Fracture of the beam in a typical place. .. The expression sounds ridiculous: how can you break the beam? Sunny, light? And if you can, where is it, this is a typical place?
Fracture of the beam in a typical place. .. The expression sounds ridiculous: how can you break the beam? Sunny, light? And if you can, where is it, this is a typical place?
And here to doctors the phrase is absolutely clear, for "ray" is the abbreviated name of a radial nerve, which is served by a radial nerve.
Bones of an absolutely remarkable structure, for it provides the operation of several joints at once: the humerus, the two radiolucent( upper and lower), and the wrist. That's somewhere near the last of these joints and there is a fracture of the ray - the lower third of the radius and is the "typical place".
Contents
- About the causes and risk factors
- Anatomical and physiological reference
- Symptoms - from "goose bumps" to "numbness"
- How to distinguish one form of defeat from another?
- Neuropathic disorder
- Neuralgic lesion
- Neuritis and its manifestations
- Neuropathologist approves and confirms
- Therapy methods
- To the issue of prevention
About the causes and risk factors of
The peculiarities of joining the bones constituting the upper limb are, in case of norm, the optimal variant of the functioning of the radial nerve serving it,in the case of pathology - become a stumbling block for their activity. For, as the narrowing of the bone-tendon( bone-fascial) tunnels, so deformations of bones themselves become difficult to overcome, or completely insurmountable obstacles for carrying out nervous "electricity" both up( from the limb to the brain) and down( from the brain to the place of application).
In addition to the gradual and planned "removal" of the nerve due to the development of rheumatism, arthrosis and other chronic conditions with proliferation of connective tissue, there are rapidly and rapidly developing disorders that lead to nerve transmission by swollen tissues. It occurs just at the notorious fracture in a typical place.
But it can also be a dislocation - the displacement of the bone from its rightful place in the joint, which occurs when the bone is pulled out of it( with sudden limb extension: a sharp snatch when the core is ejected or the grenade is thrown).
Tissue swelling can be a consequence of heavy, debilitating physical labor, from which the hands become numb.
In addition to an edema caused by disturbance of the biomechanics of movement, an allergic reaction can also lead to massive edema-the food component, the drug substance. Or it can be an acute toxic edema from the bites of several dozen bees. Or the effect of poison from biting other dangerous animals.
And even not so dangerous, because even mosquito "vpivaniya" with the formation of blisters on the skin, if they are multiple, can cause in particularly sensitive people neuropathy of the radial nerve. It can also be a neuropathy of the median or ulnar nerve.
Whatever the obstacle to the path of the radial nerve - whether it is permanent or temporary - the result will be its reaction to negative impact from the outside in the form of the following diseases:
- neuropathy;
- neuralgia;
- neuritis.
But the same reaction can come from nerve damage from the inside - from disorders in the nourishing organ of the capillary network. Or from the presence of toxins in the blood:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- appeared due to domestic poisoning or habitual intoxication.
There is also a possibility of direct infection of the nerve( with leprosy).
Finally, it is possible to directly damage the radial nerve( its trunk or branches), as bone fragments in bone fracture, and foreign body due to combat, domestic, industrial or criminal trauma - from the introduction of a bullet, a fragment of an ammunition, a blank weapon, or a fragment of a tree, glass, plastic, metal.
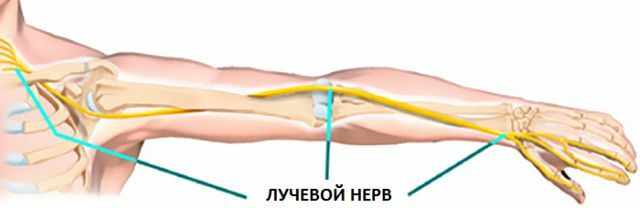
Anatomical and physiological reference
For the radial nerve, the onset of its tearing from the C5-C8, Th1 brachial plexus formed by the roots, the first potentially dangerous compression-squeezing point-is the posterior wall of the axillary cavity. This "intersection" is the widest dorsal muscle with the tendon of the long head of the triceps muscle of the shoulder.
Then, circumscribing the humerus in a spiral trough( the humerus canal - groove on the humerus, covered with the triceps head), it is just as strong as in the previous case, it risks being depressed by a long-used crutch.
The place of separation of the radial nerve into two branches - superficial and deep - on the outer surface of the elbow joint is the third gorge along the path of the nerve, where one can expect "strangulation" by compression.
The radial nerve has in its composition upward sensory branches that conduct sensations to the brain from:
- of the elbow joint capsule;
- of the posterior( dorsal) surface of the shoulder,
- and also "read" information from the rear of the forearm and the radial edge of the hand with the first three and a half fingers( excluding their terminal, distal phalanges).
The motor branches of the nerve serve to bring into working condition and maintain the musculature:
- extensor forearm and hand:
- , the outgoing thumb,
- and also extending the proximal phalanges of the other fingers; they also control the supination of the hand( turning the brush into a "begging pose"- palm upwards).
 This is such an excellent "cable" with a link working in both directions.
This is such an excellent "cable" with a link working in both directions.
But sometimes( for the above reasons) it is damaged.
