 Brain abscess is the accumulation of purulent fluid in the skull due to the impact of a pathogenic infection caused by pathogens such as: staphylococci, streptococci, toxoplases, E. coli, anaerobic bacteria.
Brain abscess is the accumulation of purulent fluid in the skull due to the impact of a pathogenic infection caused by pathogens such as: staphylococci, streptococci, toxoplases, E. coli, anaerobic bacteria.
Symptomatics directly depends on the location of the abscess and its volume. Symptomatology has no specific signs, because the disease is a complication of head trauma and organic brain damage.
The disease often begins acutely, with marked signs of hypertensive and focal symptoms along with increased fever. In other cases, the onset of the disease may be similar to meningitis or a common infection.
Very rarely, the primary degree of abscess occurs in a latent form with a small temperature and mild manifestations.
The latent stage can pass without obvious manifestations or is expressed by a mild symptomatology of hypertension - attacks of a headache with vomiting, inhibition of mental reactions. Such a stage can last from several days to several years and, under the influence of infection or without provoking factors, begins to develop rapidly.
Contents
- What causes a disorder
- What causes a disorder
- Pathogenesis and types of pathology
- Developmental stages
- Clinical picture
- Diagnostic methods
- Complex approach to therapy
- Medical treatment
- Surgical treatment
- Forecast and consequences
- Preventive measures
What causes an infringement of
The causative agents of an abscess are infectious bacteria that enterin the body in various ways:
- open head trauma;
- neurosurgical intervention;
- a purulent process that occurs in the ENT organs;
- the presence of purulent foci in the body of various localizations.
Pathogenesis and types of pathology
There are several types of abscesses:
- As practice shows, contact is most often diagnosed, which are formed against a background of mastoiditis, otitis, suppurative
 inflammations in the bone surface, adnexal nasal cavities, meninges, ocular cavities. Most of the diseases are associated with inflammation of the hearing. Purulent otitis often accompanied by abscesses. Infection penetrates from the temporal bone through the roof of the tympanum and cavernous sinuses into the middle cranial fossa, provoking an inflammation of the temporal lobe of the brain. Ear infections can penetrate into the posterior cranial fossa through the labyrinth and sigmoid sinus, causing an abscess of the cerebellum.
inflammations in the bone surface, adnexal nasal cavities, meninges, ocular cavities. Most of the diseases are associated with inflammation of the hearing. Purulent otitis often accompanied by abscesses. Infection penetrates from the temporal bone through the roof of the tympanum and cavernous sinuses into the middle cranial fossa, provoking an inflammation of the temporal lobe of the brain. Ear infections can penetrate into the posterior cranial fossa through the labyrinth and sigmoid sinus, causing an abscess of the cerebellum. - Abscesses of the nasal cavity of are formed in the frontal lobes of the brain. First local pachymeningitis is formed, then adherent limited meningitis, subsequently inflammation passes to the brain substance with the formation of limited purulent encephalitis. In medicine, also atypical cases are known, when the disease develops against the backdrop of inflammation of the vascular system. At the same time abscesses are located in the deeper parts of the brain, distant from the primary focus.
- Metastatic abscesses develop due to lung diseases - pneumonia, empyema of the pleura, bronchiectasis. Also, this pathology can be a complication of septic ulcerative endocarditis, osteomyelitis, inflammation of the internal organs. A third of all cases of metastatic abscesses are of a multiple nature and are formed in the white matter region of the brain.
- Traumatic abscesses occur due to open head injuries. When the brain envelope is affected, the infection gets through the perivascular cracks into the brain tissue. Infection penetrates with the ingress of an alien body. In this case, the abscess is located precisely in the area of damage.
Stages of development of
There are several stages of the development of the disease:
- Stage 1 is a primary inflammation of the brain during the first few days, there is no distinction from the remaining unaffected substance of the brain, perivascular infiltrates, alterations of nerve cells are detected;
- 2nd stage - occurrence of death on 4-9 days;
- 3 stage - primary encapsulation, after 10 days, pronounced necrosis of the central part is formed, along the periphery a connective tissue capsule is formed;
- 4 stage - comes in two weeks, there is a clear collagen capsule with a dead center and the area of replacement of the dead neurons around the capsule.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of cerebral abscess are divided into cerebral, general infectious and symptoms, depending on the location of the focus.
Brainwashing:
- severe headache, may occur in a particular area or have the character of "diffuse pain", i.e. felt throughout the
 head;
head; - nausea and vomiting, after which there is no feeling of relief, vomiting in this case occurs at the peak of the headache;
- weakness, decreased performance;
- increased sensitivity to light, discomfort, lacrimation, the desire to close your eyes when exposed to stimuli;
- tension in the occipital muscles as a result of infection of the meninges, when flexing the neck, difficulties arise;
- loss of consciousness.
Common infectious:
- high temperature;
- chills;
- increased sweating.
Abscess in the frontal lobe manifests as follows:
- decreased intelligence;
- appearance of a silly, upbeat mood;
- speech disturbance - it becomes fuzzy, illegible;
- gait disturbance, the patient can not walk normally.
