 Osteoarthritis( OA) is an irreversible progressive joint disease characterized by the development of a degenerative-dystrophic process with the defeat of all articular components.
Osteoarthritis( OA) is an irreversible progressive joint disease characterized by the development of a degenerative-dystrophic process with the defeat of all articular components.
OA is the most common joint pathology.
First, cartilage and peri-limb bone are affected, then ligaments, capsule and periarticular muscles are involved. Often, dystrophic changes are combined with joint inflammation, which allows treating the disease as arthrosis-arthritis.
Cartilage plays the role of a shock absorber in the joint: its smooth surface reduces friction between the bones and provides good mobility of them. With this disturbance, the cartilaginous surface turns into a rough unevenness, it can wear off to the bone.
Contents of the article
- Features of deforming osteoarthrosis
- Some statistics
- Classification of the violation
- What is caused by the destruction of joints?
- Diagnostic techniques
- Therapeutic techniques
- Wide choice
- physioprocedure and lifestyle medications
- Traditional medicine
- surgery, as an extreme method
- Complications
- Preventive measures
Features deforming osteoarthritis
OA always leads to deformation of the joint, which allows the pathology refer to as deforming osteoarthritis( DOA).In ICD( International Classification of Diseases) stands for synonyms: osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis, arthrosis, deforming arthrosis.
Main symptoms:
- Pain syndrome is the most common manifestation of the disease. Initially, the rhythm of pain is typical: their appearance after exercise and disappearance after a night rest. Pain can appear after a long fixed posture( "starting pain") and pass after active movements. In the future, the pain becomes permanent, worry at night.
- Morning stiffness in the morning, limited mobility lasting up to 30 minutes.
- Sensation of a crunch, a cod at movement in a joint, a friction of bones among themselves .
- Puffiness, an increase in temperature over the joint appear with inflammation of it.
- Gradually develop stiffness and joint deformity .
- When the spine is damaged, the nerves are gradually squeezed, that results in numbness, a violation of the sensitivity of in various parts of the body, can be disturbed by dizziness, vomiting and other manifestations.

Some statistics
OA is registered all over the world: it suffers about 16% of the world population. The incidence and prevalence of osteoarthritis varies from country to country.
In the United States, about 7% of the population( over 21 million people) is sick, and 2% are under the age of 45;in Sweden - 5.8% of the population( age 50-70 years);in Russia - about 15 million people.
With age, the incidence dramatically increases: in the elderly and senile one third is sick. Among the sick young people, men predominate, among the elderly women.
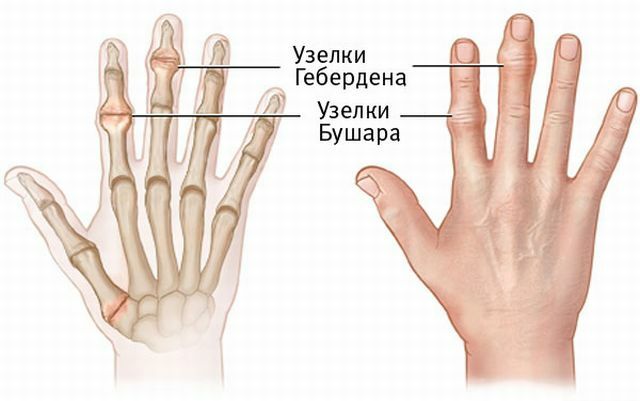
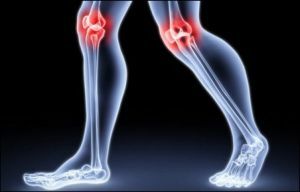
Osteoarthritis of the hip and knee joint is most common, intervertebral joints are also affected, less often - carpometacarpal and interphalangeal joints.
The severity of functional disorders is dominated by knee, hip and shoulder joint injuries.
The destruction begins with one joint, then others are involved, who took on the compensatory load. More often the first signs appear at the age of 40-45 years.
Classification of violation
There are several types of classification of the disease.
Primary and secondary osteoarthrosis( associated with dysplasia, violation of posture, joint diseases, trauma, etc.) is isolated, with and without synovitis phenomena.
There are clinical forms:
- monoarthrosis - one joint is affected;
- oligosteoarthrosis - a lesion of 2 joints;
- polyostoarthrosis - more than 3 joints involved.
