 Tranquilizers are medicines that are used to relieve panic, anxiety, stress and depression. Preparations of this group are called anxiolytics. The name came from two Greek words, literally denoting the dissolution of anxiety.
Tranquilizers are medicines that are used to relieve panic, anxiety, stress and depression. Preparations of this group are called anxiolytics. The name came from two Greek words, literally denoting the dissolution of anxiety.
The tranquilizing effect is manifested as follows:
- attenuation of internal stress;
- decrease the feeling of anxiety, anxiety, fears.
Influences on cognitive, that is, cognitive functions of the brain, these drugs do not, or it is extremely weakly expressed. They do not affect the disturbances of the psyche - hallucinations, delusions.
Indications for use for all tranquilizers are various anxiety disorders. They are also prescribed to eliminate acute stress - for a short course of treatment.
Content
- 65 years ago. ..
- difference between tranquilizers and antidepressants
- Classification drugs group
- Day tranquilizers
- drugs benzodiazepine
- Phenazepam - it popular most
- Nozepam - a popular and inexpensive
- Serotonin tranquilizer
- Unclassified drugs
- Amizil
- Hydroxyzine( Atarax)
- What can I buy without a prescription?
65 years ago. ..
The first tranquilizer was created in 1951.It was called Meprobamate. Clinically, he was tested only four years later, in 1955  .And the name of the group -tranquilizers - appeared even later, in 1957.
.And the name of the group -tranquilizers - appeared even later, in 1957.
Tranquilizers of the benzodiazepine series were created in 1959, the first drug was Diazepam. At the same time, anxiolytic efficacy was detected in the antihistamine hydroxyzine.
To date, a group of tranquilizers includes about a dozen substances on international non-proprietary names, for trade names the list of drugs is much larger - several dozen.
The difference between tranquilizers and antidepressants
Tranquilizers by their action reduce the severity of emotional manifestations - whether positive or negative emotions.
Antidepressants also "cheer up", that is, they help to strengthen positive emotions and reduce negative ones.
There is a difference in the mechanism of action. Anxiolytics stimulate the activity of benzodiazepine and GABAergic receptors, suppressing the limbic system.
Antidepressants are inhibitors of the reuptake of serotonin, a substance that increases mood. With the action of antidepressants, the concentration of serotonin in the synaptic cleft increases - as a result, its effectiveness increases.
Classification of the drugs of the
group. The entire group of tranquilizers is divided into subgroups - by interaction of drugs with different types of receptors: 
- benzodiazepine receptor agonists ( benzodiazepine tranquilizers) - Phenazepam, Clozepid, Mezapam, Tofizopam;
- serotonin receptor agonists - Buspirone;
- substances with different types of action - Atarax, Amisil, Mebikar.
The first subgroup is used most often. It includes drugs that are derivatives of benzodiazepine. For them, too, there is a classification based on the duration of the drug:
- long-acting - these include phenazepam and Chlorazepam, the effect lasts up to 48 hours;
- mean duration of action of is Alprazolam and NosePam, they remain effective for 24 hours;
- in the third group - short-acting - medication Midazolam is included, its duration is less than six hours.
There is one more kind of classification - by generations:
- the very first tranquilizers, or the first generation of - Hydroxysin and Meprobamate;
- to to the second generation of include benzodiazepine tranquilizers - Diazepam, Chlorazepam;
- in the third generation includes Buspirone.
The chemical structure is distinguished:
- benzodiazepine derivatives - Phenazepam, Diazepam;
- carbamide esters - Meprobamate;
- derivatives of diphenylamine - Atarax;
- derivatives of different groups - Spitomin.
Daytime tranquilizers
 This is a separate group of drugs in which sedative and hypnotic effects are minimized. There is no suppression of cognitive functions. Thanks to this, drugs can be taken during the working day.
This is a separate group of drugs in which sedative and hypnotic effects are minimized. There is no suppression of cognitive functions. Thanks to this, drugs can be taken during the working day.
One of the representatives of day anxiolytics is Grandaxin. The active substance of this drug is tofizopam.
Produced in the form of tablets. Pharmacological action is similar to the action of benzodiazepine tranquilizers, with the exception of a hypnotic effect. It is indicated for neurotic-like conditions, stressful situations, with severe premenstrual and climacteric syndrome.
Dosage is selected individually, on average 150 mg per day for three doses. Of side effects, headache and dyspeptic phenomena are noted.
Contraindicated in respiratory failure, during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Benzodiazepine-based drugs
Benzodiazepine tranquilizers can have the following effects on the body:
- anxiolytic - the main for this group, eliminating anxiety;
- sedative - mild sedative effect;
- sleeping pills action;
- muscle relaxant , that is, contributing to the elimination of muscle tension;
- anticonvulsant .
The presence of these effects is due to the effect of drugs on the limbic system of the brain. The strongest effect benzodiazepine tranquilizers have on the hippocampus. Less pronounced action - on the hypothalamus and the reticular formation of the brain. In the hippocampus, these drugs suppress the process of back passage of the nerve impulse.
This mechanism of action is associated with the effect of these drugs on benzodiazepine receptors. They, in turn, have a close relationship with GABAergic receptors. 
Therefore, when benzodiazepine anxiolytics stimulate "their" receptors, other receptors are stimulated. Thanks to this, there is an anxiolytic and sedative effect.
The ability to relax strained muscles in tranquilizers is due to the inhibition of spinal reflexes - impulses emanating from the spinal cord. The same effect determines the anticonvulsant effect.
By its structure, benzodiazepine tranquilizers are lipophilic substances. Due to this property they are able to easily penetrate the biological barriers of the body, including blood-brain.