Cerebellar lesion: 
- movement coordination disorder;
- gait acquires a shakiness, a person can lean from side to side;
- nystagmus of the organs of vision, eyes run in different directions;
- decrease in overall muscle tone.
Purulent process in the temporal lobe of the brain:
- speech impairment, the person does not recognize the speech of others;
- loss of visual fields;
- seizures that affect the entire body or limbs.
Brain base abscess:
- disruption of the oculomotor apparatus, the eyes do not turn sideways;
- appears strabismus;
- may cause loss of vision in one or at once in two eyes;
- partial or complete paralysis of hands and feet.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of the disease on the basis of such studies:
- collection of anamnesis of the disease( previous head trauma, purulent inflammation of the ENT organs);
- neurological examination, which reveals violations of speech, vision, oculomotor functions;
- ophthalmoscopy is performed to detect the swelling of the optic nerve due to high intracranial pressure;
- CT and MRI are performed for a layer-by-layer examination of the brain in order to detect an abscess, its location and volume.
Differential diagnosis will depend on the stage of pathology. At the initial stage, the abscess is differentiated from purulent meningitis, in which there is a decrease in the elasticity of the neck muscles, a stable high temperature, and no focal symptoms.
The course and signs of an abscess also need to be differentiated from a tumor. Symptoms of these pathologies are very similar to each other by the process of leukocytosis and high temperature. An important factor in the diagnosis will be the presence of factors that triggered the onset of an abscess.
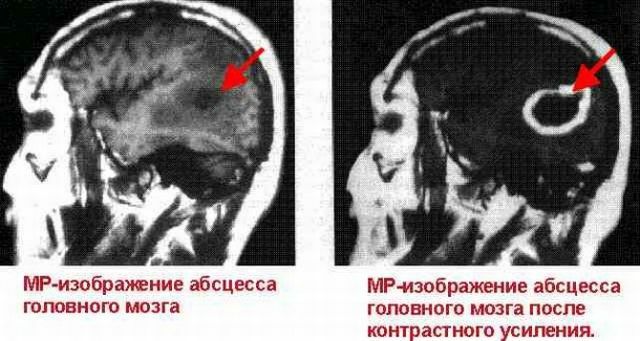
Complex approach to therapy
The methods of treatment will depend on the stage of the development of the disease, the volume of the abscess and its location.
Medical treatment
To cover the greatest spectrum of pathogens, the following drugs are used:
- If the abscess does not arise from head trauma, antibiotics are prescribed: Vaccinomycin, Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, Cefixime, Metronidazole.
- In the case of a posttraumatic abscess, Rifampicin is used.
- In the case of an abscess caused by the causative agent Cryptococcus neoformans, amphoreticin, Fluconazole is prescribed.
- In patients with a disorder caused by the causative agent Toxoplasma gondii, Sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine are used.
 After isolation from the crop pathogen therapy is changing. If the crop is sterile, antibiotic therapy continues for at least six weeks.
After isolation from the crop pathogen therapy is changing. If the crop is sterile, antibiotic therapy continues for at least six weeks.
With effective results after antibacterial therapy, glucocorticoids are prescribed.
Very often an abscess helps increase the intracranial pressure, which is fraught with cerebral edema.
In this case, drugs of a corticosteroid group are prescribed, for example, Mannitol for removing edema and normalizing the pressure.
Surgical treatment of
The main method of treatment is usual or supply-and-out drainage. It is carried out by inserting a catheter into the cavity of the abscess to remove purulent fluid and further administration of antibacterial agents.
Sometimes an additional catheter is installed to infuse the solution for rinsing. Drainage should be carried out in conjunction with antibiotic therapy, taking into account the susceptibility to the drug of the causative agent.
With multiple abscesses, the focus is draining, which can cause dangerous consequences in the form of a purulent fluid entering the ventricular system of the brain. With the accumulation of pus in the area of the cerebral membrane, draining is used without the use of a supply-and-extract system.
Surgical method of treatment is not used for such abscesses that are localized in vital and deep zones - the visual hillock, the brain stem, subcortical nuclei. In this case, an alternative method is needed - a stereotaxic procedure - puncture of the brain abscess with further rinsing of the cavity and administration of antibiotics. Washing is carried out once or repeatedly.
After treatment the patient needs a long rehabilitation.
Forecast and consequences of
With a qualified and adequate treatment, the prognosis for the patient's life will be quite favorable. The percentage of deaths of  does not exceed 10%.
does not exceed 10%.
And yet, brain abscess is a serious disease, which can lead to very dangerous complications:
- inflammation of the skull bones - osteomyelitis;
- ingress of purulent fluid into the ventricular system of the brain, which leads to a disbalance in the volume of fluid that provides nutrition and the process of metabolism in the brain;
- occurrence of recurring epileptic seizures.
Preventive measures
Prevention in this case will consist in the timely and full treatment of primary purulent processes affecting ENT organs, pneumonia and any foci of infection in the body.
After getting craniocerebral injuries, a full-fledged treatment of wounds is necessary, which allows to significantly reduce the risk of abscess.
A full and balanced diet is also very important in prevention. It is necessary to eat meat, vegetables and fruits, as well as vitamins A, E, C, B.