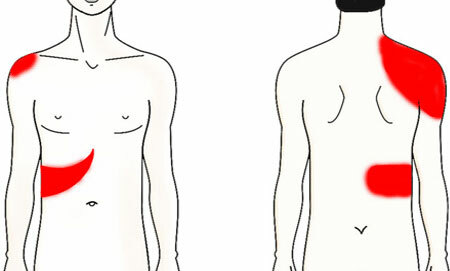
Acute cholecystitis is one of the most common causes of surgery and a common complication of cholelithiasis. What it is? Acute cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder wall, which occurs as a result of the development of infection in the cavity of the bladder.
The disease is classified into 2 types( taking into account the existing background of development): calculous and non-calculous. The most common acute cholecystitis affects women.
Contents
- 1 Causes and development of the disease
- 2 Types of cholecystitis
- 3 Symptoms of acute cholecystitis
- 4 Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- 5 Treatment of acute cholecystitis, first aid
- 5.1 Complications
- 6 Prevention of acute cholecystitis
Causes and development of the disease
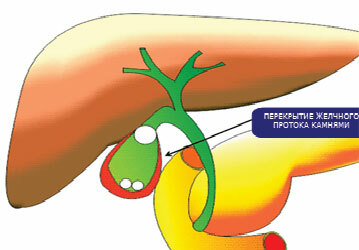
Bile is not usually sterile and constantly gets into itmicroorganisms from the duodenum, but only when there is stagnation within the gallbladder, favorable conditions for reproduction andinfectious agents and the development of inflammation.
The causes of bile congestion in 90% of cases are gallstones that block the bile duct and create a mechanical obstacle to the outflow of bile. With the development of inflammation in this case, an acute calculous cholecystitis is formed.
"Calculous" literally means - "stone".Stones in the gallbladder are detected in 10-20% of individuals, and their age is over 40 years. In Western countries, where there is a predominance of fats in food( national features of the kitchen), cholesterol stones are the most frequent in terms of chemical composition.
In the African countries and in Asia, pigmented stones are detected, which is associated with the common in these regions infectious diseases of the bile ducts( especially relevant in this context is malaria).
Acute cholecystitis caused by congestion of bile is much less likely due to other causes. In these cases, acute cholecystitis will be acalculous, that is, bespokamennym:
- thickening of bile and the formation of a bile cork that overlaps the bile duct;
- dyskinesia of bile ducts - a decrease in the ability of the walls of the bladder and ducts to contract, creating conditions for stagnation;
- anatomical feature of the structure of the gallbladder and duct, hindering the outflow of bile( developmental abnormalities);
- squeezing the duct with a tumor, trauma;
- inflection of the gallbladder;
- deformation and displacement of the duct, due to inflammatory changes in neighboring organs;
- mechanical pressure from the outside, for example, when wearing uncomfortable stitching clothes( for example, corsets).
Types of cholecystitis
Depending on the depth of inflammation, the walls of the gallbladder are distinguished:
- Catarrhal - non-purulent superficial inflammation;
- Phlegmonous - purulent inflammation with the defeat of all layers of the gallbladder;
- Gangrenous uncomplicated - the wall of the bladder is partially or completely exposed to death( necrosis);
- Gangrenous complicated - a breakthrough thinned by inflammation and necrosis of the gallbladder wall with the ingress of bile into the abdominal cavity, which leads to the development of complications.
In severity, acute cholecystitis is divided into 3 types:
1 .The mild degree is characterized by the duration of the disease less than 72 hours and the absence of signs observed in a more severe course, there are no violations in the work of other organs.
2. The average severity is characterized by the presence of at least one of the following characteristics:
- period of the disease is more than 72 hours;
- high level of leukocytes in the blood - above 18 * 109 / L;
- gallbladder can be palpated( in normal palpation it is inaccessible due to its small size);
- presence of signs of local( not widespread) peritonitis, necrosis and bloating, peri-bubble abscess, and liver abscess.
3. Severe degree characterized by the presence of at least one sign of organ failure:
- low blood pressure( less than 80/50 mm Hg);
- impaired consciousness;
- respiratory depression;
- kidney dysfunction, which is expressed by oliguria - a sharp decrease in the amount of urine, and an increase in creatinine levels of more than 176.8 μmol / l, indicating renal failure;
- changes in laboratory performance of the liver( increased prothrombin time, decreased protein and other substances metabolized in this organ);
- decreased platelet counts less than 100 * 109 / L
Symptoms of acute cholecystitis
Symptoms are often associated with inaccuracies in the diet, in the form of eating fatty foods, alcohol, and also observed after an emotional shock. The severity of symptoms depends on the stage of the disease and the activity of the inflammatory process.
