According to medical statistics, among prostate malignant tumors, prostate adenocarcinoma is most often diagnosed in men. The disease is characterized by elderly patients, in rare cases, a similar form of cancer is diagnosed in men before the age of 50 years. Adenocarcinoma of the prostate is considered to be the most common cause of death in elderly patients. According to research, prostate cancer reduces a man's life by a dozen years.

Causes of the development of the pathology
There are many factors provoking the development of adenocarcinoma factors. The main causes of prostate cancer specialists are:
- Elderly age. As statistics show, a large majority of men over the age of 70 suffer from various forms of prostate oncology.
- Incorrect power mode. There is much debate about the effect of the diet on the development of prostate cancer. There are results from many studies, the results of which prove that adenocarcinoma of the prostate can develop against the background of abusing fats of animal origin, as well as in obese men.
- Hereditary predisposition. A lot of studies prove that patients with close relatives had cases of prostate cancer, the probability of developing adenocarcinoma is much higher than in people who do not have such.
- Lifestyle. Important way is the way of life of a man. Observations show that lack of mobility and sedentary professional activity contribute to the development of oncological neoplasms of the prostate. Low activity leads to stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs.
- Hormonal failures. With age, men develop hormonal changes that can also contribute to prostate cancer.
In rare cases, an imbalance of nutrients or cadmium intoxication contributes to the development of adenocarcinoma. Experts suspect the possible impact on the development of prostate cancer factors such as UV radiation, race, infections and other things, but so far these versions have not been confirmed.
In adenocarcinoma of the prostate, there are logical precancerous conditions. In a number of cases, this is atypical hyperplasia, characterized by abnormal growth and changes in the structure of tissues for certain reasons. Such a pathological condition can be transformed into an oncology under the influence of certain circumstances. As a precancerous state, intraepithelial neoplasia often appears. This condition is characterized by the formation of new pathological cells and tissues.
Forms and stages of adenocarcinoma development
Depending on the intensity of developed oncology, specialists identify a large-acinar and small-acinar variant of prostate cancer. The latter form is diagnosed in 95% of cases, whereas large-scale form is found in only 5% of patients.
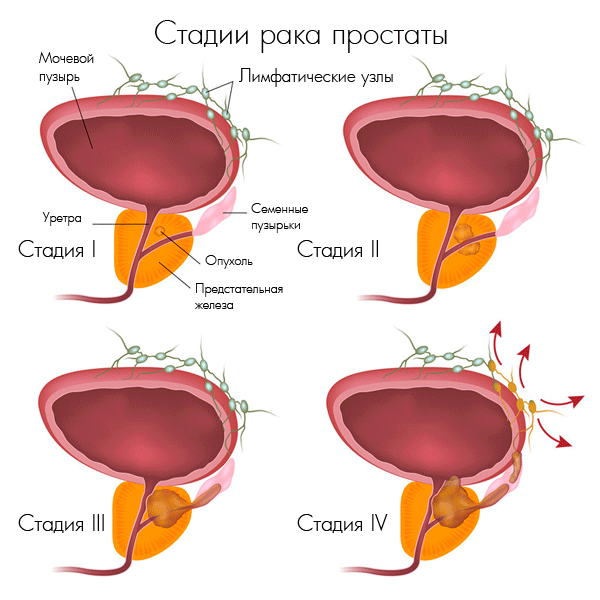
Prostate adenocarcinoma occurs in several stages. The first stage is characterized by a very low diagnosability, since the structural changes in the tissues are insignificant and can be detected only during a biopsy. In the analysis results, only minor changes will be visible.
The second stage is characterized by minor lesions of individual fragments of the prostate and its membranes. At this stage, oncology becomes fully detectable, as tissue changes can be detected by careful examination.
The third stage is characterized by active development and growth of tumor formation, accompanied by the growth of cancer cells. Cancer affects the bladder of the prostate, there is a risk of switching oncology to nearby organs and tissues. The tumor grows through the hematogenous or lymphogenous pathway, as well as during the germination of cancer cells into healthy tissues.
The fourth stage is characterized by the defeat of the digestive and urogenital system located next to the gland of organs. Tumor cells continue active growth, metastasis is observed in the lymph nodes and abdominal cavity. If the case is severe, the pathological cells affect almost all organs.
At the initial stages of adenocarcinoma development it develops imperceptibly and slowly, but at the last stages the pathology is practically incurable, since at these stages the tumor is characterized by rapid metastasis.
Classification by Gleason
Specialists often apply Glisson's classification to prostatic adenocarcinoma, based on a histological characteristic:
- 4 and fewer points - a highly differentiated adenocarcinoma, characterized by a structure of tumor cells close to normal, so-called."Good" cancer.
- 5-6 points - moderately differentiated cancer, which is characterized by significant pathological changes in the cellular structure of tissues.
- 7 and more points - cancer is low-grade, when the tumor cells completely lost the signs of healthy cells, so-called."Malignant cancer."This form has the worst possible prognosis and usually ends up for the patient lethal.
Clinical picture of adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma is considered beneficial before the onset of symptoms, since the onset of characteristic signs often indicates the neglect of the oncological process in the prostate. Typically, a typical clinic appears in the late stages, when there is metastasis in the liver, lungs, bones and lymph nodes.
Highlights specific signs of development of prostate adenocarcinoma:
- Urination disorders. To this group of symptoms, specialists consider frequent urge to urinate, usually at night, incontinence or difficulty urinating.
- Metastases. Metastasis of cancer cells is indicated by signs due to aches and soreness in the bones, severe swelling of the extremities and their paralysis due to the compression of the vertebrae.
- Lesions of nearby organs. This group of symptoms includes the presence of bloody impurities( hematuria) in the urine, a red-brown shade of seminal fluid( hemospermia), tenderness in the perineum, coccyx and in the lower abdomen, impotence.
- General intoxication. The poisoning of the body is indicated by signs of increased drowsiness and fatigue, loss of appetite and general exhaustion, signs of anemia.
Treatment options for the disease
What tactics the doctor will choose for the therapy of adenocarcinoma depends on the stage of its development. The specialist takes into account the pathology associated with prostate cancer, the age characteristics of the patient. There are several options for treating the pathology of the prostate gland. Sometimes a doctor generally excludes treatment, observing the behavior of the tumor. Usually, expectant management is applied to men with highly differentiated cancers, which is accompanied by a rich set of concomitant pathologies. In this case, the cancer is less dangerous than the complications after its therapy.
Radiation therapy is sometimes used when cancer formation is destroyed by ionizing radiation. There is still some kind of radiation treatment - brachytherapy - a procedure that involves the introduction of a radioactive needles into the prostate. Brachytherapy has proved to be a more effective technique than ionizing treatment. Cryotherapy or freezing of cancer cells is very effective in treating small tumors. Such treatment is usually combined with hormonal therapy.
Most often, surgeons-oncologists have to resort to the method of radical prostatectomy, which means the removal of the prostate. This technique is used in cases where there is no metastasis, and the tumor is located within the gland. In cases where other therapeutic techniques can not be performed, hormonal treatment is prescribed. This method involves surgical castration, the use of androgen blockers, drug castration with Zoladex, etc.
With timely detection of cancer and adequate therapy, the predictions are favorable, the patient will be able to lead a normal life, but the last stages are incurable.