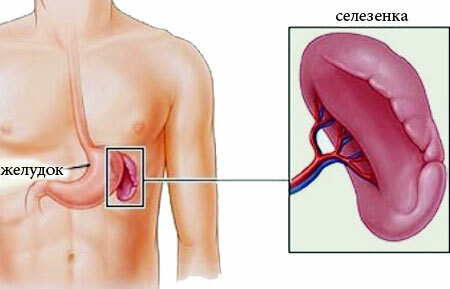
The spleen is an organ the size of a fist, located on the left under the rib cage. Due to various diseases, it can increase in size - this phenomenon is called splenomegaly. What is this, how to treat this violation - we discuss this in detail in this publication.
Contents
- 1 Splenomegaly - what is it?
- 2 Splenomegaly in children
- 3 Symptoms of splenomegaly in children and adults
- 4 Diagnosis of splenomegaly
- 5 Tactics for the treatment of splenomegaly
- 5.1 Complications
- 6 Splenomegaly - to which doctor to contact?
Splenomegaly - what is it?
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. Pathology can be caused by many causes and occurs in both adults and children. The spleen plays an important role in the fight against infections. It forms leukocytes, which are the first to begin the destruction of pathogens penetrated into the body.
 Other functions of the spleen:
Other functions of the spleen:
- Filtration and destruction of damaged and old blood cells;
- Production of a backup quantity of red blood cells, which are used by the body if necessary, for example, with blood loss;
- Synthesis of proteins;
- Storage of blood cell stock( platelets, erythrocytes, leukocytes);
- Destruction of insoluble compounds resulting from burns.
Splenomegaly is seen as a symptom of a disease and is accompanied by a violation of each of these important processes. For example, the spleen begins to filter out not only damaged, but normal blood cells that accumulate in it, interfere with the proper functioning of the organ.
Causes of splenomegaly
There are many diseases that cause splenomegaly. This phenomenon may be temporary, depending on the effectiveness of treatment of the underlying disease. In addition to pathologies of the spleen - tumors, cysts, organ infarcts, abscesses, - with splenomegaly, the causes can be as follows:
- acute and chronic bacterial infections - sepsis, tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis;
- viral pathologies - hepatitis, rubella, measles;
- mycoses - blastomycosis, histoplasmosis and other fungal infections of blood and internal organs;
- protozoal infections - leishmaniasis, malaria, toxoplasmosis;
- helminthiases - echinococcosis, schistosomiasis;
- circulatory disorders - development of portal hypertension, cirrhosis;
- systemic diseases of the hematopoietic organs - leukemia, lymphomas, myelofibrosis;
- pathology associated with metabolic disorders - glycogenosis, Wilson's disease;
- autoimmune diseases, in which immunity takes the cells of the body for foreign - rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus.
The cause of development of splenomegaly is also anemia of different types - pernicious, hemolytic and others.
Splenomegaly in children
In childhood, the spleen is sometimes slightly enlarged without any disturbances in the child's body. This is the physiological norm and is observed in a third of newborns, in 15% of six-month-old children and in a small part of younger schoolchildren.
The maximum spleen size in children is given in the table:
| Age, years | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Width / length, mm | 65/25 | 72/34 | 79/37 | 84/39 | 88/39 | 91/41 | 96/41 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 100/43 | 102/43 | 103/44 | 108/44 | 113/45 | 118/46 | 120/48 | 120/49 | 121/51 |
Splenomegaly in children is a symptom of the same diseases as in adults, there is no difference.
There are two forms of splenomegaly:
- Inflammatory inflammation of the organ tissues( bacterial, protozoal, viral infections, helminthic invasions, abscesses and infarction);
- Non-inflammatory, caused by disorders, not associated with infections and inflammations( in anemia, systemic, autoimmune diseases).
A moderate splenomegaly is also isolated when the length of the spleen does not exceed 20 cm, and the heavy spleen is 21 cm or more.
Symptoms of splenomegaly in children and adults
pain on the left under the ribs is one of the symptoms, photo
Since the enlargement of the spleen is a manifestation of a particular disease, it has no general symptoms. Distinguish only the signs of splenomegaly associated with its two forms.
1 - manifestations of inflammation:
- high temperature, up to 40 ° C;
- acute cutting pain in the left hypochondrium;
- mild nausea;
- sometimes vomiting and diarrhea;
- palpable palpation of the left flank under the ribs.
2 - symptoms of splenomegaly without inflammation:
- drawing, aching, unexpressed pain in the left hypochondrium;
- body temperature remains normal, and if increases, then up to 37.5 ° C maximum;
- with palpation of the side pain is not strong.
Diagnosis of splenomegaly
Primary diagnosis of splenomegaly is performed by palpation of the abdomen in the region of the left hypochondrium. To clarify the diagnosis, the following studies are shown:
- General clinical blood test for detecting the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes and platelets;
- Taking of hepatic samples;
- MRI and computed tomography;
- ultrasound examination;
- A bone marrow biopsy that provides more complete information on the condition of blood cells.
Puncture biopsy of the spleen is extremely rare, as it carries the risk of bleeding.
Tactics for the treatment of splenomegaly
Therapy for splenomegaly in adults and children is to identify and eliminate the pathology that caused the increase of this organ. Depending on the specific disease, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Antibiotics - for bacterial infections;
- Antiviral drugs;
- Antiparasitic drugs for the control of helminthiases;
- Hormones with immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory action - in autoimmune pathologies;
- Antineoplastic agents;
- Antifungal agents for the treatment of fungal infections;
- Vitamins - for beriberi, combined with anemia.
Surgical removal of enlarged spleen( splenectomy) is indicated if conservative treatment of splenomegaly does not have an effect.
Surgery is also necessary for:
- hypersplenism, when healthy blood cells break down in the spleen;
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- Banty syndrome;
- hemolytic jaundice.
The operation is more often performed by means of laparoscopy - through small incisions. As a result of removal of the spleen, the body's ability to resist infections is reduced. In this connection, before and after splenectomy, antibiotics are needed. Also vaccinated against meningitis, hemophilia, pneumococcal infection and influenza.
Complications of
To possible complications splenomegaly include:
- Hyperplenism is a deficiency in the blood of the formed elements due to their disintegration in the spleen( leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia);
- Rupture of the organ;
- Exacerbation of the course of pathology, against which the spleen was enlarged.
Splenomegaly - which doctor should I contact?
Since the spleen belongs to the organs of hematopoiesis, the hematologist is engaged in the treatment of its pathologies. But since the pain in the left side under the ribs and other manifestations of splenomegaly can be the result of various diseases, then first you should register with the therapist, describing in detail all the symptoms to him.
After examining and studying the results of the main analyzes, he will send to a more narrow specialist for further diagnosis and treatment.