 Calve disease, or aseptic necrosis of the vertebral body, belongs to a group of diseases that are referred to in orthopedics as osteochondropathies.
Calve disease, or aseptic necrosis of the vertebral body, belongs to a group of diseases that are referred to in orthopedics as osteochondropathies.
For the first time this pathology was described in 1925 by the French scientist J. Calvet, after whom she was named.
A few years after the research of Calvet, new information about this disease began to arrive. The most detailed study was made in 1938 by Dr. Mezzari in the study of the body of a child who died of diphtheria.
Histological data, which he received as a result of work, confirmed the assumption that the disease belongs to osteochondropathy.
Contents of the article
- What kind of a disease is this?
- Causes of the disease
- Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Methods of therapy
- Complications of the disease
- Prevention of the disease
What kind of a disease is this?
Calvet disease is a non-infectious( aseptic) necrosis of the vertebral body, or more simply, its necrosis, which is non-infectious.
The disease is characterized by protrusion of the spinous process of the vertebra, the tension of the near-vertebral muscles, soreness and limitation of mobility in the affected area of the ridge.
As a rule, the disease affects the thoracic vertebra, which is located at the highest point of the kyphosis.
It is he who carries the greatest load. Significantly less often, aseptic necrosis is diagnosed in the lumbar spine.
Sometimes two vertebrae are immediately affected, located in the neighborhood or through one healthy.
Non-infectious necrosis can affect not only the spine, but also the head of the femur. This pathology is known as Legg-Calvet-Perthes disease. 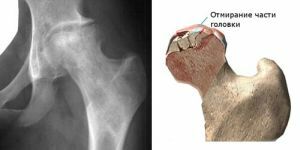
By their nature, both diseases are identical and differ only in localization: Calvet affects the vertebrae, and Legga-Calvet-Perthesa - the head of the femur.
To the distinguishing features can be attributed and the causes of development: if the first arises from the violation of blood supply, the causes of the appearance of Calvet to the end are not clear.
Causes of the disease
There is no consensus on the nature of the disease, but most scientists believe that it develops because of eosinophilic granuloma.
As a result of damage to bone tissue, an infiltrate with a large number of eosinophilic erythrocytes is formed on it. They then lead to the development of necrosis of the vertebral body.
When the presence of a granuloma is not confirmed, doctors consider other reasons:
- embryonic embryo development;
- chemotherapy;
- trauma or pathology of the spine;
- is a disorder of bone tissue metabolism;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- Gauchers disease;
- aneurysmal bone cyst;
- insufficient blood supply to bone tissue.
Necrotic processes, which are characteristic of osteochondropathy, lead to changes in the vertebral system.
Under the influence of the strength of adjacent vertebrae, it becomes thinner, and the intervertebral discs adjacent to it become thicker. These changes are clearly visible on the radiographic image of the affected area.
After a while in the diseased vertebra, reconstruction begins and the bone structure is gradually restored.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Calve's disease usually has a subtle start, and only in rare cases it is possible to raise the temperature to 37-38 ° C.The main symptom of the disease is back pain, but it is also possible the manifestation of other symptoms:
- increased fatigue in the region of the back;
- pronounced kyphosis;
- limitation in muscle tension;
- limitation of the functioning of the spine in the vertical position of the body;
- protrusion of the spinous process.
 Very often, aseptic necrosis is detected by an orthopedic or traumatologist accidentally during the X-ray of the spine. This type of diagnosis is the most informative, if you take pictures in the lateral projection. But even then the radiography does not give an exhaustive answer.
Very often, aseptic necrosis is detected by an orthopedic or traumatologist accidentally during the X-ray of the spine. This type of diagnosis is the most informative, if you take pictures in the lateral projection. But even then the radiography does not give an exhaustive answer.
In order to study in detail the changes occurring in the vertebrae, the patient is examined using a conventional or spiral computed tomography.
It should be noted that this is a fairly rare disease, so it can easily be confused with a vertebral column fracture, spinal tuberculosis, ankylosing spondylitis, and some deviations in the development of the ridge.
Diagnosis of aseptic necrosis requires a high level of professionalism.
Methods of therapy
Treatment of noninfectious necrosis of the vertebral body is carried out by conservative methods.
These include the unloading regime for the spine( the patient must be in a horizontal position), restorative measures, physical exercises, reflexotherapy, magnetotherapy, therapeutic massage.
Correction of vertebral deformity is performed using a plaster crib. As soon as he regains to 2/3 of his height, the patient is allowed to get out of bed.
Such treatment may take several years. Control of its results is carried out every 6 months by carrying out radiography. 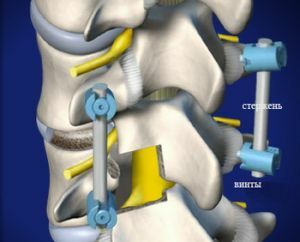
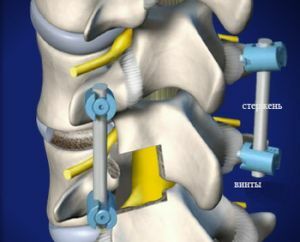
If conservative treatment does not help, and Calve's disease develops further, surgery is performed. Its goal is stopping vertebral distortion by fixing the spine .
To date, several surgical techniques have been used: fixation with staples or plates, the method of interbody spondylodesis and others.
All of them are more effective, however, the vertebra is not 100% operable.
Complications of the disease
As a rule, Calve's disease does not pose a great danger to human life, but sometimes it can cause complications.
If untimely treatment occurs, deformation of the bone tissue, which triggers a dystrophic process. It in turn leads to micro fractures of the bone.
Another complication of the osteochondropathy of the vertebral body is the apparent kyphosis - the curvature of the upper spine.
In addition, neither the conservative nor the surgical method of treatment is able to completely cure the disease. Therefore, with age, a person may develop osteochondrosis.
Prevention of the disease
Prevention of Calve disease is in daily physical exercise to build muscle mass. Strong muscles are, first of all, a pledge of a healthy spine.
Also, to improve local blood circulation, it is necessary to strengthen the vessels. Massage, swimming, and a contrast shower are good at this.
In addition, in the period of greatest likelihood of the disease, namely in 7-12 years, it is recommended to limit physical activity.
Large strain on the spine at this age is strictly prohibited. These are the most important recommendations for the prevention of osteochondropathy. As such, there is no system of preventive measures.
 Despite the fact that Calve's disease requires a long and difficult treatment of the spine, in most cases its outcome is favorable. Over time, the dead parts of the vertebra undergo a restructuring and are completely restored.
Despite the fact that Calve's disease requires a long and difficult treatment of the spine, in most cases its outcome is favorable. Over time, the dead parts of the vertebra undergo a restructuring and are completely restored.
Sometimes the disease passes by itself without any treatment.
At the same time, it is worth considering the fact that aseptic necrosis of the vertebral body is a rare enough pathology. It is practically not diagnosed in adults and very rarely in adolescent girls.
To reduce the incidence of necrosis, it is necessary to regularly prevent the disease. To do this, it is enough to engage in physical education, avoid excessive physical exertion, lead a healthy lifestyle.