And then the picture of the world created in the brain with his participation is distorted.
Abnormal perception of the world can become for two reasons:
- The first is nerve receptor damage to that collects information from the body surface.
- The second - information on the damaged "wire" does not pass completely ( nerve palsy), or passes with great difficulty, losing credibility on the way to the "headquarters".
These three levels of impaired perception and conduction( on the increase of the degree of disorder) are called:
- neuropathy;
- by neuralgia;
- neuritis.
What you need to know about the radial nerve - anatomy and physiology:
Symptoms - from "goose bumps" to "numbness"
Given that the radial nerve holds on the brush for the whole of I( it's big), II, III finger and medial half IVfinger, and also on the outer half of the forearm, pain sensations of different intensity will arise precisely in this area. They have a diverse nature - from "crawling crawl" and "numbness" - to the sensation of "burning with boiling water" and sharp - "to fainting" - pain.
But in addition to pain, there are also disorders in the motor sphere. Because the normal activity of the muscles providing the work in this area of the nervous structures is disrupted.
Hence the symptom of a "dangling brush"( due to the weakness of its muscles, the raised hand hangs like an empty glove), it is also difficult to bring-finger I, finger extension and wrist extension, forearm and hand.
The sensitivity level of the rear of the hand, the first three and a half fingers and the back surface of the forearm ranges from paresthesia to  hypoesthesia.
hypoesthesia.
Weak muscles are different, extending the wrist and fingers, it also affects the muscle-supinator, the brachial muscle;the performance of the carapordial reflex is disturbed, the pain appears in the process of violent measures for supination of the forearm and extension of the fingers.
In addition, there are painful sensations during palpation in the locations of the radial nerve.
With a long-term state, muscle atrophy occurs in the indicated area.
This clinical picture most often arises:
- when the radial nerve is "squashed" in the process of prolonged sleep in one position( due to alcoholic intoxication, severe fatigue), or due to fracture, walking on crutches;
- because of chronic alcoholic or lead intoxication;
- after infection.
How to distinguish one form of defeat from another?
In a number of publications devoted to lesions of the radial nerve and especially traumatic etiology - often the term "neuritis" or "neuropathy" is often used to refer to the same manifestations, which introduces a certain confusion in the perception of information.
This is because there is no clear boundary between these concepts, nor is there a clear boundary between the threshold of perception - the sensitivity of patients with this pathology.
Neuritis is an inflammatory-degenerative process in the trunk or branches of the radial nerve( in contrast to neuralgia - soreness along the nerve as arising spontaneously, and "awakened" by palpation or movement).
Neuropathic disorder
Strictly speaking, neuropathy is considered to have no anatomical substrate pathology caused largely by the general disorder of the nervous system in an individual that is excessively impressionable, with some features of the perception of the world - in a hysterical or neurotic personality. Personality, the appearance of "goosebumps" from cold or fright is already considered a disease.
In this case, they talk about neuropathy - a case when there is no disease. But there is a "pre-pathology" - increased susceptibility to sensations or exaggerated attention to manifestations of the activity of one's body.
 What causes the neurotic to assume that he has a painful condition. In support of his he is given a lot of symptoms-sensations, which do not have any serious material basis, which is confirmed repeatedly by repeated studies.
What causes the neurotic to assume that he has a painful condition. In support of his he is given a lot of symptoms-sensations, which do not have any serious material basis, which is confirmed repeatedly by repeated studies.
Neuropathy in terms of sensations in the upper limb has the same basis as hysterical or neurasthenic disorder. Neurotic or suffering from hysteria, with painful attention, finds at different degrees of pain in different parts of the body.
And in the far-gone version there may appear a loss of sensitivity, and even impaired motor state of the nervous system.
Unlike the true pathology, they disappear without a trace at the end of a hysterical fit. Or - by switching the patient's attention to the manifestations of a new pathology discovered in oneself, which come to replace yesterday's.
Treatment of this pathology is similar to measures to combat hysteria.
There is also a form of radiation neuropathy, such as the "convict" - or "shackled" - "paralysis" that occurs when wearing handcuffs. This is a lesion of the radial nerve at the carpal level, including the development of either a radial tunnel syndrome or Turner syndrome.
The first variant develops in connection with nerve transmission( its superficial branch) in the "anatomical snuffbox", the second one is a consequence of the ray fracture in a typical place. Both syndromes manifest themselves by the numbness of the rear of the fingers and the entire hand, the burning pains of the rear of the first finger, radiating both in the forearm and the shoulder. And violations sensorics are limited to the limits of the large( I) finger.
Neuralgic lesion
Neuralgia of the radial nerve is characterized by extremely sensitive disorders( paroxysmal intense pains strictly in the zone of its strike) with absence of loss of sensation and motor disorders in it. Changes in the structure of the affected nerve are completely absent.
A feature of neuralgic pathology is a clear connection of the pathology of the nerve with the need to pass it through the narrow natural anatomical openings and channels and the existence of trigger regions, when palpation of which the pain paroxysm is naturally provoked.
