Hypothyroidism is a disease in which the body lacks hormones of the thyroid gland. Depending on the causes and symptoms, hypothyroidism is primary and secondary. The primary type of disease is manifested by a decrease in the functional activity of the thyroid itself, because of which hormones are produced in less quantity. Secondary hypothyroidism is closely associated with the pituitary and hypothalamus, which control the production of thyroid hormones.
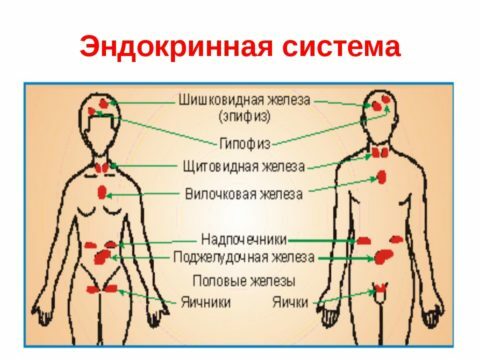
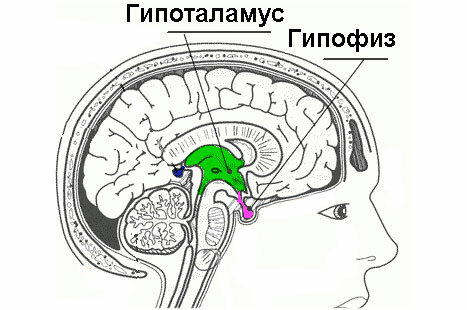
The thyroid gland is one of the important organs of the human endocrine system. Her work is regulated by the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. The pituitary body is responsible for the overall growth of the body, and the hypothalamus ensures the balance of the internal environment. In a healthy person in the endocrine system, internal processes occur as follows:
- The hypothalamus produces special substances that stimulate or inhibit the pituitary gland;
- The pituitary gland monitors the functioning of the thyroid follicles;
- The thyroid gland follicles produce hormones that are involved in all processes occurring in the body.
As paradoxical as it may sound, with a secondary hypothyroidism, an absolutely healthy thyroid gland produces a small amount of hormones. This occurs when the performance of the three glands: pituitary, hypothalamus and thyroid gland. In other words, thyroid disease is not the cause of secondary hypothyroidism.
Causes of secondary hypothyroidism
In modern medicine, the following causes of a secondary type of thyroid disease are identified:
- Post-traumatic brain injuries;
- occurring in the pituitary or hypothalamus hemorrhage of the brain;
- Infectious diseases that affect the hypothalamus or pituitary gland;
- The occurrence of malignant or benign brain tumors;
- Wrong formation of the brain;
- Necrosis of pituitary tissues caused by large blood loss in injuries or surgeries;
- Radiation or chemotherapy in the treatment of malignant tumors.
Any of the causes leads to a disruption in the smooth functioning of the endocrine system.
Symptoms of
The secondary form of thyroid disease differs from the primary location of the underlying cause of the pathology. The thyroid gland itself suffers from the primary form. In another case, adjacent organs are affected: the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. Children and adults susceptible to this disease, constantly feel the following symptoms:
- In the cardiovascular system: poor blood coagulation, high cholesterol, persistent pressure changes, low hemoglobin level in the blood;
- In the digestive system: bloating, constipation, loss of appetite, poor digestion of food, belching, taste preferences may change;
- In the reproductive system: in men, there is a decrease in erection, reproductive function, in women there is a violation of the menstrual cycle, there are problems with conception;
- The metabolism is broken: the skin becomes pale and dry, the nails are brittle, the hair loses its natural sheen and falls out. Often there is swelling of the extremities and tongue;
- In the respiratory system: there is pulmonary edema, even after minor physical exercises, shortness of breath, dysphagia;
- The central nervous system also suffers changes: deep depression, irritability, insomnia, falls working capacity and concentration of attention.
All these symptoms do not occur simultaneously, depending on the individuality of the body and the human immune system, only some of them can be observed. It all depends on how much the pituitary or hypothalamus has suffered.
Diagnosis
The sooner a diagnosis is made, the more likely the patient will have a full recovery. With the first symptoms, do not delay the visit to the doctor, modern diagnostic methods are able to identify the secondary form at the initial stage of the disease.
For the accurate diagnosis, the physician prescribes the following diagnostic types:
- MRI and computed tomography of the brain, which allows you to determine the condition of the pituitary and hypothalamus;
- Blood test. With the help of laboratory studies, the level of thyroid hormones is determined;
- Ultrasound examination of thyroid gland;
- If ultrasound has detected the presence of cysts and nodules, a biopsy of the neoplasm is necessary.
The most important indicator of the presence of secondary hypothyroidism is the level of TSH( thyroid-stimulating hormone).If the primary form of the disease, this figure is increased, then with secondary hypothyroidism, TSH is much lower than normal.

While the diagnosis has not been confirmed, do not self-medicate - this can only exacerbate the course of the disease.
Treatment of
After an accurate diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a course of treatment. Like other types of thyroid disease, secondary hypothyroidism is treated with hormonal drugs. Depending on the cause of the disease, the following therapy is prescribed:
- In the presence of infection of bacterial origin, the patient is prescribed a course of antibacterial drugs;
- With a viral infection, treatment consists of antiviral drugs in conjunction with drugs that can support immunity;
- In the presence of brain injuries, a course of drugs is prescribed that can normalize the blood supply to the brain;
- If a tumor process is detected by ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging, a biopsy should be performed on the nature of the lesion, and only then a decision is made about the surgical intervention.
To determine the course of therapy in a child, it is taken into account the age, the cause of the disease( congenital or acquired), the individual characteristics of the organism of a small patient. Whatever the cause of secondary hypothyroidism, after its elimination the patient is prescribed a course of substitution therapy, which can last from several months to many years.
Secondary hypothyroidism refers to the category of diseases, untimely and incorrect treatment of which entails serious complications, negatively affecting the performance of all human organs. If you have problems in the gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system, cardiovascular system, you should immediately contact a doctor.
Deviation in the endocrine system will first of all be shown by a blood test for thyroid hormones. If the laboratory data are far from the norm, the attending physician should conduct additional diagnostic methods: ultrasound examination of the thyroid organs, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography.
After diagnosing and revealing the cause of secondary hypothyroidism, the patient is prescribed treatment, the main component of which is hormonal drugs.



