The thyroid cyst is a benign formation with a cavity inside, located on the gland itself. In endocrinology there is no definitive strict line between the node, cyst and adenoma, but the cyst consists of a colloid content, and the adenoma is formed from epithelial tissue.

Description of the disease
Colloid cysts of the thyroid gland are not considered dangerous in terms of degeneration into malignant formation. Danger may represent the causes that caused the formation of the cyst. These can be infections, follicular dystrophy, hyperplasia, thyroiditis.
Symptomatic of colloid cysts of the thyroid gland depends on the size of the formation. Very large cysts can cause the formation of nodes that are dangerous in terms of transformation into malignant formations.
In case of complications of colloid cysts of the thyroid gland the following symptoms are possible:
- Pain sensations in the area of the cyst formed;
- Intoxication of the body;
- Enlargement of lymph nodes, more often - in the clavicle, less often - submandibular lymph nodes;
- Increases body temperature from 38 degrees Celsius.
Reasons for the formation of
The reasons for the formation of colloid cysts of the thyroid gland initially depend on the structure of the organ itself. The gland consists of several tens of millions of follicles, which are filled with colloid. The colloid in this case is a protein liquid with a gel-like consistency, in which the hormones produced by these follicles and contained in them are contained.
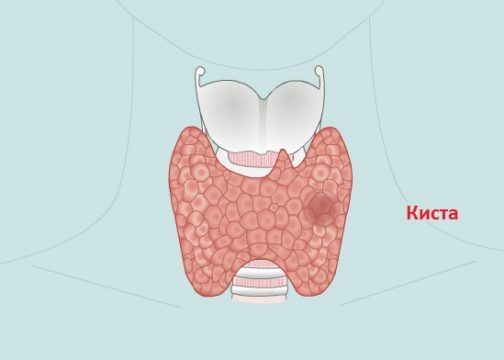
If the outflow of colloidal fluid and hormones is violated, the follicle begins to grow in size, forming small cysts. The reasons can be hidden in the excess expenditure of hormones T4 and T3.Such excess consumption is possible in the following cases:
- Severe psychological shocks;
- Rehabilitation after severe illness;
- Subcooling or, conversely, heat stroke.
All these factors contribute to the disturbance of the outflow of colloidal follicle contents. In this case, the thyroid tissue begins to slowly lose elasticity, and the cysts are filled with a liquid containing the particles of the destroyed cells.
Such factors may provoke the outflow and cyst formation:
- Heredity;
- Iodine deficiency;
- Thyroiditis;
- Congenital anomalies of thyroid;
- Imbalance of the hormonal background;
- Trauma of the gland;
- Intoxication, poisoning.
Symptoms of
Most often, colloid cysts of the thyroid gland are characterized by asymptomatic flow due to the fact that their development is slow and they do not exert pressure on the arteries. As a rule, they are found during the surveys for other reasons or chronic diseases.
Symptomatic symptoms can occur if the cyst becomes large, reaching about three centimeters in size. As the cyst increases, there may be discomfort in the neck. There are also known cases when the cyst grew quickly enough, but then it resolved itself independently. This is observed in cases where the growth of the neoplasm was caused by hormonal failures.
The main symptoms of colloid cysts of the thyroid gland are:
- Sensation of lump or throat swelling;
- Enlargement of lymph nodes on the neck;
- Change of voice, hoarse;
- Chills;
- Headaches;
- Increased body temperature;
- Changing the contours of the neck, assessed visually.
Colloid cyst, in fact, is a large-sized node. The main cause of development is iodine deficiency, somewhat less the influence of hereditary factors. At the first stages such formations do not show any symptoms, they have diameters no more than ten millimeters and can not be dangerous to health.
As the nodal formations of both lobes can compress the trachea and esophagus, make it difficult to swallow, touch or press on the nerve endings. During this period, the patient also suffers from sweating, tachycardia, emotional instability.
Most endocrinologists are inclined to the fact that there is no need for surgical intervention with such a diagnosis, it is enough to conduct medical therapy and to examine the condition of the cyst every few months through ultrasound.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of the cyst, ideally, should be done regularly and in a hospital setting. But since the disease is more often detected during routine examinations, the diagnosis is carried out on an outpatient basis.
