 Spasticity or spasticity is called motor impairment, the cause of which is increased muscle tone.
Spasticity or spasticity is called motor impairment, the cause of which is increased muscle tone.
In normal condition, muscle tissue is elastic and flexion or extension of limbs occurs without any difficulty. When the flexion and extension are felt the resistance of the muscles, this indicates an increase in their tone.
According to the patients, when spasticity is felt, "stiffness" in the muscles.
Contents of
- What's going on?
- complex reasons
- aggravating factor
- spasticity and spasms
- Types and disorders
- pathogenesis of post-stroke spasticity
- pathogenesis of spasticity in multiple sclerosis
- Evaluation criteria
- Symptoms
- Examinations
- treatment methods depending on the cause
- Pharmacotherapy
- Physiotherapy
- Surgery
- Conclusionsimple and complex
What's going on?
The internal spasticity mechanism is not fully understood, according to experts, this disorder occurs as a result of various disorders in the structures of the brain and spinal cord.
Externally, spasticity manifests itself as an increase in muscle tone, which is significantly increased in the process of stretching the muscles.
In other words, spasticity provokes muscular resistance with passive movements. It is at the beginning of the movement that the resistance of muscles is the strongest, and when the speed of passive movements increases, the resistance force also grows accordingly.
Muscle spasticity is the cause of such changes in muscles, tendons and joints as fibrosis, atrophy or contracture. This leads to increased motor disorders.
Complex causes of
The main cause of spasticity is the imbalance of signals passing from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles.
In addition, the causes may be: 
- spinal cord injury and brain injury;
- stroke;
- infectious diseases, accompanied by inflammatory processes of the brain( encephalitis, meningitis);
- hypoxia( damage due to lack of oxygen);
- presence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Aggravating factors
If the patient has a spasticity, the following factors can exacerbate the situation:
- constipation and intestinal infection;
- skin infections, which are accompanied by inflammation;
- infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- clothing, restraining movement.
Regardless of the severity of the disease, these factors can lead to deterioration.
Spasticity and spasms
Spasticity often accompanies the presence of spasms, which manifest themselves in involuntary contraction of one or a group of muscles. In some cases, spasms are accompanied by pain, of varying intensity.
The occurrence of spasms can occur as a result of the action of some stimulus, or independently. 
Spasticity can manifest itself in a mild to severe degree. In the first case, this condition is not a serious obstacle for the patient, and he is able to lead a normal life, whereas in severe form a person is forced to move in a stroller.
It should be noted that the severity of a condition such as muscle spasm can change with time.
But there are cases of positive impact of spasticity. For example, in patients with paresis( weakness) in the legs, it is possible to stand alone due to muscular spasm.
Types and types of violations
By qualification, there are three main types of spasm:
- Flexor type is called increased tonus of flexor muscles when flexing limbs in joints and lifting them.
- The esstenosis type is an increase in the tone of the extensor muscles in the process of extension of the limbs in the joints.
- To , the adductor type is defined as the increase in tone at the cross in the region of the shins and closure of the knees.
Pathogenesis of post-spastic spasticity
Often spasticity occurs in patients who have suffered a stroke. In such cases, the physiotherapeutic effect is ineffective, and the presence of spasms makes it difficult to restore the patient. 
Muscles are in a constant tone, they begin to undergo pathological changes, joints and tendons also suffer. In addition, there are contractures( deformations), greatly exacerbating the problem.
Development of spasticity does not occur immediately, as a rule, it occurs 2-3 months after a stroke, but the first signs can be noticeable to a specialist much earlier.
Shoulders, elbows, wrists and fingers are usually affected, and in the lower part of the body hips, knees, ankles and toes suffer. At the same time, the spasticity touches the flexor muscles in the upper limbs, and the extensors in the lower extremities.
In the absence of the necessary treatment, contractures in the joints and bones appear for several years.
Pathogenesis of spasticity in multiple sclerosis
Spasticity is a concomitant phenomenon of multiple sclerosis in most cases. It appears as an unexpected contraction of a muscle group, arising spontaneously or as a reaction to an irritant.
The severity of muscle spasms in patients with multiple sclerosis can be different, both mild and severe, manifested as strong and prolonged spasms. The form of gravity may change with time.
With multiple sclerosis, spasticity occurs in the muscles of the limbs, in rare cases affects the muscles of the back.