Depending on the location: 
- gonarthrosis of the knee joint;
- coxarthrosis of the hip joint;
- omarthrosis of the shoulder joint;
- OA of other joints.
Based on radiological manifestations, 5 stages of DOA are isolated.
There are functional disorders of the joints:
- PH 1 - temporary disability;
- FN 2 - permanently lost ability to work;
- FN 3 - the need for extraneous care for the patient.
What causes joint destruction?
Until the end of the cause of the destruction of cartilaginous tissue have not been clarified. Changes in tissue cells lead to softening of cartilage, a decrease in its thickness, narrowing of the joint gap, thickening of the osseous part, the formation of osteophytes( bone spines) and cysts.
The risk factors for development include:
- age: the risk of pathology increases with age;
- sex: in women OA is more common;
- obesity;
- congenital deformation of joints and bones;
- injury;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- increased stress on joints( sport, lifting of gravity);
- operations on joints;
- hormonal disorders.
The genetic predisposition to the disease associated with the mutation of the type II gene( cartilage protein) is not excluded.
Diagnostic Techniques
For diagnosis, the following can be used:
- patient complaint survey;
- joint examination: configuration, swelling, redness, soreness with palpation, amplitude of movements;
- radiograph reveals a narrowing of the joint gap, the presence of bone spines;
- MRI gives more clear images of joints and surrounding tissues than on X-ray images;
- ultrasound;
- blood test allows you to differentiate OA from other joint damage;
- analysis of fluid from the joint to avoid inflammation in it.
Treatment methods
An effective way to treat osteoarthritis, which can stop the progression of the process, no.
Existing curative methods are aimed at achieving the objectives:
- unloading joints;
- reduction of pain and inflammation;
- reduction in the rate of progression;
- improved joint function.
Distinguish such methods of treatment:
- medicamentous;
- is not medicated;
- methods of traditional medicine;
- surgical treatment.
A wide selection of medicines
Medical therapy in the treatment of osteoarthritis consists in the appointment of drugs that have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, chondroprotective action:
- Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect of is possessed by drugs from the group of NSAIDs( Naproxen, Ibuprofen,
 Diclofenac, Xsefokam, Melbeck, etc.).They can be used inside, in injections, externally in the form of gels, creams, ointments( Deep Relief, Fastum, Diklak).With prolonged use, drugs can cause side effects from the digestive tract( pain in the stomach, nausea, diarrhea).Contraindication for them is a peptic ulcer. Local external application of drugs of this group avoids side effects.
Diclofenac, Xsefokam, Melbeck, etc.).They can be used inside, in injections, externally in the form of gels, creams, ointments( Deep Relief, Fastum, Diklak).With prolonged use, drugs can cause side effects from the digestive tract( pain in the stomach, nausea, diarrhea).Contraindication for them is a peptic ulcer. Local external application of drugs of this group avoids side effects. - In the fight against pain, heat or cold can help. Local irritating, distracting remedies ( Capsicum, Deep Heath, Apizatron, Finalgon, etc.) are used, cold compresses.
- The intra-articular injection of corticosteroids ( Kenalog, Diprospan, Metipred) facilitates the reduction of pain and inflammation. Because of the side effects, such injections are rarely used( 3-4 injections per year).Relief is not long-lasting up to several months.
- Hyaluronic acid preparations can be injected into the joint, which help restore the properties of intraarticular lubrication, and improve cartilage nutrition. These include Gialgan, Ostenil, Singhial, Sinocorm. Reducing the friction of bones, they reduce the intensity of pain for several months. Their application is effective in the early stages( I-II centuries).1 injection per week is given, the course is prescribed 3-5 injections in 1-2 years. Opinions of specialists about the effectiveness of intra-articular injections of corticosteroids and hyaluronic acid are ambiguous.
- Chondroitin sulfate, Aflutop, Glucosamine include -mediated restoration of cartilage tissue( ).In many Western countries, these funds are used only in the form of bioadditives, since their therapeutic effect is not proven.
Physiotherapy and lifestyle
Additional methods:
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- exercise therapy;
- acupuncture;
- diet;
- sanatorium treatment.
