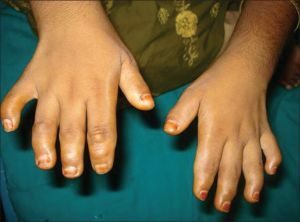
 The pathological development of phalanges of the fingers is called brachidactyly.
The pathological development of phalanges of the fingers is called brachidactyly.
The disease is attributed to a hereditary defect, which is characterized by reduced linear dimensions of the hands, feet, and phalanges of the fingers on the legs and hands.
Shortness refers to the main feature of such pathological development of bones.
The brachidactyly genes from parents pass to children and cause limb anomalies. People with underdeveloped phalanges and shortened fingers live a normal life, but the choice of profession is different.
Congenital anomaly of the extremities occurs in men and women with the same frequency. Its occurrence is possible not only with a decrease in the size of the fingers, but also with their complete absence. Synonyms of pathology include hypophalangeia and microdactyly.
Causes of Defect
Based on the research it was established that the main cause of underdeveloped phalanges and shortened toes on the limbs is heredity.
Brachydactyly is inherited by a dominant trait.
In the general structure of diagnosing genetic defects of development, the anomaly of the limbs represents a rather high incidence rate.
The effect of exogenous factors on the fetus and heterozygous mutations of the tyrosine kinase receptor gene leads to such pathological development of the hands, feet, toes and hands.
This gene is expressive in osteoblasts and chondrocytes and participates in their reproduction and maturation.
Types of limb abnormalities
To date, there are several types of anomalies that determine the degree of pathological development of brachydactyly.
The presented clinical picture makes it possible to classify the disease and distinguish the main variants of bony changes in phalanges.
The hereditary transmission of a defective gene causes several major types of anomalies.
Anomaly of the type "A", to the distinguishing characteristics of which include a reduced length of the middle finger, phalange deviation, and 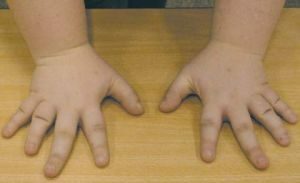 also pronounced dysplastic changes of the nail plates of the defective fingers.
also pronounced dysplastic changes of the nail plates of the defective fingers.
Disease of the extremities can have different degrees of severity, which define five variants of manifestation.
These include:
- Type "A 1" is characterized by a general delay in finger growth against the background of a modified rudimentary phalanx of the middle finger. In addition, the defect develops in combination with the reduced length of the main phalanges on the thumbs of the hands and feet.
- Type "A 2" is diagnosed on the basis of the middle finger. It is distinguished by the much shorter size of all phalanges on both hands. The remaining phalanges on the upper and lower limbs have no abnormal development. In addition to the reduced length of the phalanx of the defective finger, a radial deviation having a rhomboid shape can develop. Such changes are accompanied by pathological development of bones.
- Type "A 3" differs in the curved or distorted position of the phalanx of finger at number five. Anomaly is determined on both hands and is called clinodactyly. Distortion can develop in the medial or lateral direction.
- Type "A 4" is diagnosed on the basis of pathological development of the second and fifth fingers on the hands of both hands. Anomaly is represented by their reduced size and underdevelopment of the middle phalanx. If foot problems are identified, clubfoot can be diagnosed and have a valgus - heel view.
- Type "A 5" will be determined based on the complete absence of middle phalanxes on the defective second and fifth wrist fingers. Reduced their appearance, dysplasia of nail plates also refer to the distinctive characteristics of this type of clinical picture.
Also distinguished:
- Type "B" refers to a congenital malformation, manifested in partial or complete fusion of the second and third fingers. To its principal differences is the pathological development of nail phalanges and a simultaneous abnormality of the hands and feet. Brachydactyly of this type is accompanied by pathology of the spine, skull and dentition units. Splicing occurs during embryonic development and is transmitted only through the male line.
- Type "C" is a severe form of congenital defect in finger development. Along with the shortening of the basic phalanges, their fusion is observed, as well as simultaneous underdevelopment of metacarpal bones. Children with this diagnosis will be characterized by low growth and problems with mental development.
- Type "D" is diagnosed by pathological phenomena on the first fingers of the hands and feet. To the second name, anomalies of this type include brachimegalodactyly.
- Type "E" refers to a hereditary defect that is rarely found in clinical practice. It is distinguished by an isolated anomaly of metacarpal and metatarsal bones. Pathology is accompanied by a symmetrical underdevelopment of clavicles.
 What diseases can cause arthralgia of the knee joint. What you need to know about pain relief?
What diseases can cause arthralgia of the knee joint. What you need to know about pain relief? Genetic disease polydactyly of the extremities manifests itself in an increased number of toes on the limbs. Methods of treatment find out here.
Symptoms of abnormal finger development
When diagnosing children with an isolated development of brachidactyly, the symptoms of the pathology will be minimal and refer to a cosmetic defect.
But in most cases, the abnormality of finger development is manifested against a background of more serious genetic diseases, among which it is necessary to note:
- Down Syndrome;
- shortening of the neck;
- chest funnel-shaped;
- skull of brachycephalic type;
- rib deformation;
- instability of the joints;
- mental retardation;
- obstructed supporting and motor function;
- absence of phalanges and fingers;
- dysplastic lesion of the nail plates;
- unusual configuration of short fingers.
In the absence of phalangeal fusion and polydactyly, sick children are not limited in movement of hands and feet.
Diagnosis of defect

In the photo of brachydactyly Megan Fox
Diagnosis of congenital defect in finger development can be carried out at different stages. If there are patients with brachydactyly in the family, it is recommended to perform a three-dimensional ultrasound of the fetus.
The gestational age should be 20 - 24 weeks. When an anomaly of an isolated species is found, artificial abortion is not recommended.
And the identified chromosomal syndromes provide grounds for abortion.
To diagnostic activities after the birth of a child are:
- visual and clinical examination;
- X-ray of fingers and bone tissues on hands, feet;
- DNA diagnostics, the results of which are crucial for establishing the correct diagnosis.
The results of studies confirm or exclude the diagnosis of a congenital defect in the bone tissue of the hands and feet.
Treatment and prevention
To date, surgical methods are the only effective way to treat bone abnormalities in the phalanges of the fingers on the upper and lower extremities.
The surgical intervention allows to effectively solve the problems of interphalangeal fusion , to increase the size of the hand and foot, and also to eliminate short-hairedness.
Restoration of the supporting and motor function of the limbs is the main goal of the operations. And aesthetics and solving the problems of cosmetology defect refers to the secondary tasks of the surgical method.
Conservative methods of treatment include physiotherapy, massage and physical therapy.
They are used to restore the function of the hand, stop, improve the work of the muscular framework and ligament apparatus, as well as increase the motor activity of the limbs. 
Also traumatologists - orthopedists prescribe them for the prevention of deforming arthrosis of the joints of the hands and feet. The rapid development of genetic engineering gives hope for the treatment of the immediate cause of the pathological development of phalanges of the fingers.
Prevention of brachydactyly provides for visits to medical genetic counseling, where parents can learn about the likelihood of a sick child in the family.
They assist families with an anamnesis of this pathology in making the right decision in planning future offspring and consequences.
Timely appeal for help to specialists will solve problems with congenital anomaly of limbs and avoid irreparable consequences.