Diagnostic measures involve the following methods:
- Visual inspection of a patient;
- of the gland;
- Palpation of lymph nodes and thyroid;
- Blood test for thyroid-stimulating hormones, thyroxine, triiodothyronine;
- Puncture to exclude the oncological nature of the disease.
Another accurate method of diagnosis is scintigraphy, as a variation of X-ray research methods. During the procedure it is possible to determine:
- Hot sites, which speak of the absorption of iodine compounds during the formation of nodes and cysts.
- Warm nodes indicate the spread of iodine compounds in the tissues of the gland and cysts.
- Cold knots, talking about possible oncological processes, preventing the penetration of iodine into the thyroid tissue.
In addition, computer tomography, bronchoscopy, angiography can be prescribed.
Ultrasonic research
Separately, we should talk about the ultrasound diagnosis of the cyst. This method is appointed after examination and palpation of the patient. This method is one of the most effective in examining the condition of the gland, helping to determine the presence of nodes, cysts or tumors.
The indications for the ultrasound investigation are:
- Changing or deforming the shape of the neck and its contours;
- Enlargement of lymph nodes;
- Pathological parameters of the hormone TSH in the blood;
- Hormonal imbalance;Infertility, impaired menstrual cycle;
- Emotional instability, insomnia;
- Treatment with hormonal drugs;
- Hereditary factor of the disease by endocrinological pathologies;
- Climax;
- Pregnancy.
In addition, all these indications can also become factors that trigger the development of colloidal formations.
Ultrasound scores can help in outline contours and sizes of the gland, as well as contours, outlines and sizes of education. The evaluation of echogenicity, the position of the thyroid gland is carried out. The structure of education, as well as the number of formations in multiple cysts, is assessed, the lymphatic drainage is assessed.
Methods of treatment
Methods of treatment of the disease vary depending on its size, complications and concomitant diseases. Treatment can be regular medication or surgery, and also without the use of drugs.
Often, when detecting thyroid neoplasms, continuous monitoring is necessary to be able to monitor its contours and not miss the moment of possible increase.
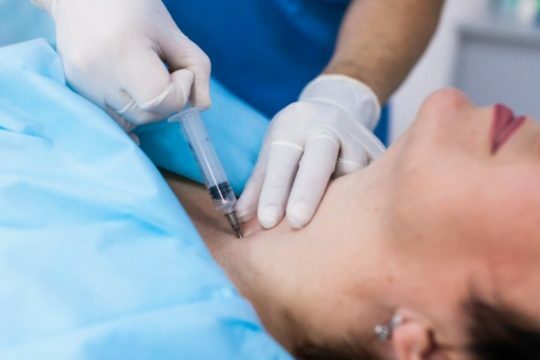
The main and most accurate method is puncture, in which the sclerosis of the neoplasm is also performed. In this case, it is not only removed, but also amenable to examination, as its contents are sent for histological analysis.
If after such removal the abnormal follicle is formed again, relapses are repeated constantly, a complete surgical procedure for removal is shown.
If a small follicle is found that does not hamper the functioning of the thyroid gland, the treatment is carried out by prescribing hormonal preparations. Usually it is thyroid hormones.
Recently, doctors are increasingly refusing hormonal therapy and suggest that patients first correct the nutrition in favor of iodine-containing products, and prescribe medications containing iodine. Virtually all follicular formations are benign and require only constant monitoring.
Purpose of operation
Surgical treatment is necessary only in cases when the pathology reaches a large size, blocks the airways, squeezes the larynx, neck. If it breaks the hormonal background, suppurates, deforms the size and shape of the neck, or if the follicle is recognized as a malignant entity. By the way, you can confidently put such a diagnosis only after puncture and histological examination of the contents in the follicle.
The types of operations can be as follows:
- Resection of a part of the gland upon detection of a large bilateral cyst;
- Removal of only one organ fraction;
- Complete removal of the gland, lymph nodes and tissues in the detection of cancer.
Complete removal is prescribed in especially rare cases when the formation is transformed into malignant, which is rare in follicular neoplasms. In addition to traditional surgery, it is possible to apply methods of fine-needle biopsy, puncture, sclerotherapy, laser coagulation.