Physiotherapy procedures reduce the intensity of pain, muscle spasm, inflammation, stimulate microcirculation and metabolic processes in the joints. The doctor selects them individually, depending on the stage of the disease and the leading symptoms.
These kinds of physical procedures can be used:
- diadynamotherapy;
- phonophoresis;
- magnetotherapy;
- amplipulse;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- hyperbaric oxygenation;
- UFO.
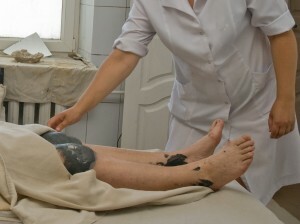 LFK and massage provide an opportunity to relieve muscular muscle spasm, increase the tone of a weakened muscle group, improve trophicity and function of the affected joints.
LFK and massage provide an opportunity to relieve muscular muscle spasm, increase the tone of a weakened muscle group, improve trophicity and function of the affected joints.
The principle of exercise therapy: light dynamic loads and complete static discharge. The doctor recommends special exercises and means of support during movement( crutches, cane, corset), elastic locks( knee pads), special shoes or tabs for it.
Walking( not less than 30 min.) Is recommended on level ground, cycling, swimming. It is necessary to exclude the presence in a fixed position for a long time, lifting the weight, sitting in soft armchairs. The bed should be stiff, the chairs with a straight back.
The patient's diet should be aimed at normalizing body weight. Outside exacerbation, sanitation is possible at resorts with therapeutic muds, hydrogen sulphide, sulfuric, radon sources.
Effective iodine-bromine, sulfide, bischofite, sea baths, applications of peat and mud mud, ozocerite.
Traditional medicine
The best recipes for the treatment of osteoarthritis folk remedies:
- a mixture of dry mustard, vegetable oil and honey in equal parts bring to a boil, from the broth to make a compress for 2 hours;
- with OA of knee joints, wrap them with internal pork fat, cover with polyethylene on top, fix with bandage and keep around the clock for 1 week;
- rubbing can be made from horseradish, lilac or chestnut flowers, potato sprouts( at the rate of 50 grams of flowers for 0, 5 liters of vodka);
- take 2 tablespoons each.flowers of sweet clover and St. John's wort, hop cones, mix and grind with 50 g of butter;apply to the joint for 2 hours;
- take 4 tablespoons.needles of any tree on a glass of water, simmer 30 minutes, strain the broth, make a compress for 1 hour.
Surgery as an extreme method
Surgical treatment: several types of operations are developed and used:
- Arthroscopic deformity of or "cleaning" of the joint with the help of an arthroscopic device: through special punctures, the destroyed parts of the cartilage are removed
 .The operation gives an improvement in the early stages of 1-2 years.
.The operation gives an improvement in the early stages of 1-2 years. - Osteotomy or reconstruction of bones : bones are fixed at a different angle for the redistribution of the load. Improvement of well-being is noted up to 5 years.
- Joint replacement : the damaged joint is replaced with a prosthesis made of high-strength plastic or metal. The operation is more often performed on the knee and hip joints with severe pain and impaired function.
Complications of
Degenerative changes in the tissues of the support apparatus with OA lead to complete destruction of the cartilage, marked by a disruption in the function of the joint.
Stiffness and pain can be so pronounced that the patient loses his ability to work and needs outside help in everyday life.
Preventative measures
Prevention of OA includes such methods:
- Weight control and getting rid of excess body weight."Hard" diets for joints are no less harmful than overeating. At excess weight the diet should be picked up by the dietician.
- The motor mode must be balanced. Force loads during exercises should be excluded, to study the cardiovascular profile according to
 ( walking, running, swimming, etc.).
( walking, running, swimming, etc.). - Elimination of injuries.
- Avoid overcooling of joints. You can use knee pads, belts from dog hair.
- Wearing shoes with comfortable heel.
- Chondroprotectors by appointment of an orthopedic physician, although the preventive benefit from them is not supported by all specialists.
Osteoarthrosis is a chronic, progressive lesion of the joints that causes impairment of function and disability.
There is no effective treatment for the disease. Early treatment to the doctor at the first manifestations of the disease will provide treatment that slows the progression of the process.
In the later stages, the only way to alleviate the condition is the operation of joint replacement.