Symptoms of catarrhal cholecystitis are as follows:
- acute pain. With cholecystitis, it can first be paroxysmal, then it becomes permanent. Often gives in the scapula, shoulder and neck on the right;
- nausea, vomiting, which does not bring relief;
- body temperature is moderately elevated - 37.5-38 ° C;
- a moderate increase in heart rate to 80-90 beats per minute, slightly increased blood pressure;
- slight tension of the muscles of the press, but it may be absent.
Symptoms of phlegmonous cholecystitis:
- intense pain in the right hypochondrium, which is aggravated by changing the position of the body, coughing, breathing;
- nausea with this form of cholecystitis is more pronounced and more frequent than with catarrhal form, multiple vomiting;
- body temperature above 38 ° C;
- heart rate increases to 100 beats per minute;
- tongue wet, belly swollen;
- , when breathing a patient, deliberately does not involve the right half of the abdomen in movement, so as not to increase painful sensations;
- with a palpation of the abdomen on the right, under the ribs, there is a sharp pain, there is also expressed a protective muscle tension;
- sometimes an enlarged gallbladder can be probed in the right hypochondrium.
Development of a gangrenous form of cholecystitis occurs if the weakened defenses of the body can not contain further development of the infection.
At first, there may come a period of "imaginary well-being", which is manifested by a decrease in the intensity of pain. This is due to the dying off of the sensitive nerve cells of the gallbladder. But then all the symptoms intensify, and when the wall of the gallbladder( perforation) breaks out, clinical signs of inflammation of the peritoneum - peritonitis:
- , severe pain emanating from the right hypochondrium extend to the greater part of the abdomen;
- temperature is high 39-40 ° C;
- pulse 120 beats per minute or higher;
- breathing is quick, it becomes superficial;
- appears inhibited and patient lethargy;
- the tongue is dry, the stomach is swollen, the tension of the abdominal muscles is expressed;
- stomach is not involved in breathing.
Gangrenous cholecystitis is common in the elderly. This is due to the liquefaction of the ability of tissues to restore, a violation of blood circulation due to atherosclerosis and a general slowing of metabolism.
Therefore, elderly people often have a worn out course, a mild symptom: there is no strong pain and tension of the abdominal muscles, there is no increase in white blood cells in the blood, which significantly complicates timely diagnosis.
Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis

Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis is based on clinical and additional data:
1. The presence of complaints of the following character - pain in the right upper quadrant over 30 minutes, nausea, vomiting, changes in body temperature. Previously, 50% of patients could have had hepatic colic.
2. Medical examination reveals a characteristic symptom of Murphy - involuntary retention of breath as a result of severe pain when pressing into the right hypochondrium region;also reveal the tension of the abdominal muscles, can be palpated an enlarged gallbladder in 30-40% of patients;10% of patients have jaundice;
3. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics:
- blood test shows an increase in the number of leukocytes - leukocytosis, the value of which will depend on the severity of inflammation;
blood biochemistry will reveal an increase in C-reactive protein, bilirubin in the development of jaundice, alkaline phosphatase, AST, ALT( specific hepatic enzymes); - urine analysis changes only the process deterioration - with the development of jaundice in the urine appears bilirubin, with the development of necrosis and severe intoxication protein and cylinders are detected;
- Ultrasonography of the gallbladder is the most accessible and informative method that allows to reveal stones, inflammatory thickening of the wall of the bladder. In conducting the study, Murphy's symptom is observed in 90% of cases, which is a diagnostic sign of acute cholecystitis;
- scintigraphy can not always be carried out practically, but is the most reliable method of proving the overlap of the cystic duct;
- MRI is performed to identify acute cholecystitis in pregnant women, with abdominal pain;
- radiography is informative in 10-15% of cases, when stones contain calcium and are visible during transmission. X-rays also reveal the presence of gas in the wall of the bladder, which happens in acute emphysematous cholecystitis in the elderly and patients with diabetes mellitus.
Treatment of acute cholecystitis, first aid
First-aid first aid for acute cholecystitis should be done competently, so as not to cause aggravation of inflammation and not "lubricate" the clinical picture - otherwise it will be difficult for a doctor to quickly diagnose correctly.
If you have acute pain, you need to pack the patient and call an ambulance. To reduce pain, apply cold to the liver region. The use of thermal procedures is extremely dangerous by aggravation of inflammation, as the blood filling of the gallbladder increases and the risk of purulent complications increases.
It is not recommended to take any medication before a doctor's examination. This is especially true of painkillers - they can mask the moment of perforation of the gallbladder wall, and this condition requires urgent surgical treatment.
For the same reason, you need to refrain from eating and drinking, as in surgical treatment you will need anesthesia. Doing it with a full stomach - this means exposing the patient to the risk of aspiration of vomit, which leads to severe aspiration pneumonia( lethality with this complication from the lungs is very high).
All further activities for acute cholecystitis, symptom detection and treatment should be performed by ambulance doctors, and then by surgeons in the hospital.