Evaluation criteria
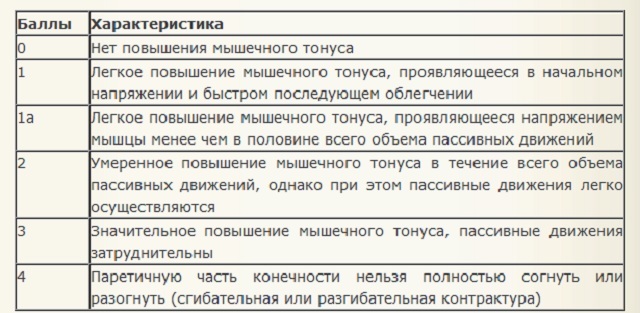
The severity of spasticity is estimated by points, the most common is the Ashworth scale. In accordance with her, the following degrees of impairment are distinguished:
- 0 - muscle tone is normal;
- 1 - muscle tone is increased slightly and manifests itself in the initial stages of stress with rapid relief;
- 1a - a slight increase in muscle tone, which manifests itself in a smaller part of the total number of passive movements;
- 2 - the tone is increased moderately throughout the entire passive movement, while it is carried out without difficulty;
- 3 - the tone is increased significantly, there are difficulties in the process of passive movements;
- 4 - part of the limb, affected by paresis, does not fully bend and does not unbend.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of spasticity of muscles include:
- increased muscle tone;
- convulsions and involuntary muscle contractions;
- process of deformation in bones and joints;
- painful sensations;
- disorders of posture;
- increased activity of reflexes;
- appearance of contractures and spasms.
In addition to the above, patients with sharp movements experience acute pain in the limbs.
Diagnostic measures
 In the process of diagnosis, the expert first of all studies the medical history, as well as what medications the patient takes and suffers from close relatives of the patient with neurological disorders.
In the process of diagnosis, the expert first of all studies the medical history, as well as what medications the patient takes and suffers from close relatives of the patient with neurological disorders.
Spasticity is diagnosed using tests, the essence of which is in the evaluation of limb movements and muscle activity in active and passive movements.
When examining a patient, the specialist determines whether there is resistance to the limbs with passive flexion and extension. If resistance is present, this is a sign of spasticity, and increased ease during movement can be a sign of paresis.
Treatment methods depending on the causes of
With proper and timely treatment, you can completely remove the spastic. The goal of the treatment is to improve the functionality of the limbs and to stop the pain.
Methods of treatment and drugs are selected depending on the severity of the disease, what disorders it was caused and how long the patient is sick.
Treatment is conducted in several ways, namely:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical intervention. Let's look at each method in detail.
Drug treatment
As a rule, several drugs are prescribed, the action of which is aimed at relieving pain and relaxing the muscles. Drug therapy is carried out using:

- Dantrolene;
- Gabaleptin;
- of baclofen;
- Imidazoline;
- preparations-benzodiazepines.
Short-acting anesthetic agents are also used, for example, Lidocaine or Novocain.
In addition, muscular injections of botulinum toxin can be prescribed. The essence of the treatment is to interrupt the process of nerve transmission, thereby contributing to muscle relaxation. The effect of the drug is long-term and lasts for several months.
Botulinum toxin is indicated in cases where the patient, for example, after a stroke, has no contractures in the muscles. This drug is most effective in the first year of the disease.Physiotherapy
The methods of physiotherapy include:
- medical gymnastics;
- massages;
- acupuncture;
- electrophoresis.
 The complex of exercises for each patient is selected individually, depending on the condition. It should be noted that exercise therapy is effective in the fight against spasticity after a stroke.
The complex of exercises for each patient is selected individually, depending on the condition. It should be noted that exercise therapy is effective in the fight against spasticity after a stroke. Massage methods can also be different, in some cases massage is required in the form of light stroking movements, other cases require active kneading.
Spastic acupuncture for the most part has a general effect, the effect of this method on the problem is not so great.
Electrophoresis is assigned to stimulate muscles with thermal and electrical effects.
Surgical intervention
This method is used in severe cases, for example, if the spasticity prevents walking. The essence of the surgical method in the introduction of Baclofen in the cerebrospinal fluid or the suppression of sensitive nerve roots.
Treatment should be performed only in special clinics and medical institutions, where the treatment course is a complex of measures.In the absence of timely treatment, the spasticity adversely affects the joints and tendons, provoking atrophy and other pathological changes, for example, the appearance of contractures.
Conclusion is simple and complicated at the same time
As for the forecast, it is individual in each case. The outcome depends on how much the muscle tone is increased, what is the degree of
 severity of the disease and other factors.
severity of the disease and other factors. Spastika leads to the appearance of contractures that can significantly complicate the process of caring for the patient.
As prevention measures should be monitored the correct position of the head, hands and feet of the patient. For this, special adaptations can be used, for example, langets and orthoses.
It is also recommended to change the position of the body more often, and when performing various movements, monitor changes in muscle tone. In case of deterioration, it is necessary to immediately seek help from specialists.