In the body, these drugs form a link to blood plasma proteins. In addition, they are able to accumulate in adipose tissue. They are excreted through the kidneys and in a small amount - through the intestines.
Phenazepam is the most popular
. Phenazepam is available in the form of tablets and injectable solutions. Pharmacological action is characterized by pronounced 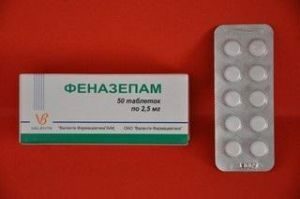 anxiolytic effect, moderate anticonvulsant, myorelaxing and hypnotic effects.
anxiolytic effect, moderate anticonvulsant, myorelaxing and hypnotic effects.
The action is based on the stimulation of GABA-receptors, mediated through the stimulation of benzodiazepine receptors. In this case, the excitability of subcortical formations in the brain decreases, the activity of spinal neurons decreases.
The drug is indicated in the following pathological conditions:
- neurotic and neurotic-like reactions;
- feelings such as anxiety, fear, emotional imbalance;
- acute reactive psychosis;
- hypochondria;
- disorders of the autonomic nervous system;
- sleep disorders.
Phenazepam tablets are given in a dose of up to 1 mg. In the treatment of sleep disorders, a single dose is 0.25 mg. Acute stress or reactive psychosis requires an increased dose - up to 3 mg.
Of the side effects noted small cognitive disorders - memory and attention violations. There may be dizziness and headache, dyspepsia, allergic reactions. Long-term use contributes to the development of the addictive syndrome.
The drug is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- congenital muscle weakness;
- severe renal and hepatic pathology;
- reception of other tranquilizers and antipsychotic drugs;
- period of pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Nosepam - a popular and inexpensive
A drug from the second subgroup of benzodiazepine tranquilizers. The active ingredient is oxazepam. Has a pronounced anxiolytic and sedative effect. There is a moderate anticonvulsant effect. The mechanism of action is similar to phenazepam.
Indicated in the following pathological conditions: 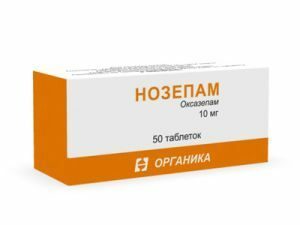
- neuroses and neurosis-like reactions;
- sleep disturbances;
- dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, in particular, in women in menopause.
The dosage of the drug is selected individually and can reach 120 mg per day. Of side effects, dizziness and headache, attention and gait disturbance are noted.
There may be disturbances in mental balance - emotional instability, psychomotor agitation. In the blood can be found leukopenia and agranulocytosis. Dyspeptic disorders and disorders of urination. With prolonged reception, the addictive syndrome may also develop.
Contraindicated if there is:
- impaired consciousness - shock, coma;
- acute alcohol poisoning;
- receiving other psychotropic drugs with a depressant effect on the central nervous system;
- congenital muscle weakness;
- closed angle glaucoma;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- depressive disorder;
- period of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- age is less than six years.
Serotonin tranquilizer
 The drug from the second subgroup is a serotonin receptor agonist - Buspirone or Spitomin. It is able to bind to serotonin and dopamine receptors. The main effect, like that of benzodiazepine tranquilizers, is anxiolytic.
The drug from the second subgroup is a serotonin receptor agonist - Buspirone or Spitomin. It is able to bind to serotonin and dopamine receptors. The main effect, like that of benzodiazepine tranquilizers, is anxiolytic.
It develops more slowly, within two weeks. Buspirone's sedative, hypnotic and miorelaxing effects are not characteristic of Buspirone.
In the body, the drug also binds to plasma proteins. All its metabolism takes place in the liver, and the substance is released in the form of metabolites through the kidneys.
Indicated for the treatment of various anxiety conditions, neuroses. In contra-indications to reception of a preparation such conditions, as pregnancy and thoracal feeding, a serious pathology of heart, a liver and kidneys.
The initial dose for treatment is 15 mg per day, divided into three doses. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 25 mg.
Unclassified preparations
The third group includes several tranquilizers that can not be classified.
Amisil
Amisyl is a holinoblocker of central action. Its main effect is sedation. It is associated with the suppression of m-holinoretseptorov located in the brain.
The drug also has an anticonvulsant effect and is able to depress the cough center in the medulla oblongata.
Hydroxysine( Atarax)
Hydroxysin, or Atarax, is a derivative of diphenylmethane. This is one of the oldest tranquilizers, which has not lost its effectiveness to date. The anxiolytic effect is moderate. There are other effects of this drug:
- soothing;
- antiemetic;
- is an antihistamine.
The drug is able to penetrate the biological barriers of the body. Metabolism occurs in the liver, the main metabolite is 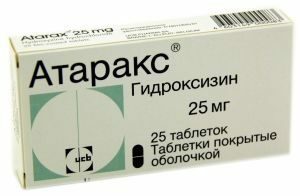 cetirizine - a strong antihistamine.
cetirizine - a strong antihistamine.
Atarax is indicated in the following pathological conditions:
- marked anxiety;
- neurological and psychiatric disorders, accompanied by internal stress and emotional imbalance;
- in the treatment of chronic alcoholism.
The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding, with intolerance to the hydroxyzine itself or its metabolites.
The therapeutic dose is from 25 to 100 mg, divided into several doses during the day.
What can I buy without a prescription?
Almost all tranquilizers are dispensed in pharmacies according to a prescription, however, daytime anxiolytics can be purchased without prescriptions of doctors, a list of these funds was proposed above.
Drugs of this group are indispensable in the treatment of anxiety disorders, neuroses and sleep disorders. However, all of them, with the exception of diurnal, are assigned to a short course, because they are rapidly developing addiction and drug dependence.