Neuritis and its manifestations
The extreme severity of the neuritis of the radial nerve - with the defeat of its main trunk in the region of the spiral canal - "crutch paralysis" - is inherent in the loss of all nerve functions as an organ( in the case of injuries of more distal disturbances are only partial and depend on the severitydamage to its fibers).
The clinic is characterized by:
- the inability to arbitrarily unbend the wrist and elbow joints, the inability to point one finger with his
 anesthesia;
anesthesia; - "hanging"( "falling") brush "with the characteristic" sticking "of the II finger to I;
- bending disorder in the elbow, supination of the hand and forearm;
- loss of reflex from the three-headed brachial muscle - an extensor elbow reflex and a decrease in the carporadial reflex;
- with anesthesia( hypoesthesia) of the posterior surface of the forearm and shoulder, paresthesia of the back surface of I, II and partly of III finger, while retaining the sensory properties of their distal phalanges.
Often and hypotrophic disorders in the posterior group of the muscles of the forearm and shoulder when:
- punctures the nerve in the middle third of the outer region of the shoulder( pressure on the nerve head in the syndrome of "Saturday night" or "park bench");
- unsuccessful injection( injectable form of neuritis);
- for chronic lead intoxication the picture is similar to the above, with the difference that the extensor elbow reflex and the norm in the cutaneous perception for the posterior humeral surface are preserved.
Overloads of muscles forming the circumference of the elbow joint lead to the formation of a "tennis elbow"( with the development of myofasciopathies and excess of perineural tissues).
With this variant of the defeat, the prerequisites for hypotrophy, weakness and pain in the extensors of the forearm, pain in the case of forcibly active extension of the fingers are created - strengthening paresthesias and pain of the back of the hand in work, as well as intense pain in the upper third of the forearm and in the ulnar fold. In this case, the sensitivity of the skin of the forearm on the hand can be completely preserved.
Neuropathologist approves and confirms
To clarify the diagnosis and establish the cause and the "floor" of the lesion of the radial( nerve) nerve - in addition to consulting a neurologist - a certain minimum of research is required, including the use of:
- radiography ;
- computed tomography area of the elbow, or wrist joint, or both articulations;
- electromyography ;
- electroneurography of .
In order to determine the disorders of biomechanics of movements, participation in the diagnostic process of a traumatologist will be valuable, and for the creation of a rehabilitation program for bone pathology - an orthopedist.
If necessary, the condition of the hormonal background is clarified and collagenosis-excluding studies involving the endocrinologist and rheumatologist, as well as blood testing for the level of sugar content and its biochemical condition.
Methods of therapy
Therapy of "radiation disorders" depends on the cause of the onset of pathology.
Antibacterial and antiseptic agents are used for chronic infection. If the fracture leading to neuritis is due to diabetes mellitus, the hormonal background is corrected.
But the main means of treatment of lesions of the radial nerve will be the use of methods of rehabilitation, vascular and metabolic therapy in combination with exercise therapy, physiotherapy, massage and manual techniques.
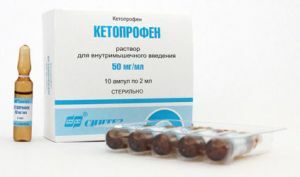 The first echelon of medical aid for neuralgia and neuritis of the radial nerve is followed by agents with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory action( Ketoprofen, Voltaren, Naproxen) in conjunction with other anti-inflammatory agents and analgesics( up to novocaine and hydrocortisone blockades), and immobilization is used to create rest for the suffering limbphysiological position.
The first echelon of medical aid for neuralgia and neuritis of the radial nerve is followed by agents with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory action( Ketoprofen, Voltaren, Naproxen) in conjunction with other anti-inflammatory agents and analgesics( up to novocaine and hydrocortisone blockades), and immobilization is used to create rest for the suffering limbphysiological position.
To stimulate the regeneration of the nervous tissue, prevent muscle tissue disorders and maintain their tone, the use of tissue preparations, vitamins and agents to improve microcirculation( Milgrammy, Aloe, Actovegin), as well as the inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase - Proserin.
A good healing and restoring movement in the limb effect is the use of massage and therapeutic gymnastics( including in water), various methods of physiotherapy( magnetotherapy, UHF) and electromyostimulation.
If necessary, surgical methods are used to restore the state of the radial nerve - plastic surgery in the form:
- neurology - excision of the compressive nerve of epineural cicatricial tissue;
- epineural seam - plasty of the damaged nerve with the use of grafts, allowing to sew its ends.
Radiation nerve injury can cause permanent disability of the limb function in the form of paralysis, paresis, contractures, which can lead to disability due to loss of ability to work, and with bilateral development - and self-service.
To the issue of prevention of
The main measure of prevention of injuries of the radial nerve is the prevention of upper limb injuries in the form of avoiding excessive stress on bone and muscle. But the complete absence of their training leads to uncertainty when walking and movements and guarantees injuries.
To the prevention of injuries and leads to the rejection of the usual household intoxication, compliance with the rules of the regime and rest, participation in active games and dances.
Treatment of chronic diseases of any genesis also helps to prevent these unfortunate consequences. Seeking medical help at any difficulty with health should be the norm of behavior of modern man.