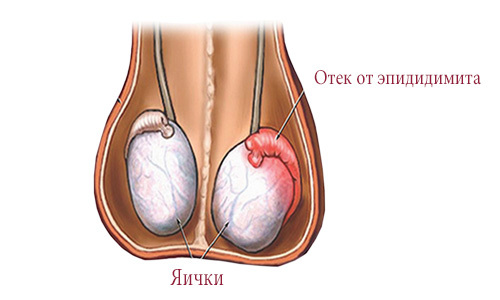
Some representatives of the strong half of humanity, due to their sexual characteristics, are forced to face purely male diseases. One such - funikulit - inflammation of the spermatic cord. It is rarely found "in its pure form", usually accompanying the referent, epididymitis and its varieties. At the initial stage of development of funikulita inflammatory processes affect the spermatic cord, but with the development of pathology, the nearby tissues are also affected.
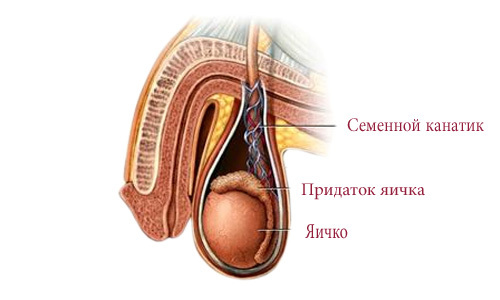
The spermatic cord is a paired organ, formed as a result of lowering the testicles. This is a kind of a string about 20 cm long. It turns out that the testicles hang on seminal cords. The main structure, which is an integral part of the spermatic cord, is the vas deferens, extending from the appendages to the ducts of the testes.
Causes of the disease
Specialists identify several specific causes that cause inflammation of the spermatic cord. Provide an inflammatory process can various infections that can penetrate iatrogenic, hematogenous or intrakanalikulyarnym way. The iatrogenic mechanism of infection occurs when infectious agents enter the organ during surgical intervention, such as a vasectomy and other operations. The hematogenous path is a process of infection by infection through the bloodstream from other infectious foci. Intrakanalikulyarnoe infection occurs through the penetration of infection from the urethra. Such infection is possible if a man has urinary inflammations such as prostatitis, balanoposthitis, cystopyelonephritis or urethritis. According to statistics, a similar mechanism of infection is most common with a funicular. To provoke inflammation in the spermatic cord can also be trauma.
If funikulit develops in chronic form, then on the background of urogenital pathologies or hypothermia, sudden exacerbation of the disease can occur. Most often, the causes of worsening of the chronic form of the disease are associated with STDs, inflammations of the ureters or kidneys.
Specialists classify all funiculitis into two groups:
- Specific - when the inflammatory process has an etiology associated with specific pathogenetic agents like actinomycetes or tuberculous mycobacteria, but similar pathological forms are not common.
- Nonspecific - when inflammation is caused by chlamydia, gonococcus, staphylococcus, Trichomonas, mycoplasmas, protea, E. coli and other microorganisms.
Symptomatic of funicularitis
The beginning of the inflammatory process is indicated by some compaction and a thickening of the cord. The patient feels intense soreness and considerable discomfort in the place of inflammation. With palpation, you can easily feel it yourself. Inflammation of the spermatic cord is also characterized by an increase in the total body temperature. If the spermatic cord has become inflamed on the background of tuberculosis agents, the disease often occurs in a languid and almost asymptomatic form, and a swelling with a tuberous surface is clearly felt at the site of the lesion.
Important! Incorrect treatment of funiculitis can provoke a dropsy of the spermatic cord or funicular. In more difficult cases, a man can become completely sterile due to complete infection of the seminal lumen.
Funicular is found in an acute form, it can have a chronic course. For acute funiculitis is characterized by a strong symptomatology, manifested swelling and hyperemia in the affected area, a strong pain syndrome in the groin, joint and muscle pains, general weakness and temperature rise. Soreness often gives to the scrotum and lower back. The general picture of inflammation can be supplemented with typical symptoms of pathologies of the genitourinary sphere: rezi or difficulty with urination, dysuric signs, discharge from the urethra, etc. If the swelling of the scrotum is added to the listed signs, then the inflammatory process has spread to the testicle and appendage. Acute funicular is capable of provoking peritonitis or phlegmon, sometimes it resembles an inguinal hernia.
The clinical picture of chronic funiculitis is differentiated by erased symptoms. Theoretically, the patient is concerned about similar signs of acute form, only in a less pronounced version. But in practice, the chronic course of such a disease is most often characterized only by a mildly manifested pain syndrome, which worries the patient during periods of exacerbations.
Methods of treatment of pathology
Diagnosis of inflammation of the spermatic cord usually does not cause difficulties. An experienced specialist is sufficient to conduct a patient's questioning, palpation of the scrotum, tests and ultrasound to make the pathology picture clear, and the diagnosis was reliable. Treatment funikilita differs ambiguity, because its etiology is quite versatile. The therapeutic approach is determined in accordance with a variety of the inflammatory process, its causes and the symptomatic picture of the course of the disease. Treatment is mostly conservative, surgical methods are usually resorted to in case of complications like phlegmon, etc. It is recommended to adhere to a special diet for the period of treatment, including elimination of salinity, smoked products, sharp and fatty foods, alcoholic beverages.
The most severe consequence of this pathology is excretory infertility associated with obstruction of the vas deferens. Therefore at the first signs of inflammation it is necessary to contact a urologist.
To begin with, the patient should at all times of treatment need to give up any sexual contacts. To eliminate discomfort and relieve soreness, when suppuration is recommended to apply ice on the scrotum( only use caution, ice can be kept no longer than 5 minutes!).In the future, treatment for dry heat is indicated for the purpose of resolving the infiltrate. Acute forms of inflammation are treated with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial medications, and the patient must strictly observe bed rest. Acute pain syndrome is effectively eliminated by a novocaine blockade of the spermatic cord. Treatment of chronic inflammatory forms is supplemented by various physiotherapeutic procedures. If the appeared compaction of the spermatic cord does not resolve after a 1.5-month course of therapy, then they resort to its removal.
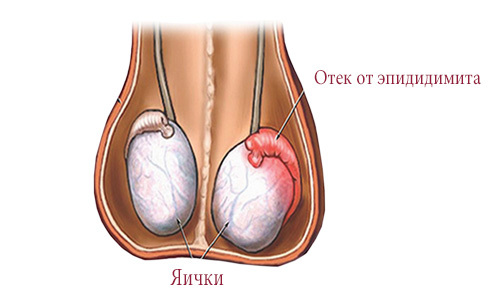
Timely therapy of the disease will help to avoid the many complications of such as orchitis and epididymitis, dropsy and infertility, funicelocele, impotence and spontaneous emission of sperm. Therefore, it is strongly recommended that men be more attentive to their own health condition( especially if there have previously been minor injuries of the perineum or scrotum), with suspicions of developing pathology, to avoid any complications, contact the appropriate specialist.