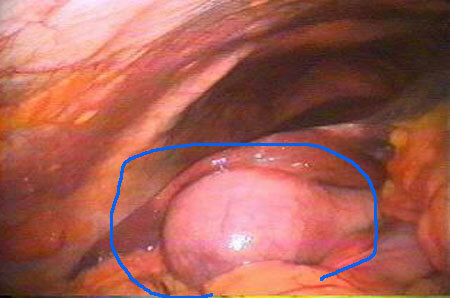
in the photo isolated gallbladder in acute cholecystitis
Emergency surgery for acute cholecystitis is always led by the development of peritonitis, which is caused by the diffusion of bile in the breakdown of the gallbladder. That is, surgical treatment is the main one in complicated gangrenous acute cholecystitis. In other cases, the method of treatment depends on the severity of acute cholecystitis.
Once the diagnosis is established, infusion, antibacterial and analgesic therapy is immediately started, oxygen is delivered through the nasal catheter if breathing is disturbed. Conduct monitoring of blood pressure, pulse, adequacy of urination.
Tactics of treatment depending on the degree of severity is as follows.
1. Easy degree.
Antibiotics in tablets, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antispasmodics are prescribed. Usually, the use of medication is sufficient to improve the condition, after which they decide whether to perform a cholecystectomy - removal of the gallbladder.
Most patients can undergo laparoscopic surgery - laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
If there is no effect from the treatment, and the operation is associated with risks, then percutaneous cholecystostomy is recommended. In this operation, the gallbladder is punctured through the skin and evacuation of the inflammatory fluid and pus, which reduces the risk of rupture of the bladder and the entry of bile into the abdominal cavity.
Complete the operation by installing a catheter, through which then remove excess inflammatory fluid and inject antibiotics. After improvement, cholecystectomy is performed.
High operational risk is observed in patients over the age of 70, with diabetes, leukocyte levels above 15 * 109 / L, the presence of overstretched gallbladder with ultrasound, with a high risk of complications, period of inflammation lasting more than 7 days.
2. The average severity.
Patients of this group react poorly to medical treatment, therefore within a week from the onset of the disease they make a decision about an operative intervention.
The method of choice is laparoscopic cholecystectomy, in the event of technical difficulties, an open cholecystectomy is performed. In the presence of high operational risk, the percutaneous drainage of the gallbladder is carried out as a temporary effect to improve the situation.
3. Heavy degree.
Because of the severity of the general condition, intensive therapy is prescribed to restore the functioning of the affected organs and systems. The percutaneous puncture cholecystostomy is performed urgently. Stabilization and improvement of the condition makes it possible to perform the removal of the gallbladder. However, in the presence of signs of bile peritonitis, an emergency cholecystectomy is performed with drainage of the abdominal cavity.
General principles of treatment of acute cholecystitis are in the following activities:
1. Bed rest, hunger for the first 3 days, so-called water-tea break, then sparing diet with the gradual introduction of solid food, eliminating fats, sugar, alcohol.
2 .Installation of the probe during vomiting or for gastric emptying before surgery.
3 .Medication:
- Antibiotics intramuscularly and orally. Apply drugs: Cefazolin, Cefuroxime, Ertapenem, Ampicillin, Sulbactam sodium salt in combination with gentamycin;when allergic to them are prescribed fluoroquinolones in combination with Metronidazole;
- Spasmolytics: atropine, no-spa, baralgin, platyphylline;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Glucose solution, saline solutions for intravenous fluids.
Complications of
Complications of acute cholecystitis are often observed and aggravated by the course of the disease in the elderly with a weakened response, making acute cholecystitis deadly. The following complications can develop:
- Empyema of the gallbladder( accumulation of pus in his cavity);
- Perforation of the gallbladder, which leads to the development of the abscess of the bladder, inflammation of the peritoneum( peritonitis), inflammation of adjacent organs( duodenum, stomach, pancreas);
- The addition of anaerobic infection leads to the development of an emphysema form of acute cholecystitis: the wall of the bladder swells from the gases. It often happens in patients with diabetes mellitus;
- Mechanical jaundice caused by complete blockage of bile outflow from the bladder;
- Cholangitis - inflammation of the bile duct;
- Bile fistulas.
Prevention of acute cholecystitis
Primary prevention is the initial prevention of gallstones in a diet with a reduced fat content and an increase in the volume of vegetables and coarse fiber that contributes to the normal outflow of bile.
It is important to lead an active lifestyle, engage in gymnastics, physical education.
With the existing cholelithiasis preventive measure is to avoid rapid weight loss and prolonged fasting, which can provoke movement of stones and impaired motor function of the gallbladder.
Of drugs, the use of ursodeoxycholic acid is possible, which reduces the risk of biliary colic and acute cholecystitis. Conducting routine surgical treatment of cholelithiasis is the main and reliable measure that will exclude the development of acute cholecystitis. But the operation is carried out only if there are indications.