remains splenectomy( removal of the spleen).It is believed that antibodies are produced in this organ that cause platelet death, but this point has not been fully studied to the present.
- The operation is performed only during the remission period.